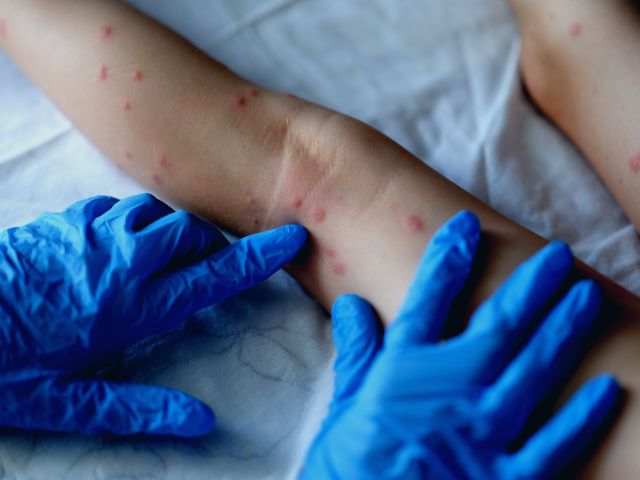
Antihistamines or H1 receptor antagonists work by blocking the action of histamine that occurs in a type I hypersensitivity reaction or an allergic reaction. They are available as prescription drugs or over the counter and can be given alone or in combination with other medications.
Antihistamine competes with the histamine binding at the H1 receptor site; however, it cannot displace the histamine already bound to the receptors.
Antihistamines cannot reverse the ongoing allergic reaction because they cannot displace the already-bound histamine to the H1 receptors, but they can prevent further allergic reactions by competing with histamine binding at the H1 receptor site.