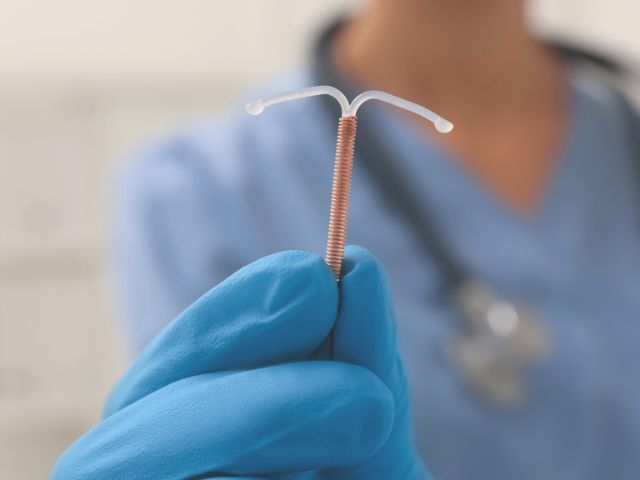
Intrauterine devices (IUD)s are the most common method of birth control worldwide. Oral contraceptive pills are a favorite in the United States, but the IUD is gaining some traction.
When women choose a long-acting reversible contraception (LARC), the IUD is a great choice.
They are:
- Highly effective
- Reliable
- Easy to use
- Reversible
- Relatively low cost
- Effective as tubal ligation
The effectiveness of this contraceptive is 99% with perfect use. It is so effective because there is a low chance of human error. Once it’s placed, women can forget about it for the most part.