Course
Alabama Renewal Bundle
Course Highlights
- In this Alabama Renewal Bundle course, we will learn how to identify and analyze quality improvement opportunities.
- You’ll also learn how to prevent workplace violence towards nurses.
- You’ll leave this course with a broader understanding of important stages of the dying process.
About
Contact Hours Awarded: 24
Course By:
Various Authors
Begin Now
Read Course | Complete Survey | Claim Credit
Quality Improvement for Nurses
Introduction
Welcome to the world of Quality Improvement (QI) in healthcare, a dedicated field committed to continually enhancing patient care and outcomes. Quality Improvement involves a systematic approach to identify, analyze, and address areas for improvement within healthcare processes, ultimately resulting in improved patient safety, satisfaction, and overall healthcare excellence (13). In this course, we will embark on a journey to explore the fundamental principles and practical applications of QI, explicitly tailored for nurses who aspire to make a positive impact in their healthcare settings.
As a nurse, you know the significance of providing high-quality patient care. However, you may wonder how you can actively contribute to improving the systems and processes in your workplace.
Imagine this scenario: You observe a recurring issue with medication administration, where doses are occasionally missed due to workflow inefficiencies. Through this course, you will acquire the knowledge and skills to apply QI methodologies like Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles to investigate such issues, implement changes, and monitor the impact of your interventions. By understanding QI principles and tools, you will be better equipped to collaborate with your colleagues, drive meaningful improvements, and ensure that your patients receive the best care possible.
Introduction
Welcome to the world of Quality Improvement (QI) in healthcare, a dedicated field committed to continually enhancing patient care and outcomes. Quality Improvement involves a systematic approach to identify, analyze, and address areas for improvement within healthcare processes, ultimately resulting in improved patient safety, satisfaction, and overall healthcare excellence (13). In this course, we will embark on a journey to explore the fundamental principles and practical applications of QI, explicitly tailored for nurses who aspire to make a positive impact in their healthcare settings.
As a nurse, you know the significance of providing high-quality patient care. However, you may wonder how you can actively contribute to improving the systems and processes in your workplace.
Imagine this scenario: You observe a recurring issue with medication administration, where doses are occasionally missed due to workflow inefficiencies. Through this course, you will acquire the knowledge and skills to apply QI methodologies like Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles to investigate such issues, implement changes, and monitor the impact of your interventions. By understanding QI principles and tools, you will be better equipped to collaborate with your colleagues, drive meaningful improvements, and ensure that your patients receive the best care possible.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How can nurses leverage their unique position at the bedside to identify opportunities for quality improvement in healthcare settings?
- Can you provide an example from your own experience or knowledge where a quality improvement project led to tangible improvements in patient care?
- What potential challenges could a nurse encounter when attempting to implement quality improvement projects?
What is Quality Improvement?
Quality Improvement (QI) in healthcare represents an ongoing, systematic effort to elevate the quality of patient care and healthcare services that involves identifying areas needing improvement, implementing changes, and evaluating the effects of those changes to ensure better patient outcomes (12).
Let’s envision a scenario where a hospital's surgical department grapples with a higher-than-average rate of post-operative infections. Through a QI initiative, the healthcare team can meticulously scrutinize the surgical processes, pinpoint potential sources of infection, and introduce evidence-based practices such as enhanced sterilization techniques or more rigorous antibiotic prophylaxis protocols. Over time, they can gauge the effectiveness of these changes by monitoring infection rates for a reduction.
Commonly used QI methodologies in healthcare include the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) process and the Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle. These approaches provide structured frameworks for healthcare professionals to tackle issues systematically and iteratively. For example, imagine a bustling primary care clinic with extended patient wait times.
Here, the PDSA cycle can come into play using the systematic iterative steps below:
- The team defines the problem (lengthy wait times)
- The team proceeds to test a change (for example, adjusting appointment scheduling)
- The team then scrutinizes the results and acts accordingly to refine the process.


Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How does the concept of Quality Improvement (QI) align with the goal to provide the best possible care for patients?
- Can you think of a specific healthcare scenario where QI methodologies like DMAIC or PDSA could significantly improve patient care?
- What are the advantages of using structured frameworks like DMAIC and PDSA in QI initiatives?
- How do DMAIC or PDSA contribute to the success of improvement projects?
History and Background of Quality Improvement
The history and background of Quality Improvement (QI) in healthcare have a rich and evolving timeline, dating back to the early 20th Century, with significant developments occurring over the years. One pivotal moment in this journey was the introduction of statistical quality control by Dr. Walter A. Shewhart in the 1920s (24). Dr. Shewhart's pioneering work laid the foundation for using statistical methods to monitor and enhance processes, a concept that would become integral to QI initiatives (24).
In the mid-20th Century, the contributions of Dr. W. Edwards Deming further propelled QI principles forward (7). Dr. Deming emphasized the significance of continuous improvement, active employee engagement, and process variability reduction. His ideas found fertile ground in post-World War II Japan, playing a crucial role in the nation's economic recovery and the emergence of renowned companies like Toyota, famous for its Toyota Production System (TPS), incorporating QI concepts (7).
Until today, QI has become indispensable to healthcare systems worldwide (16). To illustrate, envision a scenario where a hospital grapples with a high readmission rate among heart failure patients. By scrutinizing historical data and implementing evidence-based protocols for post-discharge care, hospitals can effectively lower readmissions, enhance patient outcomes, and potentially evade financial penalties under value-based reimbursement models (16).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How did the work of Dr. Walter A. Shewhart in the early 20th Century contribute to the foundation of QI, and how do statistical methods continue to play a role in healthcare improvement today?
- What fundamental principles were introduced by Dr. W. Edwards Deming, and how did they influence QI practices in healthcare and other industries?
- Can you provide an example of how QI methodologies, inspired by Deming's principles, have been successfully applied in modern healthcare settings to address specific challenges or improve patient care?
- How has continuous improvement evolved, and why is it considered a cornerstone of QI in healthcare?
Models
At the heart of ongoing transformations in healthcare lies various Quality Improvement (QI) models. These models provide structured frameworks for identifying and addressing areas of improvement within healthcare systems (14). These models offer healthcare professionals a systematic approach to instigate meaningful process changes, ultimately resulting in elevated care quality. See some models below.

Model for Improvement
The Model for Improvement is a widely recognized and highly effective framework for Quality Improvement (QI) in healthcare. This is because it empowers healthcare professionals to systematically test and fine-tune their ideas for process improvement, ensuring that changes are grounded in evidence and proven effective (17).
The Model for Improvement offers a structured and systematic approach to identifying, testing, and implementing changes to enhance healthcare processes and ultimately elevate patient outcomes.
Developed by Associates in Process Improvement (API), this model revolves around the iterative "Plan-Do-Study-Act" (PDSA) cycle, which forms the foundational structure of QI initiatives (17). The Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle is a systematic approach that guides healthcare teams through quality improvement, and it comprises the four key phases below, each contributing to developing and implementing meaningful changes in healthcare practices (12).
- Plan: In this initial phase, healthcare teams define the specific problem they aim to address, set clear and measurable goals, and craft a comprehensive plan for implementing the proposed change. For instance, if a hospital seeks to reduce patient wait times in the emergency department, the plan may involve adjustments to triage protocols or streamlining documentation processes.
- Do: Once the plan is established, the proposed change is implemented, typically on a small scale or within a controlled or pilot environment. This enables healthcare professionals to assess the feasibility and potential impact of the change without making widespread adjustments.
- Study: The study phase involves rigorous data collection and analysis to evaluate the effects of the change. In our example, the hospital would measure the impact of the new triage protocols on wait times, closely examining whether they have decreased as expected.
- Act: Based on the findings from the study phase, the healthcare team makes informed decisions about the change. They may adopt the change if it has successfully reduced wait times, adapt it further for enhanced effectiveness, or, if necessary, abandon it.
The PDSA cycle's iterative nature means adjustments can be made, and the cycle repeats until the desired improvement is achieved (12).
Lean Model
The Lean model, initially conceived in the manufacturing sector, has found considerable success and applicability in healthcare as a potent tool for process enhancement and waste reduction (22). At its core, Lean thinking revolves around the principles of efficiency and value optimization because it focuses on refining processes to eliminate wasteful elements while simultaneously delivering care of the highest quality (22).
Healthcare organizations have adopted Lean methodologies to tackle many challenges, from reducing patient wait times to improving inventory management and elevating overall patient satisfaction (22). For instance, when a hospital is challenged with prolonged wait times in its outpatient clinic, it can apply Lean principles to systematically analyze the patient flow, pinpoint bottlenecks, and streamline processes.
This might involve reconfiguring furniture to enhance flow, adjusting appointment scheduling, or implementing standardized work procedures. The ultimate objective is to cultivate a patient-centric, efficient environment that ensures timely access to care while meticulously conserving time and resources.
Another integral aspect of Lean thinking is the unwavering commitment to continuous improvement and the pursuit of perfection through the systematic identification and eradication of various forms of waste (19). The forms of waste are often categorized into seven types: overproduction, waiting, unnecessary transportation, overprocessing, excess inventory, motion, and defects (19). By keenly identifying and addressing these forms of waste, healthcare organizations not only enhance the utilization of resources but also curtail costs and elevate the overall quality of care delivery.
Six Sigma model
The Six Sigma model is a robust and widely adopted healthcare method for improving processes and reducing mistakes (9). It was first used in manufacturing but is now used in healthcare to make processes more consistent and improved by finding and fixing mistakes and inefficiencies (9).
An example is when a hospital is concerned about the accuracy of medication dosing for pediatric patients, a Six Sigma team might include: indicating the problem, gathering data on mistakes regarding dosing, and finding out why the mistakes happened. The strategy may encompass the implementation of standardized dosing protocols, refining staff training programs, and closely monitoring the medication administration process to ensure that mistakes are eliminated.
Six Sigma uses a framework called DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) to make improvements. This framework utilizes data-driven tools to discern problems, quantify their origins, develop practical solutions, and institute control mechanisms to sustain improvements (11). Through this systematic journey, healthcare organizations position themselves to deliver care of elevated quality, curtail costs, and bolster patient safety.
TeamSTEPPS model
TeamSTEPPS, which stands for Team Strategies and Tools to Enhance Performance and Patient Safety, is a teamwork and communication model designed explicitly for healthcare settings (4). Developed by the U.S. Department of Defense and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), TeamSTEPPS focuses on improving patient safety by enhancing team collaboration, communication, and decision-making among healthcare professionals (4).
One key element of TeamSTEPPS is using structured communication techniques to prevent errors and misunderstandings. For instance, during patient handoffs from one healthcare provider to another, TeamSTEPPS emphasizes using a structured tool like SBAR (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) to convey critical information succinctly and accurately. This ensures that essential patient details are noticed, reducing the risk of adverse events (18).
In a surgical team scenario, TeamSTEPPS principles can be applied to improve teamwork and communication among surgeons, nurses, and anesthesiologists. The model encourages briefings before procedures to set clear objectives, huddles during surgery to address emerging issues, and debriefings afterward to reflect on the process and identify areas for improvement. By fostering a culture of open communication and mutual respect, TeamSTEPPS contributes to safer, more efficient healthcare delivery (4).


Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How can healthcare organizations determine which QI model suits their specific challenges or improvement goals?
- How do QI models emphasize data collection and analysis, and why is this critical in healthcare?
- Can you imagine a real-world scenario where the Lean Six Sigma framework can successfully improve healthcare processes and outcomes?
- What are some emerging trends or innovations in QI models and methodologies, and how might they shape the future of healthcare quality improvement?
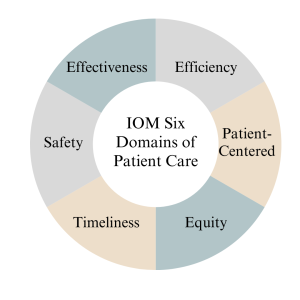
IOM Six Domains of Patient Care
The Institute of Medicine (IOM), now known as the National Academy of Medicine, introduced the Six Domains of Quality in Healthcare as a framework to assess and improve the quality of patient care (14). These domains, introduced in 2001, encompass various aspects of care delivery and patient experience, helping healthcare organizations and providers identify areas for improvement (14). The domains serve as pillars for assessing the different dimensions of care delivery, ensuring that healthcare organizations and providers address the holistic needs of patients (14).
Definitions
The Six Domains of Patient Care are essential for providing high-quality healthcare. See definitions of each of the IOM's six domains of patient care below.
- Safe: Safety is the foundational domain, emphasizing the importance of reducing the risk of patient harm. This includes preventing medical errors, preventing infections, and ensuring the safe administration of medications. Healthcare organizations implement safety protocols and engage in continuous monitoring to minimize risks (14).
- Effective: Effective care ensures that patients receive evidence-based treatments and interventions that result in the desired outcomes. It involves using the best available scientific knowledge to make informed decisions about patient care avoiding unnecessary or ineffective treatments (14).
- Patient-Centered: Patient-centered care focuses on individualizing healthcare to meet each patient's unique needs and preferences. It involves respecting patients' values and preferences, engaging them in shared decision-making, and delivering care with empathy and compassion (14).
- Timely: Timely care emphasizes reducing delays in healthcare delivery. It includes providing care promptly and avoiding unnecessary waiting times for appointments, tests, and treatments. Timely care is especially critical in emergencies (14).
- Efficient: Efficiency in healthcare means maximizing resource utilization and minimizing waste while providing high-quality care. This domain emphasizes streamlining processes, reducing unnecessary costs, and optimizing healthcare resources (14).
- Equitable: Equitable care underscores the importance of providing healthcare that is fair and just, regardless of a patient's background, socioeconomic status, or other factors. It aims to eliminate healthcare access and outcomes disparities among different patient populations (14).
Measures
Measures in the context of the Institute of Medicine (IOM) six domains of patient care refer to the metrics and indicators used to assess and evaluate the quality of care provided in each domain. According to (14), the measures below are essential for monitoring and improving healthcare services. See details below.
- The "Safe" domain measures focus on tracking and reducing adverse events and medical errors. Key indicators include rates of medication errors, hospital-acquired infections, falls, and complications from procedures. Safety measures also assess the implementation of safety protocols, such as hand hygiene compliance and patient identification bracelets.
- Measures in the "Effective" domain assess how evidence-based practices and treatments are utilized. These measures include adherence to clinical guidelines, appropriate use of medications, and the success rates of medical interventions. Additionally, outcomes such as patient recovery, remission, or improvement are indicators of the effectiveness of care.
- The "Patient-Centered" domain focuses on assessing the patient’s experience and satisfaction with care. Patient surveys and feedback are standard measures, evaluating aspects like communication with healthcare providers, involvement in decision-making, and overall satisfaction with the care received. Healthcare organizations also measure shared decision-making and respect for patient preferences.
- Measures related to the "Timely" domain evaluate the efficiency of healthcare delivery. Key metrics include waiting times for appointments, diagnostic tests, and procedures. Additionally, measures track the timely delivery of urgent care and the avoidance of unnecessary delays in treatment.
- Efficiency measures aim to quantify resource utilization and the reduction of waste in healthcare. Metrics may include the cost of care per patient, length of hospital stays, and resource allocation efficiency. Improvement in resource utilization and cost-effectiveness are vital indicators of efficiency.
- Measures within the "Equitable" domain assess disparities in healthcare access and outcomes among different patient populations. Healthcare utilization and outcomes data are stratified by demographics, socioeconomic status, race, and ethnicity to identify and address inequities. Key indicators include access to preventive care, healthcare utilization rates, and health outcomes across various demographic groups.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How can healthcare providers ensure their care aligns with patients' values, preferences, and cultural backgrounds?
- What challenges might patients face in accessing healthcare services, and how can healthcare organizations improve access for all patients?
- What are the potential consequences of poor care coordination among healthcare providers, and how can interdisciplinary teams work together to enhance coordination?
- Why must healthcare organizations continually assess and improve the quality of care they provide, and what mechanisms can be implemented to support ongoing improvement efforts?
Nursing Quality Indicators
According to (5), nursing quality indicators are essential metrics used to evaluate and improve the quality of nursing care in healthcare settings. These indicators provide valuable insights into nursing practice and patient outcomes, helping healthcare organizations and nursing staff deliver safe, effective, patient-centered care. Let's delve into some key nursing quality indicators and their significance below.
Patient Falls
Patient falls are a critical quality indicator in nursing care since they can result in severe injuries and complications for patients (5). As a result, healthcare organizations measure and monitor the rate of patient falls to identify trends and implement preventive measures.
For example, when a hospital notices an increase in the rate of falls among elderly patients in a particular unit, they may introduce interventions such as nonslip flooring, improved lighting, and patient education as fall prevention strategies to reduce the incidence of falls.

Medication Administration Errors
Ensuring accurate medication administration is crucial in nursing practice because medication errors can lead to adverse events, including patient harm or death (5). Nursing quality indicators related to medication administration errors include the rate of medication errors and adherence to medication reconciliation processes (5). For instance, nurses are encouraged to verify patient allergies and cross-check medication orders to prevent errors. If there is an increase in medication errors in a healthcare facility, it may prompt a review of medication administration protocols and additional staff training.

Pressure Ulcers (Bedsores)
Pressure ulcers are a quality indicator of patient skin integrity since they develop when patients remain immobile for extended periods (5). As a result, healthcare organizations measure the incidence and prevalence of pressure ulcers as an indicator of the quality of nursing care (5).
Patient Satisfaction
Patient satisfaction is a patient-centered nursing quality indicator since it reflects the overall patient experience and perception of care (5). Surveys and feedback mechanisms are used to measure patient satisfaction. For example, a scenario might involve patients receiving post-discharge surveys that assess various aspects of their hospital experience, including nurse responsiveness, communication, and pain management. Healthcare organizations can use this feedback to identify areas for improvement and enhance patient-centered care.
In summary, nursing quality indicators encompass a range of metrics that evaluate nursing care quality, patient safety, and patient experiences. By monitoring and responding to these indicators, healthcare organizations and nursing staff can continuously improve their quality of care, leading to better outcomes and increased patient satisfaction (5).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Why is data collection critical in nursing quality improvement efforts?
- What types of data should nurses prioritize collecting to assess patient safety?
- How can nurses ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data they collect for quality improvement purposes?
- What challenges might nurse face when collecting patient-related data, and how can these challenges be overcome?
Data Collection
Quality improvement data collection is a critical component of healthcare quality initiatives, providing the necessary information to assess the current state of care, identify areas for improvement, and monitor progress over time (2). Accurate and meaningful data collection enables healthcare organizations to make informed decisions, implement evidence-based interventions, and ultimately enhance patient outcomes. Let's explore the methods of data collection below.
- Clinical Outcome Collection: Clinical outcome data collection is essential for assessing the effectiveness of healthcare interventions (2). For example, consider a scenario where a hospital is implementing a quality improvement project to reduce surgical site infections (SSIs) following orthopedic surgeries. Data collection would involve tracking the number of SSIs occurring over a specific period and collecting information on patient characteristics, surgical techniques, and post-operative care protocols. By analyzing this data, the healthcare team can identify trends, risk factors, and areas for improvement, ultimately leading to targeted interventions to reduce SSIs.
- Patient Satisfaction Survey Data Collection: Patient satisfaction surveys are valuable tools for collecting data on patient experience (2). A primary care clinic that aims to improve patient satisfaction may administer surveys to patients after each visit, asking about aspects of care such as communication with healthcare providers, wait times, and overall experience. The collected data can reveal areas of strength and areas requiring improvement. For instance, if survey results consistently indicate longer-than-desired wait times, the clinic can adjust scheduling practices or implement strategies to reduce wait times and enhance patient satisfaction.
- Process Measures Data Collection: Process measure data collection focuses on evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare processes (2). For instance, in a medication reconciliation scenario, a healthcare organization might collect data on the accuracy and completeness of medication lists during care transitions. By tracking the frequency of medication reconciliation discrepancies, they can identify process inefficiencies and implement standardized protocols for reconciliation, leading to safer care transitions and reduced medication errors.
- Adverse Event Reporting Data Collection: Adverse event reporting is a crucial mechanism for collecting data on incidents that result in patient harm or near misses (2). For example, consider a scenario where a nurse administers the wrong medication dose to a patient but catches the error before any harm occurs. Reporting this near-miss event allows the healthcare organization to investigate the root causes, implement preventive measures, and share lessons learned with the care team to prevent similar incidents in the future.
Types of Data
Data types play a crucial role in understanding the current state of care, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing evidence-based interventions (2). Let’s explore the different types of data used in quality improvement below.
- Quantitative Data: Quantitative data involves numerical measurements and is particularly useful for assessing the frequency and extent of specific events or outcomes (2). For instance, in a hospital's quality improvement project focused on reducing hospital-acquired infections, the team collects quantitative data on the number of infections over time, allowing them to track trends and measure the impact of interventions, such as hand hygiene protocols or disinfection practices.
- Qualitative Data: Qualitative data provides insights into the "why" and "how" behind healthcare processes and patient experiences (2). This data type is collected through interviews, focus groups, and open-ended surveys. For example, in a primary care setting aiming to improve patient satisfaction, qualitative data may be collected through patient interviews to gather in-depth information about their perceptions of care. Qualitative data can uncover nuances and provide valuable context to complement quantitative findings (2).
- Patient-Reported Data: Patient-reported data includes information directly provided by patients about their health, symptoms, experiences, and preferences. Patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) and patient-reported experience measures (PREMs) are standard data collection tools. In a scenario involving chronic disease management, patients with diabetes may be asked to complete a PROM assessing their quality of life and symptom management. This data helps healthcare providers tailor care plans to individual patient needs and preferences (2).
- Process Data: Process data track the steps and activities involved in healthcare delivery to help assess the efficiency and effectiveness of care processes. For example, in a surgical quality improvement initiative, process data may include the time from patient admission to surgery, surgical team checklist completion, and adherence to anesthesia protocols. By collecting and analyzing process data, healthcare organizations can identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement in care delivery processes.
In summary, quality improvement data collection relies on various data types, including quantitative, qualitative, patient-reported, and processed data. Each data type contributes to a comprehensive understanding of healthcare quality and supports evidence-based decision-making to enhance patient care and outcomes.

