Diabetes is a common disease affecting the population. The incidence rate of diabetes has been on the rise for an extended period of time and the complications of diabetes have also increased.
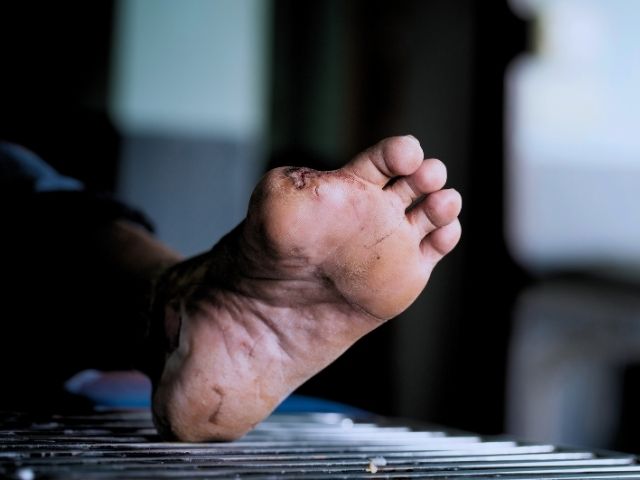
Diabetic foot is considered one of the most common complications of diabetes. Nurses play an important role in the education of diabetes and assisting patients in managing the disease.
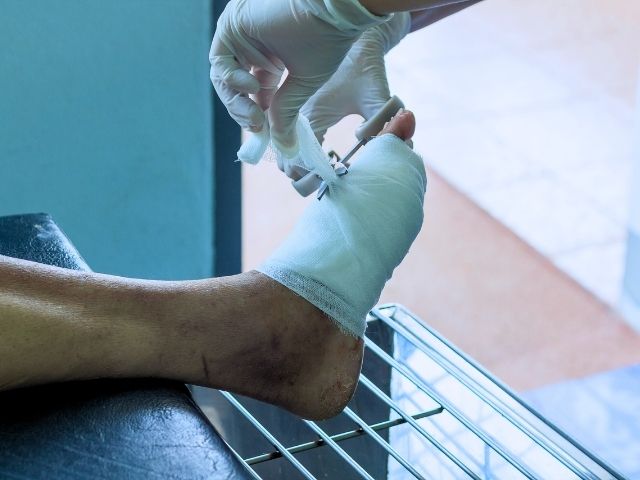
Nurses also play an important role in preventing diabetic foot, providing regular foot care, and in the prevention of foot injury in those with diabetes. Nurses are responsible for early detection of any changes in skin and foot sensation, foot care, and dressing.
Nurses are also encouraged to stay up to date on the latest diabetic foot care instructions to ensure they are providing the highest quality of nursing care to diabetic patients. Ensuring that the highest quality of care is provided will assist in achieving positive health outcomes for the patients.
Like many other diseases, the elderly population is at an increased risk for developing complications from diabetes, especially those of the foot. The increased risks could be due to many factors such as the aging process and reduced skin integrity.
Due to the increased risk for diabetic foot, many nursing homes have initiated foot care clinics where one day each week is dedicated to the foot care of diabetic patients. On this day, nurses thoroughly inspect and wash the diabetic patient’s feet. They also provide nail trimming.