Actions
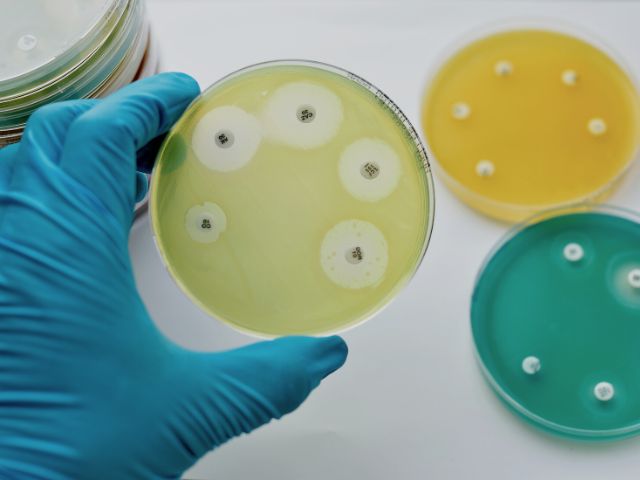
Penicillin has bactericidal actions and they bind reversibly to several enzymes outside the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane, such as penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). They are involved in cell division which interferes with the processes that inhibit cell-wall synthesis, causing rapid destruction of the bacterial cell.
This drug class serves as an effective agent against a wide range of bacteria such as active gram-positive, gram-negative, and anaerobic organisms. However, there are certain types of penicillin that are more effective against a particular organism.