Identification Stage
The identification stage for quality improvement data collection is a critical initial phase where healthcare organizations and teams define what data to collect, why it is relevant, and how it aligns with their quality improvement goals (23). This stage is essential for ensuring meaningful data collection efforts will lead to actionable insights. Let's explore the identification stage in more detail.
- Defining Objectives and Goals: During this stage, healthcare organizations must clearly define the objectives and goals of their quality improvement initiative (23). For instance, a hospital aiming to reduce readmission rates for heart failure patients may set a specific goal of reducing readmissions by 20% within the following year.
- Selecting Relevant Metrics: Identifying the right metrics and data points is crucial, and organizations should choose metrics that directly relate to their quality improvement goals (23). Continuing with the example of reducing heart failure readmissions, relevant metrics might include the number of heart failure patients readmitted within 30 days, the reasons for readmission, and patient characteristics. By selecting these metrics, the organization ensures that data collection efforts are aligned with their specific improvement goal.
- Determining Data Sources: Healthcare organizations must identify where the necessary data will be sourced (23). This may involve looking at electronic health records, claims data, patient surveys, or other sources. For instance, to collect data on heart failure readmissions, the hospital may extract relevant information from electronic health records, including admission and discharge dates, diagnosis codes, and patient demographics.
- Creating Data Collection Protocols: Establishing clear data collection protocols is essential for consistency and reliability (23). Healthcare teams should define how data will be collected, who will be responsible for data collection, and the frequency of data collection. For example, in a hospital project aiming to improve hand hygiene compliance, data collection protocols might specify that trained observers will monitor hand hygiene practices at random intervals and record their findings on standardized forms.
By carefully navigating the identification stage, healthcare organizations ensure that their quality improvement data collection efforts are purposeful and aligned with their goals. This sets the stage for collecting meaningful data to drive evidence-based decisions and interventions to enhance healthcare quality.
Gathering Stage
The gathering stage of quality improvement data collection is crucial for healthcare organizations to collect the identified data based on their quality improvement objectives and goals (23). This stage involves systematically collecting data from various sources and often requires careful planning and coordination to ensure data accuracy and completeness. Let's delve into the gathering stage in detail below.
- Data Collection Methods: To gather data, healthcare organizations must determine the most suitable methods for collecting the identified data, which may involve a combination of electronic health records, patient surveys, direct observations, and administrative databases (23). For example, in a quality improvement project aimed at reducing hospital readmissions, data may be collected by reviewing electronic health records to track patient outcomes, conducting patient surveys to gather feedback on discharge instructions, and analyzing administrative data to identify trends in readmission rates.
- Ensuring Data Accuracy and Consistency: Data accuracy is critical in the gathering stage, and organizations must implement procedures to collect data consistently and without errors (23). For instance, if a healthcare facility is collecting data on medication administration, nurses may use standardized protocols to accurately record medication administration times and doses. Regular training and quality checks may also be implemented to maintain data accuracy.
- Timely Data Collection: Timeliness is another important aspect of the gathering stage, and data should be collected promptly to ensure it is current and relevant for analysis and decision-making (23). In a scenario involving tracking patient outcomes, healthcare teams may set specific intervals for data collection, such as collecting post-surgical complication data daily or weekly, depending on the project's requirements.
- Data Security and Privacy: Protecting patient data is a paramount concern in healthcare. As a result, healthcare organizations must adhere to strict privacy and security protocols during the gathering stage to ensure that patient information is handled confidentially and complies with applicable laws and regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) (23). For example, when collecting patient-reported data, organizations may anonymize responses to protect patient identities and comply with privacy regulations.
By effectively managing the gathering stage, healthcare organizations can ensure that they collect accurate, timely, and secure data that will serve as the foundation for subsequent analysis and quality improvement efforts.
Analysis stage
The analysis stage for quality improvement data collection is a critical phase where collected data is processed, examined, and transformed into actionable insights. This stage involves various analytical techniques and tools to identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement (2). Let's explore the analysis stage in detail below.
- Descriptive Analysis: Descriptive analysis is the initial step in data analysis, focusing on summarizing and presenting data meaningfully (2). For example, in a quality improvement project aimed at reducing patient wait times in an emergency department, an analysis may involve calculating and displaying key statistics, such as average wait times, 95th percentile wait times, and the distribution of wait times (2). These descriptive statistics provide an overview of the current situation and help identify areas that need attention.
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA): Root cause analysis is a critical aspect of the analysis stage, as it helps pinpoint the underlying causes of issues or problems (2). In our scenario, if the analysis reveals prolonged wait times in the emergency department, RCA may involve a thorough investigation into the factors contributing to the delays. Potential root causes include staffing shortages, inefficient triage processes, or bottlenecks in diagnostic testing. Identifying these root causes is essential for developing effective interventions.
- Statistical Analysis: Statistical analysis plays a vital role in quality improvement by examining the relationships between variables and testing hypotheses (2). In reducing hospital readmissions, statistical analysis may be used to identify factors associated with readmission risk. For example, healthcare teams can use logistic regression to analyze patient data to determine which variables, such as comorbidities or medication adherence, are statistically significant predictors of readmission risk. This information can guide the development of targeted interventions for at-risk patients.
- Benchmarking: Benchmarking involves comparing an organization's performance data with industry standards or best practices to identify performance gaps (2). When a hospital is looking to improve patient satisfaction, benchmarking may involve comparing its patient satisfaction scores to those of similar hospitals or national averages. Identifying areas where the hospital falls behind benchmarks can inform strategies for improvement, such as implementing best practices from higher-performing institutions.
The analysis stage is critical for transforming raw data into actionable insights and understanding healthcare quality factors (2). Through descriptive analysis, root cause analysis, statistical techniques, and benchmarking, healthcare organizations can gain valuable insights that drive evidence-based decisions and interventions to improve care quality (6).
Benchmarking
The benchmarking stage in quality improvement data collection is a crucial phase where healthcare organizations compare their performance against established benchmarks or best practices (1). This gives healthcare organizations a clear understanding of their position relative to recognized standards and allows them to effectively identify areas for improvement, prioritize, and focus their improvement efforts (5). Let's delve into the benchmarking stage in detail below.
- Defining Benchmarks: In the benchmarking stage, healthcare organizations must define the benchmarks or standards against which they will measure their performance. These benchmarks can be internal (comparing current performance to historical data) or external (comparing to industry standards, best practices, or similar organizations) (1). For example, a primary care clinic seeking to improve appointment scheduling efficiency may choose to benchmark its appointment wait times against industry benchmarks for acceptable wait times.
- Collecting Comparative Data: Gathering data that allows for a meaningful comparison is critical in benchmarking, so healthcare organizations must collect data from relevant sources to measure their performance against the chosen benchmarks (1). Continuing with the appointment scheduling example, the clinic may collect data on the time it takes to schedule an appointment, the number of scheduling errors, and patient feedback. This data is then compared to industry benchmarks or best practices.
- Identifying Performance Gaps: The benchmarking process reveals gaps or disparities between an organization's performance and the benchmarks to highlight improvement areas (1). For instance, if the clinic discovers that its appointment wait times are significantly longer than industry benchmarks, this identifies a performance gap that needs to be addressed to enhance patient access and satisfaction.
- Developing Improvement Strategies: Healthcare organizations can develop targeted improvement strategies once performance gaps are identified. These strategies are based on evidence from the benchmarking process and aim to align performance with or exceed established benchmarks (1). In our scenario, the clinic may implement strategies such as optimizing appointment scheduling processes, enhancing staff training, or using technology to improve scheduling efficiency.


Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Why is data collection a crucial step in the quality improvement process?
- What types of data are typically collected during the data collection stage of quality improvement?
- How do you determine which data points are relevant to your quality improvement project?
- What methods and tools can be used to collect data accurately and efficiently?
Change Models in Healthcare
Change models are essential frameworks used in healthcare, including nursing, to guide and manage the effective implementation of quality improvement initiatives (15). These models offer structured approaches to initiate, plan, execute, and sustain changes in healthcare practice (15). Let’s discuss some prominent change models used in nursing quality improvement below.
- Kotter's 8-Step Change Model: Developed by Dr. John Kotter, this model emphasizes the importance of creating a sense of urgency, building a guiding coalition, and sustaining the change (15). For instance, in a nursing scenario focused on reducing hospital-acquired infections, the 8-step model would involve creating urgency by highlighting the impact of infections on patient safety, assembling a coalition of nurses and infection control specialists, and sustaining change by monitoring infection rates over time and continually reinforcing hygiene protocols.
- Lewin's Change Management Model: Lewin's model consists of three stages: unfreezing, changing, and refreezing (15). Let's consider implementing a new electronic health record (EHR) system in nursing. Nurses first "unfreeze" by acknowledging the need for a new system and undergoing training. Then, they "change" by adopting the EHR and adjusting workflows. Finally, they "refreeze" by becoming proficient and maintaining the new system's use as a standard practice.
- PDSA Cycle (Plan-Do-Study-Act): This model emphasizes iterative cycles of planning, implementing, observing, and adjusting (15). For instance, if a nursing unit aims to improve patient handoffs, they might "plan" by identifying handoff best practices, "do" by implementing changes, "study" by assessing the impact on patient outcomes, and "act" by making further refinements based on their findings. This continuous cycle allows for gradual, data-driven improvements.
- ADKAR Model: The ADKAR model focuses on individual change management, and this could apply to a scenario where nurses are adopting new pain management protocols (15). Nurses would first need awareness of the change (A), followed by desire (D) to participate, knowledge (K) of how to implement the new protocols, ability (A) to do so, and reinforcement (R) to sustain the change over time.
In summary, change models provide structured approaches to drive quality improvement initiatives in nursing, and by applying these models, nurses and healthcare organizations can systematically plan, implement, and evaluate changes to enhance patient care, safety, and outcomes (15).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Why are change models essential in nursing quality improvement initiatives?
- What is the primary purpose of creating a sense of urgency in change models like Kotter's 8-Step model?
- How does Lewin's Change Management Model address the need to "unfreeze" existing practices in nursing before implementing change?
- Why is individual change management crucial in nursing practice, as the ADKAR model emphasizes?
Implementing Change
Implementing changes for quality improvement in nursing is a multifaceted process that requires careful planning, effective communication, and the engagement of healthcare professionals at all levels. According to (15), successful implementation ensures that desired changes are integrated into daily nursing practice, improving patient outcomes. Let’s explore key strategies and considerations for implementing changes in nursing quality improvement below.
- Engage Interdisciplinary Teams: According to (15), collaborative engagement is crucial when implementing changes in nursing practice, and healthcare organizations should assemble interdisciplinary teams that include nurses, physicians, administrators, and other stakeholders. For example, in a scenario involving the adoption of a new pain management protocol, nurses can collaborate with physicians to ensure the consistent application of evidence-based pain management practices. This team approach facilitates a shared understanding of the change and fosters buy-in from all parties.
- Effective Communication: Clear and consistent communication is essential during the implementation phase, so nurses should communicate the rationale behind the change, its expected benefits, and the specific steps involved (15). For example, suppose a hospital is transitioning to a new electronic health record system. In that case, nurses can attend training sessions to understand its features and communicate effectively with patients about how it will enhance their care. This ensures that all stakeholders are informed and can adapt to the change seamlessly.
- Training and Education: Providing adequate training and education is critical to equip nursing staff with the knowledge and skills to implement the change effectively (15). In the case of introducing a new wound care protocol, nurses would require training on the updated practices, wound assessment techniques, and the use of new wound care products. In addition to initial training, ongoing education would ensure that nursing staff stay current with best practices to provide quality care confidently.
- Continuous Monitoring and Feedback: According to (15), implementing change is an ongoing process that requires constant monitoring and feedback since feedback mechanisms allow for adjustments and refinements to the change process. As a result, nursing quality improvement initiatives benefit from the regular collection and analysis of data to assess the impact of the change. For example, suppose a hospital introduces a sepsis screening tool. In that case, nurses can track the number of patients screened, identify missed cases, and evaluate whether early interventions have reduced sepsis-related mortality rates. By engaging interdisciplinary teams, fostering effective communication, providing training and education, and implementing continuous monitoring and feedback mechanisms, nurses can successfully implement changes that improve the quality of patient care and enhance overall healthcare outcomes (8).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Why is it crucial for nursing teams to engage in interdisciplinary collaboration when implementing changes for quality improvement?
- How can effective communication strategies help nursing staff understand the purpose and benefits of a proposed change in healthcare practice?
- What role does ongoing training and education play in ensuring that nursing staff are well-prepared to implement and sustain changes in their practice?
- What methods can be employed to gather feedback from nursing staff while implementing a new practice or protocol?
Evaluating Change
Evaluating change for quality improvement in nursing is a critical phase that involves assessing the impact and effectiveness of implemented changes on patient care outcomes, safety, and the overall quality of healthcare services. According to (15), rigorous evaluation ensures that improvements are sustained, and necessary adjustments are made. Let’s explore key strategies and considerations for evaluating changes in nursing quality improvement below.
- Establishing Clear Evaluation Metrics: To evaluate change effectively, it is essential to define clear and measurable evaluation metrics, and according to (15), these metrics should align with the specific objectives of the change initiative. For example, suppose a nursing unit has introduced a new hand hygiene protocol to reduce hospital-acquired infections. In that case, evaluation metrics may include the number of infections before and after the change, adherence to hand hygiene guidelines, and patient satisfaction scores related to cleanliness and infection prevention.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Data collection is a fundamental component of the evaluation process, and nursing teams should collect relevant data using standardized methods and tools (15). In our scenario, data on infection rates can be collected regularly, and statistical analysis can be performed to determine whether the change has had a statistically significant impact. Nurses can then use run charts or control charts to visualize trends in infection rates over time, allowing for early detection of any potential issues.
- Patient and Staff Feedback: Patient and nursing staff feedback is invaluable in evaluating change since patients' perspectives on the quality of care and their experiences following the change can provide insights into the initiative's effectiveness (15). Additionally, nursing staff can provide feedback on the practicality and feasibility of the new practices. For instance, nursing staff may suggest further improvements in infection control procedures.
- Sustainability and Continuous Improvement: Evaluating change is not solely about assessing immediate outcomes but also ensuring sustainability and continuous improvement. According to (15), nursing teams should determine whether the positive effects of the change are maintained over time and whether there is room for further refinement. For example, when a nursing unit has reduced infection rates, regular audits and monitoring should continue to ensure sustained compliance with hygiene protocols.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Why must nursing teams establish clear and measurable evaluation metrics when assessing the impact of change in healthcare practice?
- How can nurses effectively collect and analyze data to evaluate the success of a change in their nursing practice?
- What role does patient feedback play in evaluating the impact of a change on the quality of nursing care, and how can this feedback be gathered and utilized?
- How can nursing staff engage in ongoing self-assessment to determine their practice changes' effectiveness and identify improvement areas?
- What specific infection prevention measures should nurses prioritize in their daily practice to reduce hospital-acquired infections, and why are these measures effective?
- What are the primary goals of a quality improvement project to reduce hospital-acquired infections, and how can nursing staff contribute to achieving these goals?
- Why is continuous monitoring and evaluation crucial in quality improvement projects, and how can nursing staff use data to drive ongoing improvements in patient care quality?

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What specific infection prevention measures should nurses prioritize in their daily practice to reduce hospital-acquired infections, and why are these measures effective?
- What are the primary goals of a quality improvement project to reduce hospital-acquired infections, and how can nursing staff contribute to achieving these goals?
- Why is continuous monitoring and evaluation crucial in quality improvement projects, and how can nursing staff use data to drive ongoing improvements in patient care quality?
- Enhancing Medication Safety: Medication errors can have severe consequences for patients (6). A quality improvement project may target medication safety by introducing barcode scanning systems for medication administration, implementing double-check procedures for high-risk medications, and providing ongoing training to nursing staff. The project's effectiveness can be assessed by monitoring the number of medication errors reported and verifying that the new safety measures reduce the occurrence of such errors. For example, a nursing team could reduce the incidence of wrong-patient medication administration by implementing barcode scanning during medication administration.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How can nurses ensure that barcode scanning systems and double-check procedures are effectively integrated into their daily workflow in medication safety improvement projects?
- What potential challenges and barriers can nurse units encounter when implementing medication safety improvements, and how can these challenges be addressed?
- Improving Nurse-to-Patient Ratios: Adequate nurse staffing levels are crucial for patient safety and quality of care (6). A quality improvement project may involve adjusting nurse-to-patient ratios based on patient acuity levels, introducing workload management tools, and conducting regular staffing needs assessments. In this case, the project's success can be measured by tracking patient outcomes, nurse workload, and patient satisfaction scores. For example, a nursing unit could reduce nurse burnout and improve patient care by optimizing staffing ratios during peak hours.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Why is it important to regularly assess and adjust nurse-to-patient ratios in a healthcare setting, and what strategies can nurse leaders employ to optimize staffing levels?
- In a quality improvement project focused on nurse-to-patient ratios, what key factors should nurse leaders consider when determining staffing needs during different shifts and patient acuity levels?
- Enhancing Discharge Planning and Care Transitions: Effective care transitions from the hospital to home or other healthcare settings are essential to preventing readmissions and ensuring continuity of care (6). A quality improvement project may focus on improving the discharge planning process, including patient education, medication reconciliation, and post-discharge follow-up. Success can be assessed by monitoring readmission rates and patient-reported experiences. For example, a nursing team could work on reducing hospital readmissions by ensuring that patients receive thorough discharge instructions and have access to follow-up care.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What steps can nurse teams take to enhance the discharge planning process and ensure seamless care transitions for patients moving from the hospital to home care?
- What strategies can nurse teams employ to ensure that patient education during discharge planning is effective and leads to better patient outcomes and satisfaction?
The above examples illustrate the diverse range of quality improvement projects in nursing, each addressing specific challenges to enhance patient safety and care quality.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Why is continuous monitoring and evaluation crucial in quality improvement projects, and how can nursing staff use data to drive ongoing improvements in patient care quality?
- What are the primary goals and objectives of QI models, and how do they contribute to the overall quality of healthcare?
Conclusion
In conclusion, this course provides essential knowledge and skills valuable for nurses aiming to deliver high-quality, safe, patient-centered care. Quality improvement in nursing is not merely a theoretical concept but a practical approach that can be applied to various aspects of healthcare, and one critical aspect to remember is the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration. As frontline caregivers, nurses must collaborate with physicians, administrators, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals to drive improvements in healthcare delivery.
As nurses continue to play a pivotal role in healthcare delivery, the knowledge and skills gained from this course will empower them to lead and actively participate in quality improvement initiatives. By applying quality improvement principles, nurses can contribute to better patient experiences, patient outcomes, and overall healthcare quality.
Final Reflection Questions
- What have you learned from this course?
- Why is interdisciplinary collaboration essential for nurses to effectively implement quality improvement initiatives in healthcare settings, and how can nurses foster collaboration among healthcare professionals?
- How does the concept of continuous learning and adaptation align with the dynamic nature of healthcare, and what strategies can nurses employ to stay current with evolving best practices and guidelines?
- In what ways does Quality Improvement benefit both healthcare providers and patients?
- What are the potential challenges in implementing QI initiatives in a healthcare organization?
- In what ways has QI in healthcare become intertwined with the broader goals of healthcare reform, such as improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs?
- What role does leadership play in the effective implementation of QI models?
- How can leaders promote a culture of continuous improvement within healthcare organizations?
- How do QI models facilitate interdisciplinary collaboration among healthcare professionals to drive improvements in patient care?
- What challenges might healthcare organizations face when attempting to adopt and sustain QI models, and how can these challenges be overcome?
- How does the "testing and learning" concept in the PDSA cycle align with the principles of evidence-based practice in healthcare?
- In what ways do QI models promote patient-centered care and patient safety, and can you provide examples of tangible improvements in these areas achieved through QI initiatives?
- How can the Six Sigma model contribute to the reliability and consistency of healthcare processes?
- Safe: What steps can healthcare organizations take to minimize the risk of medical errors and adverse events?
- Practical: How do healthcare providers ensure that evidence-based treatments and interventions lead to positive patient outcomes?
- Patient-centered: Why is it important to involve patients in their care decisions, and how can healthcare professionals effectively engage patients in the decision-making process?
- Timely: What are some key factors contributing to delays in healthcare delivery, and how can these delays be reduced to improve timeliness?
- Efficient: How can healthcare processes and workflows be streamlined to enhance efficiency and reduce waste?
- Equitable: What are some barriers to achieving healthcare equity, and how can healthcare organizations address these disparities?
- How can nurses actively involve patients in data collection to enhance patient-centered care?
- What tools or technologies are available to streamline data collection processes in nursing practice?
- How can nurses effectively collaborate with interdisciplinary teams to gather comprehensive data for quality improvement initiatives?
- What strategies can nurses employ to maintain patient privacy and confidentiality while collecting sensitive healthcare data?
- What methods can nurse use to analyze and interpret the data they collect to identify areas for improvement?
- Why must nurses regularly review and assess the data they collect to drive continuous quality improvement in healthcare settings?
- Regarding patient falls, what strategies can healthcare organizations implement to reduce the incidence of patient falls, and how can nursing staff actively contribute to fall prevention efforts?
- How can nurses ensure the accurate and safe administration of medications, and what measures can be taken to minimize medication errors?
- What are the key nursing practices and interventions that can prevent the development of pressure ulcers in hospitalized patients, and how can nursing staff collaborate to achieve this goal?
- Why is patient satisfaction an important nursing quality indicator, and what actions can nurses take to enhance the overall patient experience?
- What impact do nurse-to-patient staffing ratios have on the quality of nursing care, and how can healthcare organizations ensure safe nurse staffing levels?
- How can nurses enhance patient education to promote better understanding and self-management of their health conditions?
- How can you ensure that the data collected is reliable and valid?
- What role does standardization play in data collection for quality improvement?
- How can you establish baseline data for comparison in your quality improvement project?
- What challenges or obstacles might you encounter when collecting data for quality improvement?
- How frequently should data be collected to monitor progress in a quality improvement project?
- How can you involve frontline staff in the data collection to ensure accuracy?
- What measures can be taken to protect patient privacy and confidentiality during data collection?
- How can you analyze the data collected to identify trends or patterns?
- What actions should be taken if the data collected indicates a problem or deviation from the desired outcome?
- What strategies can ensure that data collection remains an ongoing and sustainable practice in healthcare quality improvement efforts?
- What are the potential challenges or resistance nurses might encounter when implementing changes using these models?
- How can a guiding coalition or interdisciplinary team be effectively assembled to support nursing quality improvement efforts?
- What strategies can nurses employ to sustain changes and prevent reverting to previous practices once implemented?
- How can nursing leaders ensure that staff have the necessary knowledge and skills to embrace the changes outlined in these models?
- How can nurses use these change models to promote a culture of continuous improvement in healthcare settings?
- How can nurses ensure their implementation changes align with evidence-based best practices and clinical guidelines?
- What potential challenges or barriers might nurse teams encounter when trying to implement changes for quality improvement?
- What strategies can address resistance to change among nursing staff and promote their active participation in the implementation process?
- How can nursing leaders effectively communicate the expected outcomes and benefits of the change to gain support and commitment from their teams?
- What are the advantages of using data and performance metrics to monitor the progress and impact of change implementation in nursing practice?
- How can nursing staff ensure that changes are sustained and become integral to their daily practice rather than temporary modifications?
- Why is it crucial to consider the sustainability of change when evaluating its long-term impact on nursing quality improvement?
- What challenges or obstacles might nurse teams encounter when collecting and analyzing data for change evaluation, and how can these challenges be addressed?
- How can nursing leaders encourage a culture of continuous improvement among their teams as part of the change evaluation process?
- What strategies can be employed to ensure that the feedback and insights gathered during the evaluation phase are actively used to refine and optimize nursing practices?
- What are the potential consequences of not conducting thorough and systematic evaluations of changes in nursing practice for quality improvement?
- How can nursing staff and healthcare organizations ensure that the lessons learned from change evaluations are applied to future improvement initiatives to enhance patient care outcomes?
Workplace Violence Against Nurses
Introduction
The role of the registered nurse, while fundamentally dedicated to the care and wellbeing of patients, has long been fraught with challenges that extend beyond the complexities of medical care. One such pressing concern is workplace violence, an issue that nurses confront with alarming frequency. Recent statistics show that healthcare workers, particularly nurses, are at a higher risk for workplace violence compared to other professions.
Given the vital role nurses play in patient care and the broader healthcare system, it is imperative to understand the scope, sources, and solutions to this pressing issue. This continuing education course is dedicated to arming nurses with the knowledge, tools, and strategies to recognize, respond to, and prevent incidents of workplace violence, thereby ensuring their safety and the uninterrupted provision of quality care.
Introduction
The role of the registered nurse, while fundamentally dedicated to the care and wellbeing of patients, has long been fraught with challenges that extend beyond the complexities of medical care. One such pressing concern is workplace violence, an issue that nurses confront with alarming frequency. Recent statistics show that healthcare workers, particularly nurses, are at a higher risk for workplace violence compared to other professions.
Given the vital role nurses play in patient care and the broader healthcare system, it is imperative to understand the scope, sources, and solutions to this pressing issue. This continuing education course is dedicated to arming nurses with the knowledge, tools, and strategies to recognize, respond to, and prevent incidents of workplace violence, thereby ensuring their safety and the uninterrupted provision of quality care.
Workplace Violence
Definitions
The Occupational and Safety Health Administration (OSHA) (3) defines workplace violence (WPV for the purpose of this course) as any act or threat of physical violence, harassment, intimidation, or other threatening, disruptive behavior that occurs at the work site. This can also include verbal, written, or acts of sabotage against an individual while they are at work.
Workplace violence crosses all demographic barriers and is indiscriminate in who it can and does affect. Even seeing workplace violence influences morale, attendance, and the overall well-being of employees and their co-workers.
Types of Violence
Currently, there are four categories of workplace violence according to the American Nurses Association (5).
1: Criminal Intent - normally involves theft from the business or employees.
Example: Carol is working on documentation and notices a person lingering in the hallway. Carol doesn’t really think anything of it, assuming they are family members of one of the patients. Several minutes later, the person exits quickly from the supply room and down the stairs. Carol calls security to let them know, but they can’t locate the individual. After looking through the supply room, they find that several containers of wound dressing supplies are missing.
2: Customer/client/patient - the individual becomes violent with employees while receiving services.
Example: David was updating a family on their father’s critical condition. David could tell the family was upset, but the patient’s son seemed more frustrated than the others. During David’s explanation, the son grabbed David’s clipboard and yelled, “You’re not doing anything! You’re just letting him die!” The son then threw the clipboard at David’s head. David blocked the clipboard with his arm, receiving a rather deep cut as a result. Security became involved, and David had to go to the ER for treatment.
3: Worker on worker - an employee bullies, attacks, or threatens another employee.
Example: Emily was rounding when Dr. G. came onto the floor. This doctor was well known for being difficult to work with, and he always required the nurses to stand behind him in the room while he talked with his patients. Emily had one of Dr. G.’s patients today and was in the room, he asked her if the patient had ambulated. Emily told him they had not, but they planned to before and after lunch. The doctor made an audible sigh and while shaking his head at the patient said, “See…this is what I deal with every day. These nurses can’t get anything right. They’re all useless.”
4: Personal relationship - involves a person who has an interpersonal relationship with the nurse, but no association with the nurse’s employer or the business.
Example: Rebecca was walking to her car after work. Halfway to her car, she noticed an individual leaning against the trunk of her vehicle. Rebecca recognized this person as the someone her friend was currently dating. This person approached Rebecca aggressively and began yelling about gossiping and trying to break their relationship. Rebecca started back toward the building, hoping security was nearby, and was pursued by the female. Eventually, Rebecca made it to the building and got inside. Luckily, the door only opened with an employee badge, and Rebecca was safe. She went ahead to security.
Currently, the customer/client type of workplace violence is the most prominent, especially in healthcare and toward nurses. The American Nurses Association (ANA) reports that OSHA does not require employers to implement workplace violence prevention programs, but it supplies voluntary guidelines and may cite employers for not supplying a workplace free from recognized serious hazards.
Some states have legislated that employers develop a program while most states have advanced laws that amend existing statute for assaults of first responders by adding health care providers / nurses and/or increasing the penalty associated with such behavior. (3)
It is worth noting that since there are, in most cases, no actual requirements for employers to provide safe work environments for nurses, preventing and dealing with WPV proves problematic. It falls on nurses to understand what constitutes WPV, how to manage it, how to cope with it, how to report it, and how to ensure action is taken and a resolution is reached when WPV occurs.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- In the scenarios above, should the employees report these incidents to administration at once?
- How would you describe the earlier scenarios on workplace violence?
- Why is it important to ask how you would find and describe workplace violence?
- Can you provide any examples of workplace violence you have experienced or seen?
Epidemiology
Workplace violence can take many forms, and the possible varieties and scenarios are endless. Regardless of how it manifests, the effects of workplace violence are clear and widespread. It can affect productivity of employees, morale, attendance, turnover rates, quality of work, patient outcomes, and much more.
Workplace violence can affect and involve workers, clients, customers, and visitors. WPV ranges from threats and verbal abuse to physical assaults and even homicide. In 2010, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) data reported healthcare and social aid workers were the victims of approximately 11,370 assaults by persons; a greater than 13% increase over the number of such assaults reported in 2009 (10). Almost 19% of these assaults occurred in nursing and residential care facilities alone. Unfortunately, many more incidents probably go unreported (5).

Impact on Nurses Well-Being
Workplace violence can take a heavy toll on nurses. These tolls can be emotional, mental, and physical as well as short-term or long-term. The seriousness of these injuries can vary widely ranging from minor upset to permanent injury and in worst cases, even death. (13)
This harm doesn’t stop with the nurse. The effects of workplace violence may also include effects spanning the unit the nurse works on or even the entire facility. Low morale, reduced productivity, lack of trust in employers, and fear of going to work can be results of violent events occurring to even a single co-worker.
Workplace violence can also have a financial effect on nurses and their employers related to lost time at work from injury or callouts, costs of care for treatment related to the incident (physical and/or psychological), or even legal fees. (13)
Given that incidents of workplace violence are rapidly increasing, these impacts are expected to increase as well. It is easy to see how this harm is widespread and can potentially ripple outward into the nurse’s professional and personal life. The stress and harm do not stay at work, and can spread to the nurse’s family, social interactions, and more.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How far reaching do you think workplace violence is?
- Can you give some examples of how workplace violence has affected you or your co-workers?
- What are some examples of how workplace violence against someone else can affect you or the patients on your unit?
Barriers to Reporting
One way to combat workplace violence is knowledge of its existence, its nature, and its frequency. Unfortunately, there are many factors that either prevent or discourage nurses from coming forward with reports when they are the victims of WPV.
A study presented in a Chinese nursing journal surveyed 325 nurses. Of these nurses, 266 were spread across 165 hospitals, and these hospitals were in 72 cities.
A total of 172 nurses (64.7%) experienced violent incidents during the past year. Of these incidents, 45.5% were reported; and the reporting rate of physical assaults (69.0%) was higher than those of verbal abuse (36.9%), threatening behavior (51.7%), and sexual harassment (60.0%). Formal reporting accounted for 25.4% (15.4% in written form and 10.0% through a computer-assisted reporting system.
Almost half of the nurses (49.6%) said that the hospital had no reporting system, or they were uncertain about the reporting system. For reasons of not reporting, 51.9% of the nurses were unaware of how and what types of violence to report, and 50.6% of the nurses believed that the hospital paid greater attention to patients rather than staff. (7)
Interestingly, almost fifty percent of the nurses surveyed had limited knowledge, if any, of a reporting system available to them, while fifty percent felt the hospital favored the patients over their own employees. Combined with an actual or perceived lack of supervisory support, this encourages an environment where nurses feel powerless to protect themselves or to take proper action when threatened or harmed.
The Minnesota Nurses Association, in August of 2022, published a press release with the results of a nursing survey on the topic of workplace violence. In this survey, ninety-seven percent of the nurses surveyed observed WPV or harassment over the previous two years.
The top reasons cited by nurses who did not report workplace violence were lack of time due to overwork and under-staffing, cited by fifty-eight percent of respondents, and lack of action by hospital management, cited by fifty-three percent of nurses in the survey. (4)
It would appear from these studies that many nurses feel it is futile to report incidents of workplace violence they encounter, and even if they realized an incident was reportable, they may not be aware of a way to report it or have time to do it. This perceived powerlessness and sense of futility in the face of abuse and violence will only continue to worsen unless action is taken to remove barriers to reporting and for nurses to have access to aid and support for supervisory staff.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Can you think of any examples of when you or a co-worker tried to report an incident of workplace violence and were unable to?
- If so, what was the barrier that prevented you from reporting?
- Can you name three alternative ways to report workplace violence at your organization?
Culture of Safety
A commonly used phrase is “Culture of Safety”, but is there a standardized definition of what it is or could be? Many resources point to the safety of patients about medical errors, patient rights, and protecting the patient’s information, but few address the issue facing caregivers and especially nurses. However, there is no agreed-upon or standard definition of what exactly a “culture of safety” is or what it should look like.
The American Nurses Association approaches the concept by saying, “Establishing a culture of safety in health care is essential to the security and well-being of your patients, staff, and organization. Effective nurse leaders embrace safety protocols that ensure their organization delivers a secure, protective environment that prioritizes patients and caregivers.” (12)
Currently, there is only a single federal legislation in place about the issue.
The only federal regulation currently in place is the General Duty Clause of the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970. This clause requires employers to supply a work environment free from recognized hazards that are causing or likely to cause death or serious physical harm. However, the general duty clause offers no specific recommendations about management of workplace violence.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) issued guidelines for workplace violence prevention for health care and social service workers. First issued in 1996 and later updated, the guidelines are only advisory. (1)
It is paramount that nurses and other direct care providers accept the responsibility of creating policies and procedures within their organizations to define and enforce a work environment where violence is not tolerated and dealt with accordingly.
There is currently a small body of research and work of the effects workplace violence has on nurses as human beings. Most of the evidence focuses on how workplace violence increases the risk nurses present to patients in the form of medical errors, staffing issues due to missed work, poor documentation, etc.
The main body of evidence discussing how workplace violence affects nurses is noted in research around nurse burnout. A 2020 study published by the National Health Institute (10) states, “Workplace aggression is a source of extreme socio-emotional stress, which may lead to the experience of psychological strain.
A large body of research shows that exposure to workplace aggression and violence may severely impair healthcare workers’ mental health, including symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder, depression, and burnout.”
This study also shows an important association with workplace aggression and violence targeting nurses and drastically increased levels of emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and deep feelings of poor personal accomplishment. Over time, these feelings lead to complete burnout, and even worse, possibly psychological and/or physical conditions in the nurse affected.
Even with this preliminary information and research, we still have a long way to go to show the full and far-reaching effects of workplace violence on nurses. Again, by being proactive and acting now, we as nurses can foster this research and bring to light the issues so they can be addressed.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How does your organization define a “culture of safety”?
- Do you agree with the definition?
- How would you define a “culture of safety” from your own perspective given your experiences and challenges?
ANA Zero Tolerance Policy
In 2019 the American Nurses Association (ANA) (2) release a brief titled “Reporting Incidents of Workplace Violence”. In it, they discussed several issues surrounding workplace violence, barriers to its reporting, and made recommendations to healthcare organizations on strategies relating to the issues of workplace violence.
They also set forth a “Zero Tolerance Policy on Workplace Violence”, which provided some definitions and several recommendations on how to deal with WPV.
The introduction to the “Culture of Safety” part of this brief is as follows:
By prioritizing, developing, and sustaining an organizational culture focused on safety, we can drive the future of healthcare to a place where patients and those who care for them are free from harm. It is not only one of many priorities but is the overriding ethical imperatives for all leaders. (9)
The ANA also suggested a three-level prevention strategy, each with a part for the employer and the employee. Essentially, the role of the employer is gathering data, providing a “safe” work environment, non-punitive reporting, and development of programs to provide a safe work environment for nurses. The employee’s role is to take part in the implementation and evaluation of said programs.
Unfortunately, these are only suggestions and employers do not have to implement any programs or services to protect employees against workplace violence. Also, healthcare employers do not have to report any incidents to JCAHO who consider events of workplace violence to be “sentinel events”.
In the end, it falls on the nurses and employees directly affected by WPV to assume the charge against workplace violence, hold employers accountable, communicate with local and state legislators, and effect change to protect themselves.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Considering the recommendations and guidelines set forth by these entities, do you think they are adequate or effective? Why nor why not?
- How has this information changed your perception of the overall reporting process on workplace violence against nurses?
- What generalizations can you make from this information on the reporting process from an employer perspective?
Strategies to Prevent Workplace Violence
To end nurse abuse for good, Boston-Leary says it takes every nurse speaking up and reporting abuse within an organizational culture that has an established process for allowing nurses to report abuse without fear of recrimination and then follows up with a resolution. (8)
There are some suggested actions to help prevent and combat workplace violence in your practice setting. These actions include:
Know the definition of abuse.
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) defines workplace violence as “the act or threat of violence, ranging from verbal abuse to physical assaults directed toward persons at work or on duty.”
Agreeing on this definition is an important first step to achieving widespread acknowledgement of the distinct types of nurse abuse, particularly non-physical abuse, Boston-Leary explains. (8)
Report Abuse
Ask about how your workplace manages abuse reporting, whether it is in your current workplace or when you are applying for a position, Boston-Leary suggests. “Ask about how reporting abuse happens during any shift because there should be a reporting mechanism in place for everyone, even if it’s on a weekend or evening shift with no manager easily accessible to report to.”
If (when) you do experience abuse, it’s essential that you speak up immediately and note any witnesses who could corroborate your description of the incident, she says.
Even after you experience abuse and even if you didn’t report it, it’s important to share your past abuse with others to empower them to report abuse they experience. (8)
Change Your Culture
Join or meet a committee to build or strengthen zero-tolerance abuse policies. Based on ANA’s Zero Tolerance Policy on Workplace Violence, Boston-Leary suggests these crucial elements of a zero-tolerance abuse program:
Stop violence before it starts through education to find risks and reduce vulnerabilities for workplace violence.
Create an effective response to violence immediately after it occurs, including emergency care.
Establish long-term responses that reduce the long-term negative effects of workplace abuse. (8)
Communicate with your Legislator!
Congress was considering legislation to #End Nurse Abuse by passing The Workplace Violence Prevention for Health Care and Social Service Workers Act (H.R 1195). If approved, this law would have required health care and social service industry employers to develop and implement a comprehensive workplace violence prevention plan that protects nurses and other healthcare professionals from on-the-job abuse.
Boston-Leary believes legislators are very attuned to the trusted voice of nurses to share about what is happening in health care today (8).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What is your organization’s primary method of reporting abuse or violence against employees?
- Do you know who your local and state legislators are and how to contact them?
- Are you aware of any committees or groups within your organization that actively address the issue of workplace violence?
Nurse-led Strategies
You can join these committees or work with your employer to create them. Collaborating with your supervisory staff and HR, you can create workflows, policies, reporting methods, and provide education on prevention of workplace violence and make a difference in your overall work environment.
Regarding Your Legislators
As mentioned before, 2021 Congress was considering federal legislation to end nurse abuse by passing The Workplace Violence Prevention for Health Care and Social Service Workers Act (H.R. 1195). The bill was passed by the House on April 16, 2021, but was never passed by the Senate.
You can find your local and state legislator contact information very easily on the internet. A simple search for “how to find state legislator contact information” is a wonderful place to start. As a voting citizen, you have every right to contact them, and demand laws be created to protect you while you work.
Below are some links to help you find elected officials:
- https://www.usa.gov/elected-officials
- https://www.usa.gov/state-governor
- https://www.senate.gov/senators/senators-contact.htm
- https://www.house.gov/representatives/find-your-representative
Advocate for your own safety the same way you would for your patients!
As nurses we aren’t afraid of stepping up to bat for our patients when they need something, but we are notorious for taking a hit and letting it slide, sometimes even to our own detriment.
We owe it to ourselves to offer that same level of advocacy to ourselves and our co-workers.


Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How can you become an advocate for yourself or your co-workers when it comes to workplace violence?
- Who is the contact in your organization for instances of workplace violence?
Resources
The Joint Commission supplies resources available to report and learn about how to report workplace violence. The links included are for federal, state, professional, and other resources. The direct link to this page is:
The Joint Commission: Workplace Violence Prevention Resources
Local law enforcement
As a private citizen, you are protected by laws about assault, battery, and other attacks on your person. You are within your rights to call the police on events of workplace violence, especially if your life or health are threatened, or you are physically attacked. It is likely your employer will not support you in this situation due to legal implications. It is best to ask your HR department and supervisory staff how these situations should be managed if they occur.
Legal Counsel
Consult with a lawyer about your legal rights in situations on workplace violence and how to best manage them. Be sure to bring scenarios, information on how your employer suggests dealing with these situations, and examples of violence you have seen or have experienced.
Educate and Train Yourself
Learn as much as you can about recognizing and managing workplace violence. Your employer may supply these courses, and if they don’t, it may be prudent to request them. Also, you can seek outside education and training on these topics including self-defense classes and crisis management courses.
Practice Self-Awareness
We all have inherent beliefs, perspectives, and feelings that can prevent us from acting in certain situations. Knowing yourself and understanding possible nuances within yourself that could be a detriment to you appropriately handling a situation of workplace violence could mean the difference between prevention and becoming a victim.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What training opportunities does your organization provide on management and follow-up for workplace violence?
- What information would you ask local law enforcement or a legal counsel for on workplace violence?
- What might someone who believes abuse against nurses is “just part of the job” do when they find themselves a victim of workplace violence?
- What can you do to help individuals that may simply allow workplace violence to affect their well-being?
Conclusion
Being an agent of change can be intimidating, terrifying, and even force us to deal with feelings and beliefs we didn’t even realize were in our way. Incidents of WPV have been rising sharply over the past several years, and there is no sign of slowing. It’s up to us as front-line workers, nurses, and co-workers to take responsibility for our own safety and work environment.
Through cooperation and consistency, we can create and bring solutions to the workplace and hopefully one day, aid in the creation of laws that make our jobs safer for us to supply the care and support our patients need. We owe it to ourselves to take the necessary steps to show our employers it’s time to address this issue. “Be the change you wish to see in the world.” ~Mahatma Gandhi –
Telemetry Basics - Rhythm Recognition
Introduction
To truly understand telemetry, nurses must have knowledge about the anatomy of the heart and how electricity passes through it, how the electrocardiograph (EKG) works to receive and record the electrical activity, and how this information is transmitted via telemetry to the appropriate receiving device.
Defined as the transmission of instrumental readings by various methods such as radio waves or wires, telemetry gathers and transmits EKG readings to a central or remote monitor for interpretation and storage (71). The ability to read EKG rhythms from a variety of monitors consists of more than looking at a rhythm strip and identifying the rhythm. It consists of knowing the anatomy of the heart, how electricity travels through it and translates into the EKG we know, and what changes can happen based on injury, electrolytes, or other causes.
Introduction
To truly understand telemetry, nurses must have knowledge about the anatomy of the heart and how electricity passes through it, how the electrocardiograph (EKG) works to receive and record the electrical activity, and how this information is transmitted via telemetry to the appropriate receiving device.
Defined as the transmission of instrumental readings by various methods such as radio waves or wires, telemetry gathers and transmits EKG readings to a central or remote monitor for interpretation and storage (71). The ability to read EKG rhythms from a variety of monitors consists of more than looking at a rhythm strip and identifying the rhythm. It consists of knowing the anatomy of the heart, how electricity travels through it and translates into the EKG we know, and what changes can happen based on injury, electrolytes, or other causes.
Heart Anatomy 101
As we know, the heart consists of four chambers, two atria—right atria (RA) and left atria (LA)—and two ventricles—right ventricle (RV) and left ventricle (LV)—working in a cycle to ensure adequate blood flow occurs. The heart receives blood from the inferior and superior vena cava (IVC and SVC) and enters the RA, moves to the RV, passes through the pulmonary artery (PA) and lungs, returns to the LA, enters the LV, and exits the heart through the aorta.
Heart cells, known as myocytes, are negatively charged, or “polarized” at rest. When these muscle cells contract, they become “depolarized” or positively charged. But how do the myocytes know when to contract? Less than 1% of the cells in the heart have a special role and name. These are known as the pacemaker cells and their role is to ensure that the heart beats. This is done through the action potential that is spontaneously created by the pacemaker cells. Some of these pacemaker cells have different speeds in depolarization, meaning that the fastest pacemaker cells are the ones controlling the speed. This will make more sense later when discussing specific cardiac rhythms (69).
Starting in the right atria, the sinoatrial node (SA node) is the primary group of pacemaker cells that determines the heart rhythm. The SA node, as well as the other pacemaker cells within the heart, progress through a rapid depolarization and repolarization process (2).
Pacemaker cells do not have a true resting potential, this means they are always in an “unstable” state to create spontaneous action potential. The action potential is the brief reversal of polarity in the cell; polarity consists of potassium (K+) in the cell with a negative charge, while sodium (Na+) and calcium (Ca++) are outside of the cell with a positive charge (2).
Starting at the beginning of the cardiac cycle the pacemaker cells always have a membrane potential or voltage—the voltage of the cellular membrane as a result of permeability and concentrations of ions inside and outside the cell—of -60 microvolts (mV). From -60mV to -50mV the channels within the cells open, leading to a slow influx of Na+ inside the cell and a slow depolarization of the cell. Once the membrane voltage has reached the minimum threshold of -50mV the Ca++ channels open, causing Ca++ to move into the cell. This is known as the rising depolarization phase. The membrane voltage reaches the peak and the next thing that happens is the falling repolarization phase. This is where the K+ channels open to return the cell to a repolarized state (2).
(20)
Once these steps have occurred, the energy is transferred to surrounding cells, and the cardiac cycle continues. However, the action potential in the other myocytes is slightly different. Myocytes have a resting potential, which is different from the pacemaker cells. The resting potential is around -90mV and these cells only start the depolarization process when stimulated by an external force. During the end of the pacemaker cell’s action potential phase, additional Ca++ is passed into the neighboring myocytes through gap junctions. The introduction of Ca++ into the cell causes a sharp rise in the membrane voltage that approaches the threshold which is -70mVs. Once that threshold has been reached, the NA+ fast channels open and a rapid depolarization occurs since Na+ is brought into the cell. The Ca++ slow channels open at -40mVs, further causing depolarization with Ca++ entering the cell (2).
At the peak of cellular depolarization, the Na+ channels close, leading to a slight repolarization through some K+ entering the cell. This is minor as the Ca++ channel is still open and continues to move K+ out of the cell. A plateau is created because of this and allows for the cell to go through two important phases. The first phase starts when the membrane voltage increases from the resting potential and continues until the plateau phase ends. This is known as the absolute refractory period and is where the myocytes relax before they can respond to additional stimuli. It prevents summation and tetanus which could lead to the heart not beating. The second phase is where additional Ca++ is pulled out of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) to further push K+ out of the cell (2).
The phase ends when the Ca++ channel closes, extra Ca++ is sent back to the SR, and K+ is allowed back into the cell. The sodium/potassium pump allows Na+ to exit the cell, returning the cell to its resting potential. This rapid process occurs in every myocyte for the life of the cell. Pacemaker cells are the only cells that can generate a heartbeat. Impulses from the nervous system can increase or decrease the heart rate, but they are influencing the pacemaker cell to generate more beats, not creating them (2).
It is important to note that there are several sets of pacemaker cells within the heart. The SA node starts the process, but there are a few others spaced out along the electricity’s path to ensure that the atria and ventricles of the heart have time to fill and properly contract. The second set of pacemaker cells is the atrioventricular node (AV node) where a slight delay of 0.01-0.05 meters per second (m/s) happens to make sure that the ventricles fill up adequately. The bundle of His takes the electric impulse to the left and right bundle branches and from there, the Purkinje Fibers are triggered. These fibers have a speed of 2-4 m/s to provide enough force to eject the blood from the ventricles (69).
Correlating all of this back to telemetry, scientific development within the medical profession has allowed us to visualize this electrical activity and translate it into an effective method of diagnosing cardiac conditions such as abnormal heart rates or cell death.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Reflecting on what you know and what you have learned so far, what information would you consider important to know when it comes to reading EKGs or telemetry strips?
- What information, if any, was surprising to you in regard to the action potential of the pacemaker cells?
- Why do you think the pacemaker cells start with a voltage or an action potential?
Types of Telemetry
EKG
There are many ways to view cardiac rhythms now, however, the oldest method is the EKG. During the late 1700s, the Italian physician Luigi Galvani was experimenting with electricity and animal tissue. His experiments spanned at least three decades and inspired other physicians during and after his time. Using legs removed from the bodies of frogs, Galvani theorized that “animal electric fluid” enabled the muscles within the legs to move when touched by metals; according to him, this was “natural” fluid and not created as static electricity or friction is. He went on to theorize that the brain is an essential part of creating the “electric fluid” with nerves as the conductors (6).
Jumping forward to 1842, Doctor Carlo Matteucci made a significant contribution to EKGs. During his time researching electrical detection in animals, he discovered the electrical currents within the heart that accompany each heartbeat. Thirty-five years after Matteucci, Augustus Waller was able to use a capillary electrometer and electrodes to perform the first human EKG. These electrodes were placed on the chest and back of the participant and were vital in demonstrating there was electrical activity that preceded the contraction of the ventricles. William Bayliss and Edward Starling improved upon Waller’s research by using improved capillary electrometers to demonstrate triphasic cardiac electrical activity (1).
The Dutch physician most noted for creating the EKG known today was Doctor Willem Einthoven. He was inspired by Waller and those before him to improve the capillary electrometer, successfully identifying five deflections that were initially named ABCDE. Having to factor for inertia, Einthoven implemented mathematic correlation, resulting in the traditional EKG rhythm strips we use today with the letters PQRST depicted in the image below. Einthoven is also responsible for coining the word electrocardiogram or electrokardiogram in Dutch. This is where providers get the “k” in EKG from (1).
While Waller’s EKG utilized ten electrodes, Einthoven was able to condense that number to three, eliminating the right leg and the mouth electrodes. These three leads created Einthoven’s triangle; an important concept still used today and that will be discussed later. All of Einthoven's work resulted in him being awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1924 (1).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What do you know of the history of the EKG and telemetry? Was there anything new you learned?
- What process of developing the EKG interested you the most? Why?
- Do you think there is more that can be done to improve EKG? If so, what do you think could be done?
Bedside Monitor
Emergency departments (ED), intensive care units (ICU), and other specialized areas that require continuous monitoring of a patient’s EKG and vital signs utilize various bedside monitors to ensure they are receiving accurate, real-time information on the patient. Cords are used to connect the patient to the monitor. The electrodes to display and document cardiac rhythm and heart rate are applied to patients in the standard 5 lead placement displayed in the below image. The vitals displayed on the monitor can also be displayed outside the room on a screen with multiple patients. Nurses, paramedics, or trained telemetry monitor technicians can watch many of these monitors at a time.
(14)
The placement of the five leads consists of the following:
- RA: 2nd intercostal space, anterior axillary on the right – some providers may put this lead higher on the chest or on the right arm
- LA: 2nd intercostal space, anterior axillary on the left – some providers may put this lead higher on the chest or on the left arm
- RL: 8th intercostal space, anterior axillary on the right – some providers may put this lead lower on the abdomen
- LL: 8th intercostal space, anterior axillary on the left – some providers may put this lead lower on the abdomen
- V: 4th intercostal space, right margin of the sternum
Note: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for specific lead placement.
Helpful Tip: Many healthcare providers quickly remember lead placement based on color is smoke (black) over fire (red) and snow (white) over grass (green). This leaves brown (chocolate) in the middle.
These bedside monitors can monitor pulse oximetry, respiratory rate, temperature, capnography, blood pressure, and arterial pressure. Some devices may have other unique monitoring features. These monitors may be portable or have a way to transfer the cords to a transport monitor. They come with alarms that can be adjusted based on the patient’s unique vital signs or hospital policy.
First responders have similar devices they use when transporting patients with the added benefit of having a defibrillator and a real-time feedback device built in (91).
Remote Monitoring
Remote cardiac monitoring is similar to bedside monitoring; however, the EKG rhythm, heart rate, and pulse oximetry are not displayed at the bedside. Instead, they are displayed in a different location, sometimes a monitor room, where a trained professional is watching many patients. When they recognize an abnormal rhythm, they will contact the appropriate staff to assess the patient. They may call for the leads to be removed, a change in rhythm, or a low battery.
The EKG leads are placed the same way as the bedside monitor leads are placed (always be sure to consult the manufacturer’s instructions). The information is transmitted wirelessly via wireless medical telemetry service (WMTS) from the “tele box,” but the leads must be wired to the box. WMTS does not use Wi-Fi and protects transmissions from Wi-Fi interference (48).
Mobile Cardiac Monitor and Event Monitor
A mobile cardiac or event monitor is a device attached to the skin that can perform continuous or event-specific monitoring. This device is attached to the patient’s chest near the heart and records when activated. This device is smaller than other portable cardiac monitoring devices like the Holter Monitor which will be discussed later. Information can be transmitted to the monitoring center to be reviewed by trained staff and/or artificial intelligence. Abnormalities like tachycardia, bradycardia, atrial fibrillation, or cardiac pauses are reported to a physician. The patient may or may not know about the rhythm abnormalities occurring as some patients are asymptomatic (18).
Event monitoring consists of the following methods (23):
- Patch monitor: depending on the manufacturer, the device is stuck to the chest and left on for a designated period of time.
- Loop memory monitor: the sensors always stay on the patient and the patient activates the devices to begin recording when symptoms occur in addition to a few minutes before the event starts and after it ends. There is an implanted option as well.
- Symptom event monitor: Patients place the monitor on them and activate it like a patch monitor, but only when symptoms start.
Insertable Monitor
Insertable or implantable cardiac monitors are just like mobile and event monitors, but they are surgically inserted into the patient. They perform the same actions, but there is an added benefit to these devices. If the patient has worn an external device in the past and has known cardiac arrhythmias, they may have an implanted cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) inserted to detect and treat the abnormal rhythm. These devices are connected to the heart via wires (they may be placed in the right atria, the right ventricle, or both) and are operated by batteries that do need to be changed per manufacture direction. Patients and providers should be aware of magnets, or electrical signals from other devices that can interfere with the insertable device (61).
Healthcare providers can “interrogate” ICDs or pacemakers with a device created by the monitor’s manufacturer. When interrogated, the device’s information is transmitted to a monitor center who calls the provider to give them a verbal report of what the device has recorded; a paper copy is often faxed to the provider as well. Some newer interrogation devices may display the information of the device on the screen.
Holter Monitor
As mentioned with mobile cardiac monitors, the Holter monitor is another wearable device that can be used to monitor and diagnose cardiac arrhythmias outside of the hospital setting. This device consists of five electrodes and a monitor that the patient can wear or carry on them. It is similar to the remote telemetry devices used in the inpatient hospital setting as shown in the next image. Patients wear this device for a short time, and information is not transmitted to a monitor technician. Instead, information collected is sent to a monitoring center where it is interpreted and sent to the physician (58).
As covered in this section, there are many options for cardiac telemetry monitoring, and providers may encounter many types of them. It is important to know these devices and how they operate.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What types of telemetry/EKGs are you most familiar with? Which ones would you like to know more about?
- Are there any parts of the devices mentioned above that you have never heard of before?
- Out of all the devices which one do you like best? Which device do you not like?
- What devices do you think could be improved and how would you suggest improving them?
Lead Placement
Now that we have discussed the types of telemetry monitoring devices that are available, it is time to discuss how to properly place the EKG leads on a 12 lead, 15 lead, right-sided EKG, and where to place the V4R lead.
12 Lead EKG
For the 12 lead EKG, providers should start with the four limb leads (14):
- RA: On the upper or lower right arm
- LA: On the upper or lower left arm
- RL: on the upper or lower right leg
- LL: on the upper or lower left leg
From there, the six pericardial leads are placed strategically around the chest to create a partial circle around the heart (14):
- V1: 4th intercostal space, right margin of the sternum (this is lead V on the 5 lead EKG)
- V2: 4th intercostal space, left margin of the sternum
- V3: sits midway between leads V2 and V4 on the left
- V4: 5th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line on the left
- V5: 5th intercostal space, anterior axillary line on the left (aligned horizontally with V4, between V4 and V6) on the left
- V6: 5th intercostal space, mid-axillary line on the left (aligned horizontally with V4)
15 Lead EKG
The 15 lead EKG uses the same leads as the 12 lead EKG, but it adds V7, V8, and V9, known as the posterior leads, to encompass the posterior angles of the heart (14):
- V7: left posterior axillary line (aligned horizontally with V6, across from V5)
- V8: tip of the left scapula (aligned horizontally with V6, across from V4)
- V9: left of the spinal column (aligned horizontally with V6, across from V3)
Right Sided EKG
The right-sided EKG is important to rule out the diagnosis of a right-sided myocardial infarction (MI) or ischemia in or out while treating a patient. Lead placement is the same for the four limb leads, but the 6 precordial leads are flipped (14):
- V1: 4th intercostal space, left margin of the sternum
- V2: 4th intercostal space, right margin of the sternum (this is lead V on the 5 lead EKG)
- V3: sits midway between leads V2 and V4
- V4: 5th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line on the right
- V5: 5th intercostal space, anterior axillary line on the right (aligned horizontally with V4, between V4 and V6)
- V6: 5th intercostal space, mid-axillary line on the right (aligned horizontally with V4)
V4R Lead Placement
A full right-sided EKG is not always needed. Lead V4 on the right side of the heart is the most important lead when it comes to determining an MI on the right side of the heart (14):
- V1, V2, V3, V5, V6: same placement as the 12 and 15 lead EKGs.
- V4 is removed and placed on the right side of the chest
- V4R: 5th intercostal space, mid-clavicular line on the right (Where it is located on a complete right sided EKG)
- The “R” stands for right to ensure that those reading the EKG are aware that lead is on the right while the rest are located on the left side of the chest.
Limb Leads
Now that lead placement has been covered, we can now discuss how lead placement shows different parts of the heart.
Leads I, II, III, AVR, AVL, and AVF are considered limb leads when reading the EKG. It is important to note that the right leg lead is the grounding electrode and does not affect the EKG (83). Leads I, II, and III leads form a triangle over the chest known as Einthoven’s Triangle as reflected in the below image. Lead I always has negative polarity while lead III always has positive polarity. Lead II’s polarity depends on what side of the triangle is being discussed. If we are looking at lead I on the EKG, then lead II is positive, but if we are looking at lead III, then lead II is negative (82).
The importance of what leads are negative and positive comes from how electricity travels through the heart. It starts on the right side and moves to the left, so it would make sense for lead I to have negative polarity while leads II and III are positively charged (82). This is also why the height of a PQRST complex changes based on what lead is being looked at on an EKG as reflected below.
Augmented or unipolar leads AVR, AVL, and AVF have the heart as the negative electrode and the limb leads are the positive electrodes. AVR goes from the heart to the right arm lead, AVL goes from the heart to the left arm lead, and AVF goes from the heart to the left leg lead. Just as discussed with leads I, II, and III, the path of the electricity in the heart determines how the PQRST complex appears on the rhythm strip (82). Lead II is the preferred strip to read by providers due to the best view of the rhythm due to the way electricity travels through the heart and how lead II follows that path by starting at the right shoulder and going to the left leg.
The chest leads, V1 – V9, create a circle around the heart on a horizontal plane. These leads are unipolar as well, with the heart being the negative electrode. Multiple views of the heart are captured because of the many leads placed along the patient’s body. This can give providers valuable knowledge on what areas of the heart may be affected. The next image gives a visual depiction of how the leads display their view of the heart.
 (92)
(92)

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What lead do you think is the most beneficial in reading EKGs? Why do you think that?
- What lead do you prefer to use when reading EKGs? What makes that your “go-to” lead?
- If you could make a policy on EKGs, would you include what type of EKG should be done on patients? Would all patients with chest pain get a 15 lead EKG instead of 12?
- Do you think that one type of EKG is better than the other? Or do they all have their specific uses and benefits?
Reading EKGs: EKG Components
To be able to interpret EKGs successfully, nurses must first have knowledge about the EKG components displayed on the EKG strips and how each part correlates to a part of a single heartbeat.
P wave
The P wave is the first deflection from the isoelectric line or baseline. Correlating this to the heart, this is where the atria depolarize or contract. The contraction of the right atria starts at the beginning of the P wave while the contraction of the left atria begins in the middle and end of it. Normal P waves are apparent between 120 and 200 milliseconds (msec) before the upward deflection of the QRS complex (44)
PR Interval
The next part of the PQRST complex is the PR interval. The interval symbolized the time between the depolarization of the atria and the depolarization of the ventricle. The normal speed is 120 to 200 msec (44).
PR Segment
Next is the PR segment. This is similar to the PR interval but starts at the end of the P wave and ends at the start of the Q wave. This line is important because if there is a deviation from the isoelectric line, it could indicate a cardiac rhythm abnormality like Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome which will be discussed later. The EKG may have a “slurred” upstroke from the P to R points on the EKG, making the Q wave appear to be on the isoelectric line. This is because the ventricles were stimulated or excited early, leading to a shortened PR interval. The “slurred” area is known as a delta wave (13).
QRS Complex
The QRS complex is where the ventricles depolarize and contract. The first downward deflection of the beat is the Q wave that lasts for < 0.05 seconds. It is present in all leads save for V1 and V3 due to the angle of the vector. The R wave is the upward deflection of the complex. R waves do not have a set height, but severely elevated R waves can be an indicator of ventricular hypertrophy. The second downward deflection is the S wave. Overall, the QRS complex is 0.07 to 0.10 seconds long and variations to this time can be an indicator of abnormal heart rhythms (17).
ST Segment
The ST segment starts when the S wave ends by returning to the isoelectric line and ends when the T wave begins. This period represented the completion of ventricular depolarization (17). The ST segment lasts 0.08 seconds to 0.12 seconds (51).
T Wave
The final wave in the standard EKG components is the T wave. This wave symbolizes the ventricles repolarizing. Inverted T waves can be an indication of past or current infections. A peaked T wave—as opposed to the normal curved T wave—can be caused by hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia, and left ventricular hypertrophy (17). The T wave runs from 0.01 seconds to 0.25 seconds (51).
The image below depicts the components of an EKG with labels to assist with understanding how the waves appear.
(4)
Reading EKGs: EKG Components
To be able to interpret EKGs successfully, nurses must first have knowledge about the EKG components displayed on the EKG strips and how each part correlates to a part of a single heartbeat.
P wave
The P wave is the first deflection from the isoelectric line or baseline. Correlating this to the heart, this is where the atria depolarize or contract. The contraction of the right atria starts at the beginning of the P wave while the contraction of the left atria begins in the middle and end of it. Normal P waves are apparent between 120 and 200 milliseconds (msec) before the upward deflection of the QRS complex (44)
PR Interval
The next part of the PQRST complex is the PR interval. The interval symbolized the time between the depolarization of the atria and the depolarization of the ventricle. The normal speed is 120 to 200 msec (44).
PR Segment
Next is the PR segment. This is similar to the PR interval but starts at the end of the P wave and ends at the start of the Q wave. This line is important because if there is a deviation from the isoelectric line, it could indicate a cardiac rhythm abnormality like Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome which will be discussed later. The EKG may have a “slurred” upstroke from the P to R points on the EKG, making the Q wave appear to be on the isoelectric line. This is because the ventricles were stimulated or excited early, leading to a shortened PR interval. The “slurred” area is known as a delta wave (13).
QRS Complex
The QRS complex is where the ventricles depolarize and contract. The first downward deflection of the beat is the Q wave that lasts for < 0.05 seconds. It is present in all leads save for V1 and V3 due to the angle of the vector. The R wave is the upward deflection of the complex. R waves do not have a set height, but severely elevated R waves can be an indicator of ventricular hypertrophy. The second downward deflection is the S wave. Overall, the QRS complex is 0.07 to 0.10 seconds long and variations to this time can be an indicator of abnormal heart rhythms (17).
ST Segment
The ST segment starts when the S wave ends by returning to the isoelectric line and ends when the T wave begins. This period represented the completion of ventricular depolarization (17). The ST segment lasts 0.08 seconds to 0.12 seconds (51).
T Wave
The final wave in the standard EKG components is the T wave. This wave symbolizes the ventricles repolarizing. Inverted T waves can be an indication of past or current infections. A peaked T wave—as opposed to the normal curved T wave—can be caused by hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia, and left ventricular hypertrophy (17). The T wave runs from 0.01 seconds to 0.25 seconds (51).
The image below depicts the components of an EKG with labels to assist with understanding how the waves appear.

(4)
Reading EKGs: EKG Paper
The EKG paper has sets of squares, 25 little squares within one larger square. The smaller squares symbolize 0.04 seconds making the larger square 0.20 seconds. A single small square is 1mm while the large square is 5mm, this is because the larger square is five small squares tall.

(15)
Some EKG strips are presented in a six second format. To determine if the strip is a six-second, you must count the larger boxes. 30 larger boxes are required for the strip to be six seconds. Some may even have second markers that symbolize one second of time passed.
The 12 lead EKG can be more challenging to read and is often used to make an overall observation about the patient’s heart rate and rhythm. It can provide more information to providers than a single lead strip can.
As discussed previously, the leads are placed along the path of the heart, and providers can determine what part of the heart may be affected by knowing what leads are placed where.
| Lead | Location |
| II, III, AVF | Inferior |
| I, AVL, V5, V6 | Lateral |
| V2, V3, V4 | Anterior |
| V1, AVR | Right atrium, left ventricle |
(51)
Now that we have discussed leads, lead placement, the PQRST complex, and EKG paper, it is time to cover different cardiac rhythms that you may encounter.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What parts of the PQRST complex may not appear on the EKG strip?
- How do you remember what leads are associated with each part of the heart?
- What are some ways you can quickly determine heart rate using an EKG strip?
- Is there a part of the PQRST complex do you think is important to pay attention to? Why do you think that?
Rhythm Recognition
Normal Sinus (41):
- Rate: 60-100 beats per minute (bpm)
- Conduction:
- PR interval 120-200ms
- QRS width 60-100ms
- P wave morphology:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
- Lead II and III: 2.5 mm
- The P wave is:
- Positive or above the isoelectric line in II and AVF
- Biphasic (curves above and then dips below the isoelectric line) in V1
- Duration:
- Less than 0.12 seconds
- Rhythm Strip:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
(29)
Sinus Bradycardia (87):
- Rate: less than 60bpm
- Conduction:
- PR interval 120-200ms
- QRS width 60-100ms
- P wave morphology:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
- Lead II and III: 2.5 mm
- The P wave is:
- Positive or above the isoelectric line in II and AVF
- Biphasic in V1
- Rhythm Strip:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
(87)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- None – depending on the patient
- Cyanosis
- Peripheral edema
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Syncope or near syncope
- Lightheadedness
- Causes (not limited to):
- Normal physiology in an athlete
- Medications like beta-blockers
- Ischemia
- Heart diseases
- Sick sinus syndrome
- Hypothermia
- Hypothyroidism
- Neuro-mediated bradycardia as caused by a vasovagal reaction
- Pericarditis
- Hypoxia
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Treatment:
- None if asymptomatic, admission for observation may be indicated
- Medications:
- Atropine 0.5mg every 3 to 5 minutes for a maximum dose of 3mg
- Antidotes or reversal agents
- Transcutaneous cardiac pacing or pacemaker
- Return patient to a normothermic state if hypothermic
Sinus Tachycardia (55):
- Rate: greater than 100bpm but less than 150bpm
- Conduction:
- PR interval 120-200ms
- QRS width 60-100ms
- P wave morphology:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
- Lead II and III: 2.5 mm
- The P wave is:
- Positive or above the isoelectric line in II and AVF
- Biphasic in V1
- Rhythm Strip:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
(42)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Syncope or near syncope
- Lightheadedness
- Palpitations
- Causes:
- Infection or sepsis
- Medications
- Withdrawal
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Blood loss or anemia
- Dehydration
- Hypoglycemia
- Pulmonary embolism
- Trauma
- Cardiac tamponade
- Myocarditis
- Pregnancy
- Treatment:
- Medications
- Antibiotics
- Antidotes or reversal agents
- Insulin
- Electrolyte replacement
- Fluids
- Heparin or other anticoagulant medications
- Blood replacement
- Surgery
- Medications

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Looking at the signs and symptoms for sinus bradycardia what other signs and symptoms have you seen with patients who present with that heart rhythm?
- What other causes have you seen as the reason for sinus bradycardia?
- With sinus tachycardia, when would you be concerned with the causes of the rhythm?
- Are there any other treatments you could think of for either sinus bradycardia or tachycardia?
1st Degree AV Block (68):
- Rate: 60-100 beats per minute (bpm)
- Conduction:
- PR interval greater than 0.20 seconds
- P wave morphology:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
- Lead II and III: 2.5 mm
- The P wave is:
- Positive or above the isoelectric line in II and AVF
- Biphasic in V1
- A QRS complex always follows the P wave
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
- Duration:
- Less than 0.12 seconds
- Rhythm Strip:
(32)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- None
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Syncope or near syncope
- Chest pain
- Lightheadedness
- Causes:
- Increased vagal tones in young patients
- Fibrotic changes in the elderly
- Cardiac disease
- Inflammation
- Medications
- Electrolyte abnormalities
- Treatment:
- None if asymptomatic
- Medications
- Antibiotics
- Antidotes or reversal agents
- Electrolyte replacement
2nd Degree Type I AV Block (Mobitz Type 1 or Wenckebach) (60):
- Rate: varies
- Conduction:
- PR interval increases with each beat, eventually “dropping off” and another P wave appears
- “Longer, longer, drop, that’s a Wenckebach.”
- P wave morphology:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
- Lead II and III: 2.5 mm
- The P wave is:
- Positive or above the isoelectric line in II and AVF
- Biphasic in V1
- Rhythm Strip:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:

(27)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- None
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Syncope or near syncope
- Chest pain
- Lightheadedness
- Causes:
- Increased vagal tones
- Cardiomyopathy
- Myocardial infarction
- Cardiac surgery
- Electrolyte abnormalities
- Medications
- Treatment:
- None if asymptomatic
- Medications
- Atropine if bradycardic
- Antidotes or reversal agents
- Electrolyte replacement
2nd Degree Type II AV Block (Mobitz II) (60):
- Rate: varies
- Conduction:
- PR interval varies
- QRS width 60-100ms when present
- QRS does not follow all P waves
- P wave morphology:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
- Lead II and III: 2.5 mm
- The P wave is:
- Positive or above the isoelectric line in II and AVF
- Biphasic in V1
- Rhythm Strip:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
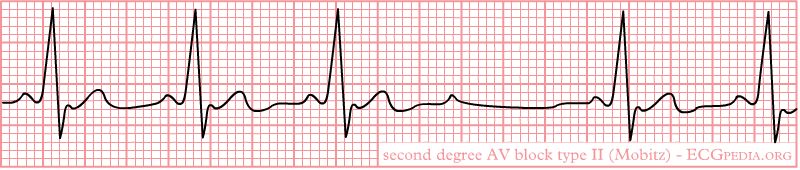
(40)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Syncope or near syncope
- Chest pain
- Lightheadedness
- Cardiac arrest
- Causes:
- Structural heart disease
- Amyloidosis
- lymphoma
- Cardiac tumors
- Transcatheter placement of valves
- Myocardial infarction
- Genetics
- Treatment:
- None if asymptomatic
- Medications
- Atropine does not work on these patients
- Antidotes or reversal agents
- Transcutaneous cardiac pacing or pacemaker since this rhythm can progress to a complete heart block or cardiac arrest
3rd Degree AV Block (78):
- Rate: varies, but usually bradycardic
- Conduction:
- PR interval varies
- QRS width 60-100ms when present
- P wave and QRS complex do not communicate (called AV disassociation)
- P wave morphology:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
- Lead II and III: 2.5 mm
- The P wave is:
- Positive or above the isoelectric line in II and AVF
- Biphasic in V1
- Rhythm Strip:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:

(33)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Syncope or near syncope
- Chest pain
- Lightheadedness
- Hemodynamic instability
- Cardiac murmurs
- Cardiac arrest
- Causes:
- Cardiac surgery
- Cardiac disease
- Medications
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Lyme disease
- Transcatheter aortic valve replacement
- Myocardial infarction
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Sarcoidosis
- Treatment:
- Medications
- Atropine usually does not work, but can be administered
- Epinephrine
- Dopamine
- Antidotes or reversal agents
- Electrolyte replacement
- Transcutaneous cardiac pacing or pacemaker
- Medications

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- 2nd degree Type I and Type II can be mixed up, what are your methods for remembering how each one appears on the EKG strip?
- What type of AV block would lead you to provide quick intervention and why?
- Have you encountered a patient with any of these rhythms? What was the cause? How was it resolved, if it was?
- Are there any causes for these rhythms that were not listed?
Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC) (88):
- Rate: varies, underlying rhythm is usually normal sinus
- The impulse to beat comes from the ventricles, not from the SA node
- Conduction:
- PR interval varies, but in a regular PQRST complex PR interval is 120-200ms
- PR interval after a PVC is longer due to the PVC and the retrograde concealed conduction goes back into the AV node junction.
- PVC QRS width is at least 120ms but usually 160-200ms
- Regular QRS width is 60-100ms
- PR interval after a PVC is longer due to the PVC and the retrograde concealed conduction goes back into the AV node junction.
- P wave morphology:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
- Lead II and III: 2.5 mm
- The P wave is:
- Positive or above the isoelectric line in II and AVF
- Biphasic in V1
- Rhythm Strip:
- Monomorphic: All PVCs are shaped the same
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
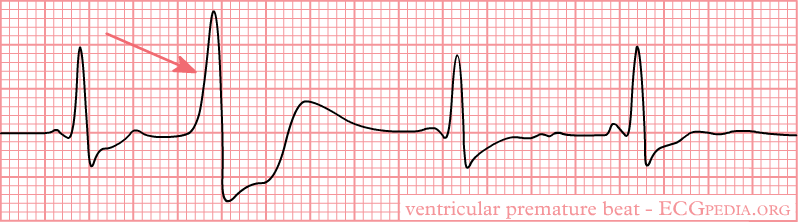
(38)
- Biomorphic: PVCs are shaped differently
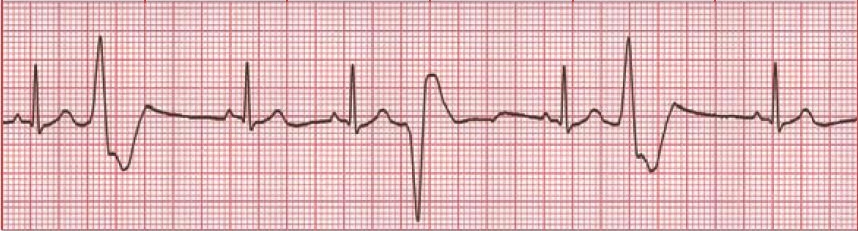
(64)
- Bigeminy: Every PVC is separated by one sinus beat.

(35)
- Trigeminy: Every PVC is separated by two sinus beats.
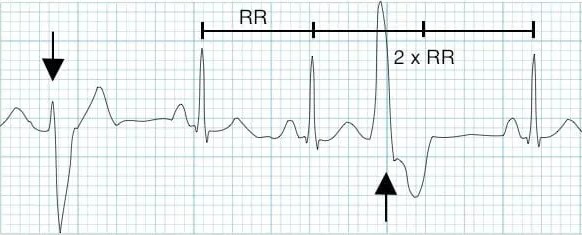
(9)
- Ventricular Couplet: Two PVC beats in a row.
(9)
- Ventricular Triplet: Three PVC beats in a row.

(9)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- None
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Syncope or near syncope
- Chest pain
- Palpitations
- Lightheadedness
- Abnormal neck pulsation
- Hemodynamic instability with frequent PVCs
- Cardiac arrest
- Causes:
- Hypoxia
- Illicit drug use
- Amphetamines
- Alcohol
- Cocaine
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Myocarditis
- Mitral valve prolapse
- Hypercarbia
- Cardiomyopathies
- Myocardial infarction
- Medications
- Treatment:
- None if asymptomatic
- Medications
- Beta-blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Amiodarone is for those with preexisting coronary artery diseases, but used with caution and close observation and monitoring
- Antidotes or reversal agents
- Electrolyte replacement
- Cardiac ablation
- Defibrillation if cardiac arrest occurs
Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC) (54):
- Rate: varies, underlying rhythm is usually normal sinus
- Conduction:
- PR interval varies, but in a regular PQRST complex PR interval is 120-200ms
- PAC
- Regular QRS width is 60-100ms
- P wave morphology:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
- Lead II and III: 2.5 mm
- The P wave:
- Can be inverted
- May be hidden in the T wave creating a hump or peaked T wave
- These rhythms can come in the same variations as PVCs:
- Bigeminy
- Trigeminy
- Couplet
- Triplet
- Rhythm Strip:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
(37)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- None
- Palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Anxiety
- Signs and symptoms of heart failure
- Early or additional heart sounds
- Pauses in rhythm
- Causes:
- Coronary artery disease
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Septal defects
- Congenital heart deformities
- Medications
- Beta-blockers
- Chemotherapeutic agents
- Congestive heart failure
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypertension
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder
- Anxiety
- Treatment:
- None if asymptomatic
- Avoiding triggers
- Medications
- Beta-adrenergic blockers
- Antiarrhythmic agents are used with caution and close observation and monitoring
- Antidotes or reversal agents
- Cardiac ablation

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Between PACs and PVCs, which one would you be more concerned about? Why did you pick that rhythm?
- Have you encountered a patient with either of these rhythms? What treatments were ordered if any?
Ventricular Tachycardia (V Tach) (45):
- Rate: greater than 100bpm
- Conduction:
- PR interval none
- QRS width greater than 140ms
- P wave morphology:
- Not present
- Non-sustained V-Tach: three or more ventricular beats over a maximum of 30 seconds.
- Sustained V-Tach: a run of V Tach for more than 30 seconds or less is treated by cardioversion
- Monomorphic V-Tach: all ventricular beats look the same
- Polymorphic V-Tach: the ventricular beats look different.
- Biphasic V Teach: where the QRS complexes alternate with each beat.
- Digoxin intoxication
- Long QT syndrome
- Rhythm Strip:
- Monomorphic V-Tach
(11)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- Palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Syncope or near syncope
- Signs of heart failure
- Hemodynamic instability
- ICD shocks if the patient has one
- Cardiac arrest
- Also known as pulseless V-Tach
- Causes:
- Ischemic heart disease
- Acute coronary artery disease
- Myocardial scar-related reentry
- Congenital heart deformities
- Cardiomyopathy
- Illicit drugs
- Cocaine
- Digitalis toxicity
- Methamphetamine
- Medications
- Beta-blockers
- Chemotherapeutic agents
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Sepsis
- Metabolic acidosis
- Inherited cardiac channelopathies
- Treatment:
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation if no pulse present
- Cardioversion if hemodynamically unstable and has a pulse
- Treatment for myocardial infarction
- Medications
- Amiodarone, procainamide, sotalol
- Antidotes or reversal agents
- ICD
- Cardiac ablation

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What would be the priorities when providing care to a patient with V-Tach with a pulse?
- If you were the only one in the room with the patient what would be your first action?
- Have you ever cardioverted a patient with this rhythm? What do you remember from the event?
- Do you think the patient should sign consent before cardioversion? Why or why not?
Torsades de Pointes (V Fib) (25):
- Rate: none
- Conduction:
- Polymorphic V-Tach with a prolonged QR interval
- P wave morphology:
- Not present
- Rhythm Strip:
(12)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- None
- Syncope or near syncope
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Hypotension
- Rapid pulse
- Cardiac arrest
- No pulse
- Not breathing or only gasping for air
- Loss of consciousness
- Causes:
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Medications
- Zofran causes a long QT interval (19)
- Congenital prolonged QT:
- Jervell and Lange-Nielsen
- Romano-Ward syndrome
- Bradycardia
- Diuretic use
- Female gender
- Age
- Treatment:
- Electrolyte replacement
- CPR and defibrillation
- Medications
- Epinephrine
- Atropine
- Cardioversion
- Treatment of the underlying cause
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) (72):
- Rate: Greater than 160bpm
- Conduction:
- PR interval not present
- QRS width less than 120 milliseconds = narrow complex, regular SVT
- QRS width greater than 120 milliseconds = wide complex, regular SVT
- P wave morphology:
- Not present
- Rhythm Strip:
- Narrow complex, regular SVT
(30)
- Wide complex, regular SVT

(79)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- None
- Hypotension
- Shortness of breath
- Lightheadedness
- Signs and symptoms of heart failure
- Shock
- Causes:
- Narrow complex, regular SVT - Orthodromic reentry phenomenon (56):
- Accessory pathway that connects the atria and ventricles without passing through the AV node
- A pulse goes through the AV node, down into the ventricles via the Bundle of His, up through the accessory pathway, and back into the AV node
- Wide complex, regular SVT - Atrioventricular reentry phenomenon (57):
- Signals from the SA node travel through the accessory pathway down the ventricles via the Bundle of His and up to the AV node, creating a backward cycle.
- This is slower than the orthodromic SVT because it is traveling against the regular path of conduction, leaving to a wide QRS complex
- Medications
- Caffeine
- Smoking
- Stress
- Alcohol
- Narrow complex, regular SVT - Orthodromic reentry phenomenon (56):
- Treatment:
- None if asymptomatic
- Vagal maneuvers
- Bearing down
- Blowing into a straw
- Medications
- Adenosine: 1st dose 6mg, 2nd dose 12mg
- Ensure rapid saline flush after pushing medication as it has an extremely short half-life
- Cardizem
- Antidotes or reversal agents
- Adenosine: 1st dose 6mg, 2nd dose 12mg
- Cardioversion
- Cardiac ablation

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- If you have encountered a patient in SVT, what vagal maneuvers have you seen used? Were they successful or not?
- If you have not encountered a patient with SVT, what vagal maneuvers could you think of that might be utilized?
- Would a patient’s age impact the vagal maneuvers used? Why or why not?
- Do you know the half-life of Adenosine? If not, will you look it up after this course?
Ventricular Fibrillation (V-Fib) (3):
- Rate: none
- Conduction:
- PR interval not present
- QRS width not present
- P wave morphology:
- Not present
- Rhythm Strip:
(39)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- Cardiac arrest
- No pulse
- Not breathing or only gasping for air
- Loss of consciousness
- Causes:
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Myocardial infarction
- Congenital heart defects
- Sudden blow to the chest right over the heart
- Medications
- Anemia
- Cardiomyopathy
- Electrocution
- Thoracic trauma
- Heart surgery
- Treatment:
- CPR and defibrillation
- Medications
- Epinephrine
- Atropine
- Electrolytes
- Surgery
- Coronary perfusion
- Treatment of the underlying cause
- Cardiac arrest
Asystole (59):
- Rate: none
- Conduction:
- PR interval not present
- QRS width not present
- P wave morphology:
- May or may not be present
- Rhythm Strip:

(21)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- Cardiac arrest
- No pulse
- Not breathing or only gasping for air
- Loss of consciousness
- Causes:
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Myocardial infarction
- Congenital heart defects
- Medications or illicit drugs
- Blood loss
- Cardiomyopathy
- Electrocution
- Trauma
- Treatment:
- CPR
- Since there is no electrical activity with this rhythm, defibrillation cannot be used
- Medications
- Epinephrine
- Atropine
- Electrolytes
- Surgery
- Coronary perfusion
- Treatment of the underlying cause
- CPR
- Cardiac arrest
Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA) (22):
- Rate: varies
- There is no pulse with this rhythm despite the fact that it may appear as an organized rhythm
- Conduction:
- PR interval none
- QRS width greater than 110ms
- P wave morphology:
- Not present
- The P wave is:
- Not present
- Rhythm Strip:
(22)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- Cardiac arrest
- No pulse
- Not breathing or only gasping for air
- Loss of consciousness
- Causes:
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Myocardial infarction
- Congenital heart defects
- Medications or illicit drugs
- Blood loss
- Cardiomyopathy
- Electrocution
- Trauma
- Hypothermia
- Pneumothorax or hemothorax
- Treatment:
- CPR
- Since there is no electrical activity with this rhythm, defibrillation cannot be used
- Medications
- Epinephrine
- Atropine
- Electrolytes
- Surgery
- Coronary perfusion
- Treatment of the underlying cause
- CPR
- Cardiac arrest

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are some misconceptions about V-Fib, asystole, and PEA?
- How do you educate other staff members and family members on these misconceptions?
- What treatments have you seen work on V Fib? What treatments did not work?
- Have you ever seen a patient’s rhythm change from asystole to another rhythm?
- What is the most prominent cause of cardiac arrest in your area?
Atrial Flutter (73):
- Rate: varies
- Depends on how many QRS complexes there are
- Atrial rate 250-350 bpm
- Ventricular rate 75-150bpm
- P waves can come in blocks
- 2 P waves per 1 QRS (2:1)
- 3 P waves per 1 QRS (3:1)
- 4 P waves per 1 QRS (4:1)
- Intervals of P waves per 1 QRS (2:1 then 3: 1 then 2:1 then 4:1)
- Conduction:
- PR interval varies
- QRS width 60-100ms
- P wave morphology:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
- Lead II and III: 2.5 mm
- Sawtooth pattern
- Rhythm Strip:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
- Depends on how many QRS complexes there are
(31)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- None
- Palpitations
- Fatigue
- Syncope or near syncope
- Shortness of breath
- Regular or irregularly regular pulse
- Causes:
- COPD
- Heart failure
- Atrial size abnormalities
- Hypertension
- Diabetes mellitus
- Age
- Male gender
- Treatment:
- None if asymptomatic
- Medications
- Amiodarone
- Cardizem
- Metoprolol
- Anticoagulation to prevent stroke
- Catheter ablation
- Treatment of the underlying cause
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) (89):
- Rate: varies
- Atrial rate 400-600 bpm
- Ventricular rate 75-175 bpm
- Anything over 100 is considered A Fib with rapid ventricular response (RVR)
- Conduction:
- PR interval varies
- QRS width 60-100ms
- P wave morphology:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
- Lead II and III: 2.5 mm
- Rhythm Strip:
- A Fib
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
(28)
- A Fib RVR

(34)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- None
- Palpitations
- Fatigue
- Syncope or near syncope
- Shortness of breath
- Regular or irregular pulse
- Patients can go in and out of A Fib or it can be permanent,
- They can go in and out of RVR
- Causes:
- Heart disease
- Genetics
- Pulmonary embolism or other hemodynamic stressors
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Heart failure
- Pericarditis
- Myocarditis
- Myocardial infarction
- Hypertension
- Diabetes mellitus
- Age
- Treatment:
- None if asymptomatic
- Medications
- Cardizem
- Metoprolol
- Amiodarone
- Anticoagulation to prevent stroke
- Catheter ablation
- Treatment of the underlying cause
Idioventricular Rhythms (47):
- Rate: varies
- Idioventricular rate 35-40bpm
- Accelerated rate 60-120bpm
- Conduction:
- PR interval not present
- QRS width greater than 120ms but can be greater than 160ms
- The normal conduction system does not transmit the signal to beat, the vertical signal is transmitted from cell to cell
- P wave morphology:
- Not present
- Rhythm Strip:
- Idioventricular rate

(36)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- None
- Palpitations
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness
- Syncope or near syncope
- Cardiac arrest
- Causes:
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Reperfusion of cardiac cells after a myocardial infarction
- Medications
- Digoxin
- Beta-adrenoreceptor agonists
- Illicit drug use like cocaine
- Cardiomyopathies
- Congenital cardiac defects
- Athletes
- Treatment:
- None if asymptomatic
- Medications
- Atropine
- Amiodarone or lidocaine
- Reversal agents
- Rarely cardiac pacing
- Treatment of the underlying cause
Junctional Rhythms (52):
- Rate: varies
- Junctional bradycardia less than 40bpm
- Junctional escape rhythm 40-60bpm
- Accelerated junctional rhythm 60-100bpm
- Junctional tachycardia greater than 100bpm
- Conduction:
- PR interval not present
- QRS width 60-100ms
- P wave morphology:
- Not present
- Rhythm Strip:
- Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
- Rhythms look the same but have more beats depending on the type of rhythm
- Accelerated Junctional Rhythm

(52)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- None
- Shortness of breath
- Palpitations, intermittent or continuous
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness
- Syncope or near syncope
- Causes:
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Can be caused by anorexia nervosa
- Thoracic trauma
- Myocarditis
- Reperfusion of cardiac cells after a myocardial infarction
- Medications
- Adenosine
- Clonidine
- Antiarrhythmics
- Lithium
- Digoxin
- Sleep apnea
- Hypoxia
- Coronary artery disease
- Congenital cardiac defects and repairs of these defects
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Treatment:
- None if asymptomatic
- Medications
- Atropine
- Reversal agents
- Transcutaneous pacing
- Permanent pacemaker
- Treatment of the underlying cause
Bundle Branch Blocks (BBB) (43, 53, 70):
- Rate: varies
- Conduction:
- Right BBB (RBBB):
- QRS interval greater than 120ms
- Septal depolarization that leads to a:
- Small R wave being present in V1
- Q wave in V6
- The left ventricle’s contraction leads to and:
-
- S wave in V1
- R wave in V6
-
- The right ventricle’s contraction leads to an:
- R wave in V1
- Deep S wave in V6
- Left BBB (LBBB):
- QRS interval greater than 120ms
- T wave inversion is due to abnormal repolarization
- From first principles:
- Septal depolarization that leads to a:
- Q wave in V1
- R wave in V6
- Right BBB (RBBB):
-
-
- The right ventricle’s contraction leads to an:
- R wave in V1
- S wave in V6
- The left ventricle’s contraction leads to and:
- S wave in V1
- R wave in V6
- The right ventricle’s contraction leads to an:
- P wave morphology:
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
- Lead II and III: 2.5 mm
- Rhythm Strip:
- RBBB
- The maximum height of the P wave is:
-
(71)
-
-
-
- LBBB
-
-
(71)
- Signs and Symptoms:
- None
- Lightheadedness
- Syncope or near syncope
- Causes:
- RBBB:
- Myocardial infarction
- Congenital cardiac defects
- Pulmonary embolism
- Myocarditis
- Pulmonary hypertension
- LBBB:
- Myocardial infarction
- Hypertension
- Cardiomyopathy
- Myocarditis
- Treatment:
- None if asymptomatic
- Treatment of the underlying cause
- RBBB:
Identifying Ischemia and Infarction
Known as coronary artery disease (CAD), acute myocardial ischemia is the decrease of blood flow to the heart by atherosclerosis or plaque. The atherosclerosis starts as a plaque streak within the large arteries and continues to build up. After the plaque has grown to a significant size, occlusion begins and blood flow to areas below the growing occlusion suffers a decrease in blood flow. This is what is known as ischemia (81).
When resting, patients may not experience any signs or symptoms. Upon exertion, however, patients may experience stable angina—chest pain, discomfort, pressure, etc.—as activity requires increased blood flow and the arteries constrict to pump blood through the body faster. This pain is relieved at rest and can be further treated by nitrates. The routine is what makes this stable angina (81).
Unstable angina begins once the artery has become occluded enough to create a significant obstruction of blood flow. Signs and symptoms can include chest pain or other discomfort that is challenging to relieve, even when at rest. Patients may be woken from sleep due to the pain and report that it takes longer for the pain to decrease or resolve completely. These signs and symptoms symbolize that the plaque within the artery is unstable and could potentially rupture (90).
Infarction is when the blood flow is completely obstructed and the cells below the obstruction begin to die off. This often occurs when the plaque within the artery ruptures, leading to the body’s natural clotting processing in an attempt to repair the rupture, and a complete occlusion of the artery occurs (46).
Now that we have discussed ischemia and infarction, it is time to discuss how a myocardial infarction (MI) appears on an EKG and how to identify it. You may also hear them referred to as STEMIs or ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
The progression of PQRST complex changes during an MI can start with hyperacute T waves. The T wave will increase with amplitude and become wider, while some ST elevation may be noted. This elevation begins to occur as injury to the heart muscle begins. From there, the ST elevation increases and creates the image often associated with an MI. Pathological Q wave may develop as the MI progresses. As discussed earlier, the Q wave is the first downward deflection of the QRS complex and is normally 1mm or less in depth. Pathological Q waves are measured by greater than 1mm wide or greater than 25% of the R wave’s amplitude (84).
T wave inversion occurs when the cells have become necrotized and begin to form fibrosis. Once all necrotized cells have become fibrotic, the Q waves will remain, but the T waves will become upright again (84).
(84)
These changes should be present in at least 2 contiguous leads or leads that are side by side. To discuss this more, we will refer to the 12 lead EKG photo we used earlier. It is important to know that there will be leads with ST elevation and there will be leads with reciprocal ST depression based on the type of MI and how these leads are placed in relation to the area of the heart that is being affected.
| Type of MI | Leads with ST Elevation | Reciprocal ST Depression |
| Inferior | I, II, AVF | I, AVL |
| Lateral | V5, V6 | III, AVR |
| Anterior | I, AVL, V5, V6 | II, III, AVF |
| Posterior | V7, V8, V9 | V1, V2, V3 |
(82)
With posterior MIs the elevation must be at least 0.5mm, there will be tall, broad R waves of at least 30ms long, and the T wave will be upright. When looking at an EKG for a posterior MI, the ST depression is what will be observed in leads V1, V2, and V3. If a posterior MI is suspected, look at the EKG from the back of the paper by flipping it over and holding it to light. This will display the ST depression as ST elevation, prompting you to consider a posterior EKG. It is advised that a posterior EKG with leads V7, V8, and V9 be done. A quick method to do this is by removing leads V4, V5, and V6; placing them in the posterior lead positions; and relabeling them on the EKG. (77).
Right ventricular MIs can occur, and it is important to assess and treat them appropriately. To assess for a right-sided MI, first look at the standard EKG. If ST elevation is noted in leads II and III, but the ST elevation is greater in lead III than lead II, consider right ventricular involvement. As discussed previously, one method is to do a right-sided EKG, with lead placement along the right side of the chest. The second, quicker way to do this is to take lead V4 and place it on the right side of the chest and mark it as V4R on the EKG (77).
Another rhythm that can be an indicator of an MI is a bundle branch block. New or suspected new BBBs are to be treated as a MI by providers. But what if you have a copy of an old EKG and the BBB isn’t new, can the patient still be having an MI? The answer is yes. However, it can be challenging to determine what is a change from the MI and what is from the BBB. The Sgarbossa criteria is useful in making these determinations and can also be used for patients who have a pacemaker (77)
Sgarbossa criteria (77):
- Concordant ST elevation that is greater than 1mm
- Concordant ST depression that is greater than 1mm
- Excess discordant ST elevation that is greater than 5mm in leads with negative QRS complexes – these are complexes below the isoelectric line
For reference, concordance means that the ST segment and QRS complex go in the same direction, either both deflecting upwards or downwards. Discordance is what should be seen in a BBB or paced rhythm. This is where the ST segment and the QRS complex go in different directions. Smith et al. created a modification to the Sgarbossa criteria to include a greater than 1mm ST elevation to an S-wave amplitude ratio of greater than 0.25mm (7).
Another method that has been created, but not validated is the Barcelona criteria. This criterion has greater than 1mm ST deviation concordance or discordance with QRS polarity in any EKG lead. Discordant ST deviation is greater than 1mm in any lead where the R or S points of the QRS complex are less than 6mm (7).
There is an EKG rhythm that can indicate a future MI which is known as Wellens syndrome. This EKG has a deeply inverted or biphasic T wave in leads V2 and V3. The patient is often pain-free when the rhythm is present, ischemic chest pain can obscure the rhythm by creating a false normal appearance of the T waves in the affected leads. Their cardiac enzymes may not even be elevated. Any patient presenting with chest pain should have serial EKGs done for this reason, since they may be pain-free at a later time. These EKG changes symbolize the critical stenosis of the proximal left anterior descending artery (LAD). This is the artery that provides the left ventricle with blood (65).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Do you remember the first patient that you had that was experiencing an MI? What stood out about that patient in your mind?
- Patients have a variety of symptoms that can be experienced during an MI, what was the most interesting symptom a patient had during an MI?
- Have you ever encountered a patient with Wellens Syndrome? Do you know if they ended up having an MI later?
Cardiac Assessment:
A traditional cardiac assessment focuses on more than just the heart; it encompasses aspects of both the neurological and respiratory systems. However, we will begin our focus with the heart.
Pain may not be a word patients use to describe what they are feeling. As mentioned, they may vocalize discomfort, pressure, cramping, burning, or tightness. Women may have jaw or arm pain as opposed to the traditional chest pain that men may experience. Ask them to rate their pain on a scale of one to ten, looking for changes in the value. An EKG based on pain, discomfort, pressure, cramping, or tightness should be completed within the time frame set by hospital policy.
The PQRST pneumonic can assist providers in remembering the specific information they need to collect (90).
P: What provokes, precipitates, or palliates/alleviates the pain or discomfort the patient is feeling? Does it get worse or better when you do certain things, i.e., walk or rest?
Q: What is the quality of pain or discomfort you are feeling?
R: Does this pain or discomfort radiate anywhere else in your body? Jaw, arm, back?
S: Are there associated symptoms with the pain or discomfort? Shortness of breath, dizziness, heartburn?
T: What time elements are involved? When did it start? Did it stop and come back? Are you currently feeling it now? Was it gradual or did it occur suddenly? Did it wake you up?
Patients should be asked about palpitations or any experienced abnormal heart rhythms detected on monitoring devices. Many individuals have smartwatches that can detect heart rates and some rhythms. If the patient is wearing one, determine if the device has recorded anything.
Edema in the legs can be a sign of acute heart failure while pain in the calf can indicate a blood clot that could have traveled from another part of the body (85). In A Fib, the blood can clot in the ventricles due to poor circulation of blood. It will pool until it clots or is ejected from the heart. Once expelled, the clot will travel until it can no longer pass through the veins (63). Ensure a thorough assessment of the patient’s distal pulses is done as well to determine circulation. The further pulse locations can be an indicator of poor circulation (85).
Moving on to the respiratory system, we will reflect on the many arrhythmias that have shortness of breath as a sign or symptom. Providers should assess lung sounds to determine if there is any fluid buildup, a sign of acute heart failure. Determine if the shortness of breath is all the time, upon exertion, or at rest. Also, it is important to ask if the patient has been woken from sleep due to a shortness of breath. Sometimes arrhythmias occur at unexpected moments, even in the middle of the night (85).
Syncope was another common sign or symptom of cardiac arrhythmias due to decreased perfusion to the brain. Providers should determine if the patient currently feels lightheaded or dizzy, if they felt that way in the past, or if they have fainted. They should ask when this feeling happens—at rest, while moving, or both—and if they get any warning signs or auras beforehand. Always ensure you ask the patient to describe what happened so it can be added to the assessment (85).
A full medical history should be obtained, with a special focus on any past cardiac medical history the patient or their family has. Providers may consider asking the following questions:
- Have you been diagnosed with coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, peripheral vascular disease, valve problems, heart failure, high cholesterol, or other heart conditions?
- Have you had a heart attack or stroke in the past?
- Have you had any surgical procedures to help with your heart function? This may include things like ablation or stent placement.
Asking about medications can assist providers in determining any missed diagnoses with the patient while asking about social history can provide information about smoking, illicit drug use, alcohol consumption, and exercise habits (85).
Conclusion
Thanks to advancements within the medical profession, cardiac telemetry can be greatly beneficial to patients in and outside of the hospital setting. From devices you can carry, to devices implanted inside someone, patient outcomes have improved for identifying, treating, and managing cardiac arrhythmias that had once been deemed unmanageable. With proper knowledge of EKG rhythms, nurses can confidently provide the proper care for their patients by being an advocate for those they care for.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Have you seen changes in the patients admitted to your facilities that you could correlate to these indications?
- Do you agree with this list? Is there anything you feel should be added or removed? Why?
- Are there any time frames (how long a patient is on a telemetry monitor) that you think should be adjusted?
- Do you think sending patients home with wearable monitors could be used in the future to prevent admission in some of the patients who meet the criteria for admission with telemetry?
Conclusion
Thanks to advancements within the medical profession, cardiac telemetry can be greatly beneficial to patients in and outside of the hospital setting. From devices you can carry, to devices implanted inside someone, patient outcomes have improved for identifying, treating, and managing cardiac arrhythmias that had once been deemed unmanageable. With proper knowledge of EKG rhythms, nurses can confidently provide the proper care for their patients by being an advocate for those they care for.
Heart Failure Updates
Introduction
In 1997, Heart Failure (HF) was designated an epidemic due to the significant increase in hospitalizations. (2) This increase in hospitalizations appears to be due to accurate management of HF patients who re-hospitalize for stabilization and medication management rather than a new diagnosis or end-stage disease.
HF occurs when the heart is too weak to pump blood to the body and lungs. The blood then backs up into the heart, lungs, and lower extremities, causing less blood supply to the body. HF can also be so severe that it can cause death in patients. (1)
It is crucial for nurses to understand the pathophysiology of HF, risk factors, and what education and treatment a nurse can incorporate in the plan of care, which will slow the progression of disease and maintain quality of life.
Introduction
In 1997, Heart Failure (HF) was designated an epidemic due to the significant increase in hospitalizations. (2) This increase in hospitalizations appears to be due to accurate management of HF patients who re-hospitalize for stabilization and medication management rather than a new diagnosis or end-stage disease.
HF occurs when the heart is too weak to pump blood to the body and lungs. The blood then backs up into the heart, lungs, and lower extremities, causing less blood supply to the body. HF can also be so severe that it can cause death in patients. (1)
It is crucial for nurses to understand the pathophysiology of HF, risk factors, and what education and treatment a nurse can incorporate in the plan of care, which will slow the progression of disease and maintain quality of life.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How can you find the costs associated with HF patients at your place of work? What treatments are helping manage HF patients?
- How would you assess an HF patient on your initial encounter as a nurse?
Statistical Evidence/Epidemiology
Epidemiologists study a disease's incidence, mortality, and prevalence to predict health care costs, how many people have a disease, how it affects society, and when the numbers of a disease change.
According to the CDC, there are approximately 6.2 million patients with heart failure in the United States. The diagnosis was noted on 13.8% of death certificates in 2018. (2) $30.7 billion was spent on HF in 2012, including health care costs, days away from work, and medications that treat HF.
Although HF is higher in the elderly population, the more significant number of patients ages 35 and above who die with HF are concentrated in the southeast, southwest, Indiana, Wisconsin, and Illinois, with some counties in Utah, Oregon, Montana, South Dakota, and Nebraska.
Readmission rates declined when the Hospital Readmission Reduction Program (HRRP) began in 2012 to reduce costs and deliver care more safely.
Hospitals are penalized by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid to lower readmission rates to less than 30 days for some diagnoses, and HF was among them. Hospitals began to look closer at the readmission rates, which helped them to focus on improved management. (2) . Using the information below, nurses can better assess the patient and add more information to their care plan.
The classifications of HF as defined by the New York Heart Association are:
- No symptoms with regular physical activity.
- Some mild symptoms with physical activity but not at rest
- Comfortable at rest but with moderate symptoms with some minor physical activity.
- Severe shortness of breath with rest. (2)
Providers typically use echocardiograms to measure heart failure using the ejection fraction (EF) percentage. Ejection fraction demonstrates the blood pumping rate from the left ventricle to the body.
An EF of below 30% indicates severe disease, while an EF at or above 50% indicates milder or no condition. Left ventricular failure with an EF of 50% or above is considered HF with preserved EF. An EF of 30% or below is considered HF with reduced EF. There is now a new category called HF with mid-range, which shows an EF of 40%-50%.
Approximately 15% of the HF population shows mid-range EF.
Incidence - is the number of new disease cases in certain patients. In HF, this number also helps scientists understand how the prevalence of the disease results from a lifestyle change. These studies aid in determining the burden of HF on society, which in turn helps to make changes in public policy and, eventually, how HF patients are treated. "For HF, incidence as a measure of new cases is particularly helpful to assess how the occurrences of HF might have changed over time as a result of changes in risk factors." (2)
Prevalence - measures the commonality of a disease, in this case HF, in the at-risk population at or over a given time. It also measures how often an HF patient will be encountered. (6)
Mortality - CHF is one of the top causes of death. Mortality rates are high, and the data shows that 50% of HF patients die at or within five years of diagnosis. (2) More recent studies show mortality rates in HF are increasing, which may be due in part to an aging population.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Where can you find more information on the epidemiology of HF?
- Where do epidemiologists get their information?
- Can you define the difference between incidence and prevalence?
Etiology and Pathophysiology
Heart failure is often caused by an injury to the heart's muscle, such as Myocardial Infarction (MI), valvular regurgitation, stenosis of the heart's valves, and arrhythmia. (4) It is essential that the provider determines the cause to treat these patients appropriately.
The most common cause of HF is cardiovascular disease. When fatty deposits or plaque buildup in the vessels supplying the heart, the arteries become narrowed and decrease blood flow to the heart muscle. This can cause ischemia (lack of oxygen) to the area of the heart's power involved, causing an MI. This, in turn, causes damage to the heart's muscle, reducing its ability to pump normally.
There are two main types of HF:
- Left ventricular HF or systolic (LHF)
- Right ventricular HF or diastolic (RHF)
LHF occurs when the damage to the left ventricle occurs, and RHF occurs when the damage is to the right ventricle.
The following Table taken from the National Institutes of Health shows comorbidities for Systolic and Diastolic HF:
Systolic (LHF)
- Coronary Heart disease
- Arterial Hypertension
- Valvular Heart Disease
- Arrhythmias
- Inflammatory disease
- Idiopathic cardiomyopathy
- Toxic Cardiomyopathy (alcohol)
Diastolic (RHF)
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Arterial Hypertension
- Valvular Heart Disease (pressure load)
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
- Constrictive Pericarditis
- Amyloidosis (storage disease)
HF causes volume overload in the ventricles of the heart. This is due to enlargement and stiffness of the ventricles, so they cannot pump enough blood to the lungs and the body. (1,4) The nurse can utilize this information to care for the patient and implement essential treatments.
Genetics also play a role in HF but are varied and complex. Studies have found more than 100 genes that may contribute to cardiomyopathy. Depending on where the failure occurs, more genetic testing is recommended in some instances: Left, Right, or Biventricular determines what signs and symptoms may be present in a patient.
In a patient with an MI or volume/pressure overload, the whole heart will change in structure and function. There will be hypertrophy of the Left ventricle and the dilatation of the chambers, which will cause further deterioration in cardiac function. (4)
Certain medications may also lead to HF in some patients. These are the diabetic medications Actos and Avandia. NSAIDS (non-steroidal inflammatory drugs) and certain medicines that treat hypertension, cancer, blood dyscrasias, mental health, lung urinary issues, and infections. (1)
Aging also contributes as the heart's ability to work decreases over time. Too much alcohol and smoking are also important considerations. Heart failure may also cause complications such as kidney damage and failure, more heart problems, and liver disease caused by the backup of fluid that the liver cannot handle.
The photo below shows the difference between a normal heart and an enlarged one (12).
Preventable and non-preventable risk factors for heart disease are:
- Poor diet
- Smoking
- Lack of exercise
- Alcoholism
- Obesity
- Genetics/Race-non preventable
It is also known that Hispanic women are at higher risk for diabetes, which can lead to heart disease if their diabetes is not managed well. Also, African American men are at higher risk for heart disease, possibly leading to HF.
Interestingly, some studies have shown that the incidence of hospitalizations has declined. This may be due to early diagnosis, better use of medications and newer devices, earlier and ongoing patient education of risk factors, and stellar outpatient and preventive care of those patients living with HF or at risk in the community (2).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Why do you think certain diseases and medications contribute to heart disease?
- How would you plan to educate your new patient on this disease?
- What are the mechanisms of HF that may cause other diseases?
Diagnostic and Screening Tools for Heart Failure (HF)
Essential diagnostic screening tools are heart rate, cholesterol testing, blood pressure, and weight. Blood pressure measurement is one of the most critical tests since it can have no symptoms.
If high, it significantly increases the risk of cardiac disease. Fortunately, diet exercise can control blood pressure to lose weight if needed, and medications.
According to the American Heart Association, the standard for blood pressure is 120/80 or below and should be measured starting at age 20. (5) Next is the fasting cholesterol profile. Again, starting at age 20, a fasting lipid profile should be done. (5) This will give the provider and patient a baseline to follow and assist nurses in developing and implementing care plans.
The following chart describes lab values for cholesterol. As you can see, the values in red are at the highest risk for cardiovascular disease, which could lead to HF.
(13)
Body habitus is another crucial factor in predicting CAD. Body mass index (BMI), Waist measurements, and body structure can help predict how at risk a patient is for many diseases, including CAD, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, HF, and stroke. (7)
The typical Western diet is full of fats and sugars. In the US, many processed foods containing high salt, fat, and sugar are used.
These foods are unhealthy for the body and cause obesity and poor health. The Mediterranean diet, in turn, is full of fresh fruits and vegetables, lean meat, and a few processed foods. This is the most recommended diet for all populations.
High blood glucose is another indicator of poor health. Insulin resistance is the precursor to diabetes. A patient has insulin resistance when the body's muscles and tissues cannot respond to insulin, so glucose increases in the blood. (5)
Causes of insulin resistance are thought to be obesity with a large waist measurement. Blood glucose is usually tested with routine blood work. This gives the provider knowledge if a patient is at risk for diabetes and, therefore, heart disease. (5) Smoking and lack of physical activity can cause poor health, which may lead to cardiovascular disease.
Echocardiogram, Holter monitoring, stress tests, and nuclear stress tests are routinely used when a patient presents with symptoms of or has known cardiovascular disease. These tests provide a look at heart function and are used to determine disease progression or maintenance.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are the waist measurements in males and females that are considered for a diagnosis of obesity?
- How would you care for a patient undergoing this testing using the nursing process?
- Why is diabetes a risk factor for HF?
Medication Management
Treating HF with medications can reduce disease progression, and relieve symptoms of dyspnea, fatigue, and edema. Several classes of drugs can be used to treat HF. Each one may be used to treat a different symptom.
The classes are as follows:
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors
These medications open blood vessels decreasing blood pressure and lowering the heart’s work to keep HF from worsening. (6)
Some common ACE inhibitors are:
- Captopril
- Enalapril
- Lisinopril
- Ramipril
Angiotensin-Receptor Blockers (Arbs)
- Losartan
- Valsartan
Angiotensin-Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitors (Arnis)
Entresto is a drug combination in the class of Angiotensin-receptor neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs). ARNIs limit the enzyme neprilysin from breaking down natural substances in the body. By limiting this enzyme, the arteries can open to increase blood flow. This drug also limits the retention of sodium. (7)
Beta Blockers
Beta-blockers work to slow down the heart rate and increase blood flow by widening blood vessels. This also lowers blood pressure. (9)
Common Beta Blockers are:
- Atenolol
- Bisoprolol
- Carvedilol
- Labetalol
- Metoprolol succinate
- Metoprolol tartrate
- Nadolol
- Propranolol
Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors
Jardiance and Farxiga are Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors that were designed to treat diabetes, but they have been found to be cardio-protective. (7)
Diuretics
Diuretics allow the body to release extra fluid and sodium through the kidneys. They cause increased urination so should be taken earlier in the day.
Most common diuretics are:
- Lasix
- Bumex
- Torsemide
- Diuril
- Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)
- Metolazone
Other medications can be prescribed depending on the patient's needs, such as anticoagulants to keep the blood thin, statins to lower cholesterol, and Digoxin to control heart rate and increase pumping strength. Calcium channel blockers allow the heart muscle to relax, thereby reducing blood pressure and circulation within the heart. Potassium may be used with certain diuretics that cause potassium to leave the body.
It is needed to keep the heart's rhythm in control. Oxygen may also increase its amount in the blood, assisting with dyspnea and activity tolerance. (7) It is the nurse's responsibility to evaluate these medications and interventions for plan updates.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Which medications are the first line in controlling HF?
- Where can you find side effects of these medications?
- What would your care plan look like for a patient with HF?
Other Interventions
Several types of surgery can be utilized for the most severe cases of HF. Bypass surgery has been used for many years. This procedure bypasses blocked coronary arteries, allowing for better blood flow to the heart muscle.
Replacing damaged or stenosed heart valves will assist blood flow within the heart chambers. In some patients, biventricular pacing with a pacemaker allows both sides of the heart to work in sync. (10) An ICD, or implantable defibrillator, can shock the heart from a life-threatening rhythm back to normal.
The ventricular assist device or VAD can assist the ventricles to pump blood out to the body. (10) This device can be used either waiting for a transplant or permanently.
Heart Transplants can be used as the last intervention, with a success rate of 88% after one year and 75% after five. If a patient has sleep apnea, it can be linked to heart failure. In this case, an evaluation and treatment will be performed. (10)

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Where can you learn more about assistive devices for HF?
- How many arteries can be bypassed in surgery at one time?
- How would you care for a person with a surgical device?
Current areas of research in HF are producing more effective drug therapy, genetic testing, non-surgical devices, transplants, and mechanical support. (8)
The research is now studying drugs that improve physical symptoms when added to the standard drug treatment and care. These drugs have shown improvement in reducing hospitalizations.
The newer diabetic medications Jardiance, Invokana, and Farxiga are being studied on HF patients without diabetes to learn if they will improve function and risk reduction of MI, stroke, or cardiovascular death. (8)
Non-invasive imaging such as MRI, ultrasound, nuclear testing, and radiology are being researched in the hope that advancing these technologies will "provide additional information about coronary arteries and heart tissue, coronary strain, the function and structure of the heart." (8)
Genetic testing is under investigation to help determine if there is an inherited disease, especially in specific cardiomyopathies. These cardiomyopathies present differently and may be treated with differing modalities.
One of the newest areas of HF management and treatment is remote monitoring. Nurses are at the forefront of home monitoring in many areas as they are the clinicians making home visits.
New types of VADs are emerging as treatments for advanced illnesses. They are being manufactured to be more durable and portable. (8)

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Where can you find new research studies on HF?
- Where can you go to get educated on new devices?
- Who is conducting the new research?
Conclusion
As discussed in this course, Heart Failure affects over 6 million people in the US. Age, lifestyle, race, and genetics may predispose a patient to this disease.
HF burdens society and health care costs due to missed work, rehospitalizations, and poor outcomes. As a nurse, learning the mechanisms of HF is imperative. Understanding etiology, statistics, pharmaceuticals, and other interventions will assist nurses in administering the best care.
New research shows how emerging medications, improved implantable devices, and surgery can improve outcomes. However, patient education and prevention are vital to caring for HF patients.
Hypertension Updates
Introduction
This course aims to provide nurses and healthcare professionals with an up-to-date understanding of hypertension (HTN). The course covers epidemiological evidence, etiology, diagnostic tools, medication management, other interventions, and future research on HTN.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a chronic condition and a significant risk factor for heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and other serious health problems. The American College of Cardiology defines hypertension as systolic blood pressure greater than 130 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure greater than 80 mmHg [1].
Statistical Evidence/Epidemiology
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), hypertension afflicts 108 million Americans and contributes to almost 500,000 deaths per year in the United States [2]. The prevalence of hypertension varies by race and ethnicity, with non-Hispanic Black adults having the highest majority (57.1%), followed by Hispanic adults (43.7%) and non-Hispanic White adults (43.6%).
Hypertension is also more common among older adults, with (74.5%) of adults aged 60 and over having high blood pressure [3]. Despite the high prevalence of hypertension, less than a quarter of all adults with hypertension in the United States have their blood pressure under control [2].
This leaves millions at risk for serious health problems from uncontrolled hypertension, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and eye problems. In 2021, high blood pressure was a primary or contributing cause of death for more than 691,095 Americans [4].
[31]

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How do the current epidemiological statistics about hypertension affect healthcare planning and resource allocation?
- Given that hypertension is a significant public health problem and a major risk factor for serious health problems, what are the essential things that nurses and healthcare professionals should know about hypertension to manage their patients?
- Why do you think there exists such a pronounced disparity in the prevalence of hypertension among different racial and ethnic groups, and what societal and medical strategies might be employed to address this?
Etiology/Pathophysiology of Hypertension
Hypertension (high blood pressure) is a multifactorial disease characterized by persistent elevated blood pressure in the systemic arteries. Understanding hypertension's etiology, pathophysiology, and sequela is crucial for effective management and treatment.
There are two main types of hypertension: primary hypertension and secondary hypertension. Primary or essential hypertension (idiopathic hypertension), which accounts for about 80-95% of all cases, has no identifiable cause and results from complex interactions between genetic, environmental, and other unknown factors [5].
The cause of secondary hypertension (15-30% of cases) is often an underlying medical condition, such as kidney disease, adrenal gland tumors, diabetes, or thyroid disease [6]. Family history plays a role, although science has identified no genetic factor as the "hypertension gene" [7].
A key mechanism in hypertension is the imbalance between the forces that constrict and dilate blood vessels. This imbalance can be caused by several factors, including increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system, which leads to vasoconstriction, increased production of vasoconstrictor hormones, such as angiotensin II and aldosterone, a decreased output of vasodilator hormones, such as nitric oxide, and structural changes in the blood vessels, such as thickening of the vessel walls [8].
The most understood mechanism of hypertension involves increased peripheral vascular resistance due to constriction of small arterioles. The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) is a hormonal system that regulates blood pressure. Dysfunction of the RAAS can lead to fluid retention and vasoconstriction [9]. Endothelial dysfunction involves the inner lining of the blood vessels (endothelium) and the release of nitric oxide, which promotes blood vessel relaxation. The dysfunction of nitric oxide is a primary contributor to hypertension [10].
Secondary hypertension often involves:
- The kidneys and volume overload.
- Leading to elevated blood pressure.
- Often affecting younger patients and those with resistant or refractory hypertension.
The typical secondary causes of hypertension include:
- Primary aldosteronism (PA).
- Renovascular disease.
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD).
- Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
- Drug-induced or alcohol-induced hypertension [11].
Overactivation within the sympathetic nervous system can result in increased heart rate (tachycardia) and vasoconstriction, both of which can cause a temporary elevation in blood pressure. Within the metabolic process, insulin resistance has been associated with endothelial dysfunction and hypertension [12].

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What underlying mechanisms or factors might contribute to the development of primary hypertension when classified as having no identifiable cause, and how might this classification influence our approach to treatment and management?
- What common myths and misconceptions about hypertension have you encountered in your practice?
- How do mechanisms like vascular resistance, RAAS dysfunction, and endothelial dysfunction interact or possibly counteract each other in the pathophysiology of hypertension, and what are the implications of this interplay for targeted therapeutic interventions?
- If hypertension is a complex disease with multiple causes, how can we develop effective treatments and prevention strategies?
Diagnostic and Screening Tools
The primary current diagnostic and screening tools around hypertension include blood pressure measurement. Blood pressure consists of systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP).
SBP is the pressure when the heart is beating, and DBP is the pressure when the heart is resting. A diagnosis of hypertension can be established when the Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP) is 130 mmHg or above or when the Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP) is at least 80 mmHg [1].
The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends that all adults have their blood pressure checked at least once a year. People with risk factors for hypertension, such as obesity, diabetes, and kidney disease, should have their blood pressure checked more often [13].
Secondary tools for evaluating hypertension include ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM). ABPM is a more accurate way to measure blood pressure, measuring blood pressure over 24 hours. ABPM is an integral part of hypertensive care [14].
Urine tests can check for protein in the urine, a sign of kidney damage. Kidney damage is a risk factor for hypertension. Blood tests can be used to check for other medical conditions that can cause hypertension, such as diabetes and kidney disease, cholesterol levels, and other risk factors for heart disease.
Hormonal Tests can measure hormones produced by the adrenal and thyroid glands, which can help diagnose secondary hypertension. Regardless of the diagnostic or screening tools, early diagnosis and management of hypertension save lives [15].

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of using blood pressure measurement as the primary diagnostic and screening tool for hypertension?
- What are some of the challenges of implementing ABPM as a routine screening tool for hypertension?
- How can we improve the early diagnosis and management of hypertension in all populations?
Imaging and Other Diagnostic Tests
Ultrasound of the Kidneys: To rule out kidney abnormalities.
Echocardiogram: To assess heart function and structure. Useful if hypertension has been longstanding.
Eye Exam: A fundoscopic examination can reveal changes in the retinal blood vessels, indicative of chronic hypertension.
Telemedicine: Remote monitoring can be helpful for ongoing assessment and titration of treatment.
Healthcare Apps: Smartphone apps can log and track blood pressure readings over time.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Considering the variety of diagnostic and screening tools available for hypertension—from traditional blood pressure measurements to digital devices like telemedicine and healthcare apps—how can healthcare providers ensure that they employ the most practical combination of methods for accurate diagnosis and long-term management of the condition?
- How does an early diagnosis contribute to better management and prognosis in hypertension patients?
Medication Management
The management of hypertension has evolved over the years, with numerous classes of medications available for treatment. The type of medication best suited for your patients will depend on their needs and health history.
Treatment strategies often begin with monotherapy, a single drug, usually a diuretic, beta-blocker, ACE inhibitor, or Angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARBs) [16]. Combination therapy for patients with stage 2 hypertension or those not reaching the target BP with monotherapy, which may include two or more drug classes, is also used.[16].
Step therapy involves starting with one drug and adding others to achieve the desired effect. A tailored approach is considered if comorbid conditions are present, such as diabetes or heart failure, which may influence drug choice.
Several standard classes of antihypertensive medications are used to treat hypertension, including first-line thiazides such as hydrochlorothiazide, which help rid excess salt and water and lower blood pressure [17]. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors such as lisinopril and ramipril block the production of angiotensin II, a hormone that narrows blood vessels.
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) such as losartan and valsartan which inhibit the action of angiotensin II, leading to vasodilation [17]. Beta-blockers such as atenolol or metoprolol slow the heart rate and reduce the force of the heart's contractions, which can lower blood pressure [17].
Calcium channel blockers such as amlodipine and diltiazem relax the muscles of the blood vessels by inhibiting the movement of calcium into vascular smooth muscle cells, thus lowering blood pressure [17]. Alpha-blockers such as doxazosin work by blocking alpha-adrenergic receptors, leading to vasodilation. Vasodilators such as hydralazine and minoxidil relax the muscles in blood vessel walls [17].
Central action agents such as clonidine, methyldopa, and moxonidine work on the central nervous system to lower blood pressure [17]. Moxonidine is a new-generation antihypertensive drug that works by activating imidazoline-I1 receptors in the brain, and it may be used when other antihypertensive drugs, such as thiazides, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and calcium channel blockers, are not appropriate or have failed [18].
Thiazide-like diuretics such as chlorthalidone and indapamide have found increased use for their more prolonged duration of action and better cardiovascular outcomes when compared to traditional thiazides [19]. New evidence-based medications are coming into play, such as angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs), and a clinical trial is underway to test the effectiveness of a new drug called finerenone in preventing heart failure and kidney disease in people with hypertension and diabetes [20] [21].
Due to their safety profiles, there are special considerations with hypertensive management, including methyldopa and labetalol for pregnancy [22].
For older people, care is taken to avoid overtreatment, considering the risks of low blood pressure. For patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), ACE inhibitors and ARBs are often favored due to their renal protective effects.
Generics are preferred when appropriate to reduce patient costs [23]. Digital adherence tools, including smartphone apps and telemedicine platforms, monitor patient compliance and adjust treatment as necessary.
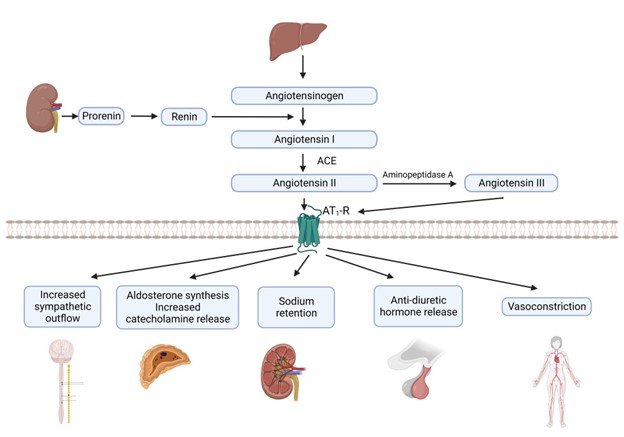
[32]

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What challenges do healthcare providers face in medication compliance among hypertensive patients?
- Given the myriad antihypertensive drug classes and treatment strategies available, coupled with considerations for special populations such as pregnant women, older adults, and those with chronic kidney disease, how can healthcare providers effectively customize treatment plans while maintaining a consistent standard of care across different patient profiles?
Other Interventions
Beyond medication, lifestyle changes, including dietary interventions like the DASH diet and exercise, have proven effective in managing hypertension [24]. The DASH diet focuses on a high intake of fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy foods and is low in saturated and total fat.
A reduction in dietary sodium has been shown to lower blood pressure, with a general recommendation to consume less than 2,300 mg per day, with an ideal limit of 1,500 mg for most adults [24]. Regular aerobic exercise such as walking, jogging, or swimming can lower blood pressure.
Weight loss of even 5-10% can significantly impact reducing blood pressure [25]. Alcohol moderation and smoking cessation can also lead to blood pressure reduction.
Behavioral therapies, including stress management techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and relaxation exercises, can help reduce short-term spikes in blood pressure. There is some evidence that suggests that Cognitive CBT can be effective in managing hypertension [26].
Biofeedback can help manage stress triggers and measure physiological functions like heart rate and blood pressure [26]. Although evidence is mixed, some studies suggest acupuncture can help lower blood pressure.
Renal denervation is an invasive procedure using radiofrequency energy to destroy kidney nerves contributing to hypertension. Central sleep apnea therapy can treat central sleep apnea and lower blood pressure.
Weight loss surgery can be an effective way to lower blood pressure in people who are obese or overweight. Several stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing, can be helpful.
Self-monitoring and regular medical check-ups can ensure that the treatment plan is effective and can be adjusted as needed. Remote consultations can offer more frequent touchpoints for adjustments in treatment plans.
Various mobile applications can help patients track blood pressure readings, medication schedules, and lifestyle changes. Community-based interventions to educate the public about hypertension risks, prevention, and management can be effective.
On a policy level, changes and initiatives that reduce sodium in processed foods can have a broader societal impact [27].

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How do non-pharmacological interventions compare with medication management in terms of effectiveness and patient compliance?
- What roles do genetics and lifestyle factors play in the development of hypertension?
- How might the interactions among genetic factors, diet, obesity, lifestyle choices, and psychological elements contribute to the complex etiology of primary hypertension, and what does this complexity imply for diagnosing and treating secondary hypertension?
Upcoming Research
Using "Omics" genomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data to tailor antihypertensive therapies to individuals' researchers are working to identify the genes that contribute to hypertension and specific genetic markers that can help predict an individual's risk for developing hypertension and their potential response to treatments [28].
This information could be used to create new genetic tests to identify people who are at risk of developing the condition. Personalized medicine seeks to create customized approaches to managing hypertension, which would involve tailoring treatment to the individual's needs and risk factors.
Non-invasive treatments, such as devices worn on the body to deliver medication or stimulate the nerves, may also be effective. Researchers are developing a new type of blood pressure monitor that can be worn on the wrist and measure blood pressure throughout the day.
A study is underway to investigate the use of artificial intelligence to develop personalized treatment plans for people with hypertension. With predictive analytics, AI models are trained to predict hypertension risk and disease progression using large-scale electronic health records [29].
In the area of new therapeutic targets, researchers are looking into novel ways to improve endothelial function and vascular health. Studies into how the gut microbiome may influence blood pressure regulation offer potential for new treatment modalities [30]. Research on how diet interacts with genes within the gut microbiome may affect blood pressure.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How might advancements in technology and research change the landscape of hypertension management in the next decade?
- How can we balance the potential benefits of personalized medicine for hypertension with the challenges of ensuring that everyone has access to these new treatments?
Awareness and Patient Education
What your patients should know:
- Early diagnosis and treatment of hypertension are essential for preventing complications.
- There are several different types of medications available to treat hypertension.
- Lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight, can also help to lower blood pressure.
Nurses and healthcare professionals should be aware of the following:
- Nurses and healthcare professionals play a vital role in educating patients about hypertension and helping them manage their condition.
- The latest epidemiological statistics on hypertension, including its prevalence, risk factors, and impact on public health.
- The etiology and pathophysiology of hypertension, including the different types of hypertension and their underlying causes.
- The diagnostic tools used to diagnose hypertension include blood pressure measurement, ambulatory blood pressure monitoring, urine tests, blood tests, and imaging tests.
- The different types of medications available to treat hypertension, as well as their side effects and interactions.
Nurses and healthcare professionals can help patients to manage their hypertension by:
- Educating patients about hypertension and its risks.
- Helping patients develop a treatment plan that includes lifestyle changes and medications.
- Monitoring their blood pressure and adjusting their treatment plan as needed.
- Providing support and encouragement.
By working together, nurses and healthcare professionals can help patients manage their hypertension and reduce their risk of complications.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are your key takeaways from this course, and how do you plan to implement these learnings in your clinical practice?
Conclusion
Hypertension is a significant public health problem in the United States and worldwide [1]. It is a chronic condition that can lead to serious health problems like heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and eye problems. However, despite its complexity, hypertension is manageable with lifestyle changes, medications, and the potential information from future genomic discoveries [25] [17].
GI Bleed: An Introduction
Introduction
Gastrointestinal bleeding (GI Bleed) is an acute and potentially life-threatening condition. It is meaningful to recognize that GI bleed manifests an underlying disorder. Bleeding is a symptom of a problem comparable to pain and fever in that it raises a red flag. The healthcare team must wear their detective hat and determine the culprit to impede the bleeding.
Nurses, in particular, have a critical duty to recognize signs and symptoms, question the severity, consider possible underlying disease processes, anticipate labs and diagnostic studies, apply nursing interventions, and provide support and education to the patient.
Epidemiology
The incidence of Gastrointestinal Bleeding (GIB) is broad and comprises cases of Upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) and lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB). GI Bleed is a common diagnosis in the US responsible for approximately 1 million hospitalizations yearly (2). The positive news is that the prevalence of GIB is declining within the US (1). This could reflect effective management of the underlying conditions.
Upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) is more common than lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB) (2). Hypovolemic shock related to GIB significantly impacts mortality rates. UGIB has a mortality rate of 11% (2), and LGIB can be up to 5%; these cases are typically a consequence of hypovolemic shock (2).
Certain risk factors and predispositions impact the prevalence. Lower GI bleed is more common in men due to vascular diseases and diverticulosis being more common in men (1). Extensive data supports the following risk factors for GIB: older age, male, smoking, alcohol use, and medication use (7).
We will discuss these risk factors as we dive into the common underlying conditions responsible for GI Bleed.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Have you ever cared for a patient with GIB?
- Can you think of reasons GIB is declining in the US?
- Do you have experience with patients with hypovolemic shock?
Etiology/ Pathophysiology
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding includes any bleeding within the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the rectum. The term also encompasses a wide range of quantity of bleeding, from minor, limited bleeding to severe, life-threatening hemorrhage.
We will review the basic anatomy of the gastrointestinal system and closely examine the underlying conditions responsible for upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding.
Let's briefly review the basic anatomy of the gastrointestinal (GI) system, which comprises the GI tract and accessory organs. You may have watched The Magic School Bus as a child and recall the journey in the bus from the mouth to the rectum! Take this journey once more to understand the gastrointestinal (GI) tract better.
The GI tract consists of the following: oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anal canal (5). The accessory organs include our teeth, tongue, and organs such as salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas (5). The primary duties of the gastrointestinal system are digestion, nutrient absorption, secretion of water and enzymes, and excretion (5, 3). Consider these essential functions and their impact on each other.
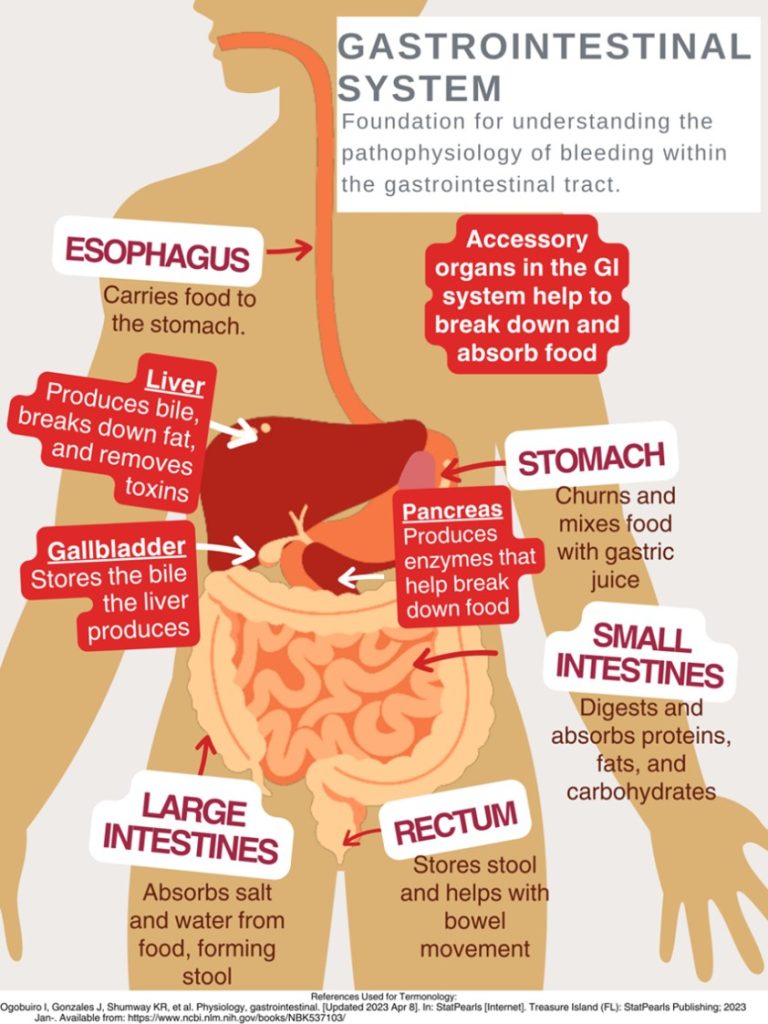
This design was created on Canva.com on August 31, 2023. It is copyrighted by Abbie Schmitt, RN, MSN and may not be reproduced without permission from Nursing CE Central.
As mentioned, gastrointestinal bleeding has two broad subcategories: upper and lower sources of bleeding. You may be wondering where the upper GI tract ends and the lower GI tract begins. The answer is the ligament of Treitz. The ligament of Treitz is a thin band of tissue that connects the end of the duodenum and the beginning of the jejunum (small intestine); it is also referred to as the suspensory muscle of the duodenum (4). This membrane separates the upper and lower GI tract. Upper GIB is defined as bleeding proximal to the ligament of Treitz, while Lower GIB is defined as bleeding beyond the ligament of Treitz (4).
Upper GI Bleeding (UGIB) Etiology
Underlying conditions that may be responsible for the UGIB include:
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Esophagitis
- Foreign body ingestion
- Post-surgical bleeding
- Upper GI tumors
- Gastritis and Duodenitis
- Varices
- Portal hypertensive gastropathy (PHG)
- Angiodysplasia
- Dieulafoy lesion
- Gastric antral valvular ectasia
- Mallory-Weiss tears
- Cameron lesions (bleeding ulcers occurring at the site of a hiatal hernia
- Aortoenteric fistulas
- Hemobilia (bleeding from the biliary tract)
- Hemosuccus pancreaticus (bleeding from the pancreatic duct)
(1, 4, 5, 8. 9)
Pathophysiology of Variceal Bleeding. Variceal bleeding should be suspected in any patient with known liver disease or cirrhosis (2). Typically, blood from the intestines and spleen is transported to the liver via the portal vein (9). The blood flow may be impaired in severe liver scarring (cirrhosis). Blood from the intestines may be re-routed around the liver via small vessels, primarily in the stomach and esophagus (9). Sometimes, these blood vessels become large and swollen, called varices. Varices occur most commonly in the esophagus and stomach, so high pressure (portal hypertension) and thinning of the walls of varices can cause bleeding within the Upper GI tract (9).
Liver Disease + Varices + Portal Hypertension = Recipe for UGIB Disaster
Lower GI Bleeding (LGIB) Etiology
- Diverticulosis
- Post-surgical bleeding
- Angiodysplasia
- Infectious colitis
- Ischemic colitis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Colon cancer
- Hemorrhoids
- Anal fissures
- Rectal varices
- Dieulafoy lesion
- Radiation-induced damage
(1, 4, 5, 9)
Unfortunately, a source is identified in only approximately 60% of cases of GIB (8). Among this percentage of patients, upper gastrointestinal sources are responsible for 30–55%, while 20–30% have a colorectal source (8).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How is the GI Tract subdivided?
- Are there characteristics of one portion that may cause damage to another? (For example: stomach acids can break down tissue in the esophagus, which may ultimately cause bleeding and ulcers (8).
- Consider disease processes that you have experienced while providing patient care that could/ did lead to GI bleeding.
Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy identify the source of bleeding in 80–90% of patients (4). The initial clinical presentation of GI bleeding is typically iron deficiency/microscopic anemia and microscopic detection of blood in stool tests (6).
The following laboratory tests are advised to assist in finding the cause of GI bleeding (2):
- Complete blood count
- Hemoglobin/hematocrit
- International normalized ratio (INR), prothrombin time (PT), and activated partial thromboplastin time (PTT)
- Liver function tests
Low hemoglobin and hematocrit levels result from blood loss, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) may be elevated due to the GI system's breakdown of proteins within the blood (9).
The following laboratory tests are advised to assist in finding the cause of GI bleeding:
- EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy)- Upper GI endoscopy
- Clinicians can visualize the upper GI tract using a camera probe that enters the oral cavity and travels to the duodenum (9)
- Colonoscopy- Lower GI endoscopy/ (9)
- Clinicians can visualize the lower GI tract.
- CT angiography
- Used to identify an actively bleeding vessel
Signs and Symptoms
Clinical signs and symptoms depend on the volume/ rate of blood loss and the location/ source of the bleeding. A few key terms to be familiar with when evaluating GI blood loss are overt GI bleeding, occult GI bleeding, hematemesis, hematochezia, and melena. Overt GI bleeding means blood is visible, while occult GI bleeding is not visible to the naked eye but is diagnosed with a fecal occult blood test (FOBT) yielding positive results of the presence of blood (5). Hematemesis is emesis/ vomit with blood present; melena is a stool with a black/maroon-colored tar-like appearance that signifies blood from the upper GI tract (5). Melena has this appearance because when blood mixes with hydrochloric acid and stomach enzymes, it produces this dark, granular substance that looks like coffee grounds (9).
Mild vs. Severe Bleeding
A patient with mild blood loss may present with weakness and diaphoresis (9). Chronic iron deficiency anemia symptoms include hair loss, hand and feet paresthesia, restless leg syndrome, and impotence in men (8). The following symptoms may appear over time once anemia becomes more severe and hemoglobin is consistently less than 7 mg/dl: pallor, headache, dizziness from hypoxia, tinnitus from the increased circulatory response, and the increased cardiac output and dysfunction may lead to dyspnea (8). Findings of a positive occult GI bleed may be the initial red flag.
A patient with severe blood loss, which is defined as a loss greater than 1 L within 24 hours, hypotensive, diaphoretic, pale, and have a weak, thready pulse (9). Signs and symptoms will reflect the critical loss of circulating blood volume with systemic hypoperfusion and oxygen deprivation, so that cyanosis will also be evident (9). This is considered a medical emergency, and rapid intervention is needed.
Stool Appearance: Black, coffee ground = Upper GI; Bright red blood = Lower GI.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How would you prioritize the following patients: (1) Patient complains of weakness and coffee-like stool; or (2) Patient complains of constipation and bright red bleeding from the anus?
- Have you ever witnessed a patient in hypovolemic shock? If yes, what symptoms were most pronounced? If not, consider the signs.
- What are ways that the nurse can describe abnormal stool?
History and Physical Assessment
History
A thorough and accurate history and physical assessment is a key part of identifying and managing GI bleed. Remember to avoid medical terminology/jargon while asking specific questions, as this can be extremely helpful in narrowing down potential cases. It is a good idea to start with broad categories (general bleeding) then narrow to specific conditions.
Assess for the following:
- Previous episodes of GI Bleed
- Medical history with contributing factors for potential bleeding sources (e.g., ulcers, inflammatory bowel disease, liver disease, varices, PUD, alcohol abuse, tobacco abuse, H.pylori, diverticulitis) (3)
- Contributory medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, bismuth, iron) (3)
- Comorbid diseases that could affect management of GI Bleed (8)
Physical Assessment
- Head to toe and focused Gastrointestinal, Hepatobiliary, Cardiac and Pancreatic
- Assessments
Assess stool for presence of blood (visible) and anticipate orders/ collect specimen for occult blood testing. - Vital Signs
Signs of hemodynamic instability associated with loss of blood volume (3):
- Resting tachycardia
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Supine hypotension
- Abdominal pain (may indicate perforation or ischemia)
- A rectal exam is important for the evaluation of hemorrhoids, anal fissures, or anorectal mass (3)
Certain conditions place patients at higher risk for GI bleed. For example, patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) have a five times higher risk of GIB and mortality than those without kidney disease (2).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Are there specific questions to ask if GIB is suspected?
- What are phrases from the patient that would raise a red flag for GIB (For example: “I had a stomach bleed years ago”)
- Have you ever noted overuse of certain medications in patients?

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Have you ever shadowed or worked in an endoscopy unit?
- Name some ways to explain the procedures to the patient?
Treatment and Interventions
Treatment and interventions for GIB bleed will depend on the severity of the bleeding. Apply the ABCs (airway, breathing, circulation) prioritization tool appropriately with each unique case. Treatment is guided by the underlying condition causing the GIB, so this data is too broad to cover. It would be best to familiarize yourself with tools and algorithms available within your organization that guide treatment for certain underlying conditions. Image 2 is an example of an algorithm used to treat UGIB (8). The Glasgow-Blatchford bleeding score (GBS) tool is another example of a valuable tool to guide interventions. Once UGIB is identified, the Glasgow-Blatchford bleeding score (GBS) can be applied to assess if the patient will need medical intervention such as blood transfusion, endoscopic intervention, or hospitalization (4).
Unfortunately, there is currently a lack of tools available for risk stratification of emergency department patients with lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB) (6). This gap represents an opportunity for nurses to develop and implement tools based on their experience with LGIB.
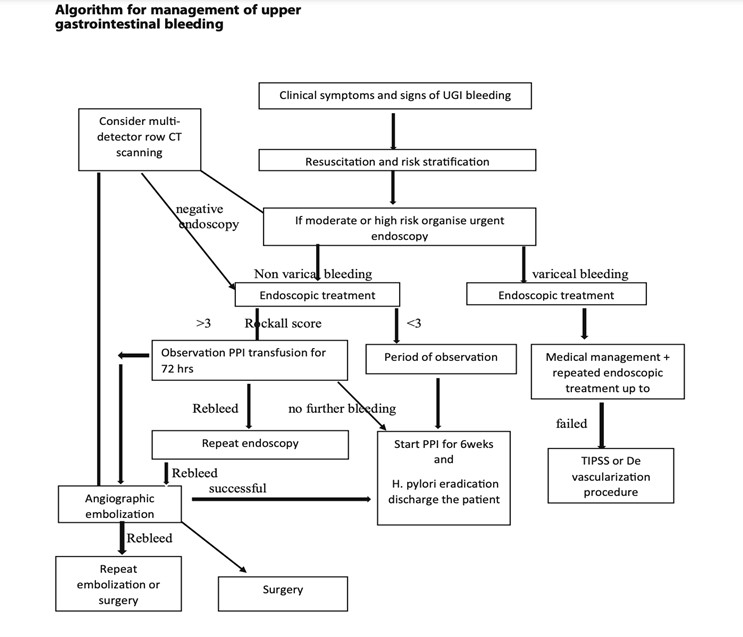
(8)

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Are you familiar with GIB assessment tools?
- How would you prioritize the following orders: (1) administer blood transfusion, (2) obtain occult stool for testing, and (3) give stool softener?
The first step of nursing care is the assessment. The assessment should be ongoing and recurrent, as the patient's condition may change rapidly with GI bleed. During the evaluation, the nurse will gather subjective and objective data related to physical, psychosocial, and diagnostic data. Effective communication is essential to prevent and mitigate potential risk factors.
Subjective Data (Client verbalizes)
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Dizziness
- Weakness
Objective Data (Clinician notes during assessment)
- Hematemesis (vomiting blood)
- Melena (black, tarry stools)
- Hypotension
- Tachycardia
- Pallor
- Cool, clammy skin

Nursing Interventions
Ineffective Tissue Perfusion:
- Monitor vital signs frequently to assess blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation changes.
- Obtain IV access.
- Administer oxygen as ordered.
- Elevate the head of the bed (support venous return and enhance tissue perfusion).
- Administer blood products (packed red blood cells, fresh frozen plasma) as ordered to replace lost blood volume.
Acute Pain:
- Assess the patient's pain (quantifiable pain scale)
- Administer pain medications as ordered.
- Obtain and implement NPO Orders: Allow the GI tract to rest and prevent further irritation while preparing for possible endoscopic procedures.
- Apply heat/cold therapy for comfort.
Risk for Decreased Cardiac Output
- Assess the patient's heart rate and rhythm. (Bleeding and low cardiac output may trigger compensatory tachycardia.) (9)
- Assess and monitor the patient's complete blood count.
- Assess the patient's BUN level.
- Monitor the patient's urine output.
- Perform hemodynamic monitoring.
- Administer supplemental oxygenation as needed.
- Administer intravenous fluids as ordered.
- Prepare and initiate blood transfusions as ordered.
- Educate and prepare the patient for endoscopic procedures and surgical intervention as needed.
Risk for Deficient Fluid Volume:
- Monitor intake and output.
- Maintain hydration.
- Administer intravenous fluids as ordered.
- Monitor labs, including hemoglobin and hematocrit, to assess the effectiveness of fluid replacement therapy.
- Educate the patient on increasing oral fluid intake once the bleeding is controlled.
- Vital signs
- Assess the patient's level of consciousness and capillary refill time to evaluate tissue perfusion and response to fluid replacement.
- Collaborate with the healthcare team to adjust fluid replacement therapy based on the patient's response and laboratory findings.
Nursing Goals / Outcomes for GI Bleed:
- The patient's vital signs and lab values will stabilize within normal limits.
- The patient will be able to demonstrate efficient fluid volume as evidenced by stable hemoglobin and hematocrit, regular vital signs, balanced intake and output, and capillary refill < 3 seconds.
- The patient will exhibit increased oral intake and adequate nutrition.
- The patient will verbalize relief or control of pain.
- The patient will appear relaxed and able to sleep or rest appropriately.
- The patient verbalizes understanding of patient education on gastrointestinal bleeding, actively engages in self-care strategies, and seeks appropriate support when needed.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How can the nurse advocate for a patient with GIB?
- Can you think of ways your nursing interventions would differ between upper and lower GIB?
- Have you ever administered blood products?
- What are possible referrals following discharge that would be needed? (Example: gastroenterology, home health care)
Case Study
Mr. Blackstool presents to the emergency department with the following:
CHIEF COMPLAINT: "My stool looked like a ball of black tar this morning."
He also reports feeling "extra tired" and "lightheaded" for 3-5 days.
HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is a 65-year-old tractor salesman who presents to the emergency room complaining of the passage of black stools, fatigue, and lightheadedness. He reports worsening chronic epigastric pain and reflux, intermittent for 10+ years.
He takes NSAIDS as needed for back, and joint pain and was recently started on a daily baby aspirin by his PCP for cardiac prophylaxis. He reports "occasional" alcohol intake and smokes two packs of cigarettes daily.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: Examination reveals an alert and oriented 65-YO male. He appears anxious and irritated. Vital sips are as follows. Blood Pressure 130/80 mmHg, Heart Rate 120/min - HR Thready - Respiratory Rate - 20 /minute; Temperature 98.0 ENT/SKIN: Facial pallor and cool, moist skin are noted. No telangiectasia of the lips or oral cavity is noted. The parotid glands appear full.
CHEST: Lungs are clear to auscultation and percussion. The cardiac exam reveals a regular rhythm with an S4. No murmur is appreciated. Peripheral pulses are present but are rapid and weak.
ABDOMEN/RECTUM: The waist shows a rounded belly. Bowel sounds are hyperactive. Percussion of the liver is 13 cm (mal); the edge feels firm. Rectal examination revealed a black, tarry stool. No Dupuytren's contractions were noted.
LABORATORY TESTS: Hemoglobin 9gm/dL, Hematocrit 27%, WBC 13,000/mm. PT/PTT - normal. BUN 46mg/dL.
Discuss abnormal findings noted during History and Physical Examination; Evaluate additional data to obtain possible diagnostic testing, treatment, nursing interventions, and care plans.
Conclusion
After this course, I hope you feel more knowledgeable and empowered in caring for patients with Gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB). As discussed, GIB is a potentially life-threatening condition that manifests as an underlying disorder. Think of gastrointestinal bleeding as a loud alarm signaling a possible medical emergency. Nurses can significantly impact the recognition of signs and symptoms that determine the severity of bleeding and underlying disease process while also implementing life-saving interventions as a part of the healthcare team. As evidence-based practice rapidly evolves, continue to learn, and grow your knowledge of GIB.
Constipation Management and Treatment
Introduction
Constipation is more than just an uncomfortable topic—it’s a challenge that nurses encounter very frequently across diverse patient populations. From post-operative recovery to chronic conditions, managing constipation effectively can significantly impact a patient’s comfort, recovery, disease management, and overall quality of life. There is a deeper need for empathy, education, and evidence-based care. This course invites you to dive into the science of managing constipation with knowledge and compassion.
Understanding Constipation
Constipation is a condition characterized by infrequent, difficult, or incomplete bowel movements, often accompanied by hard or dry stools (3). It is one of the most common problems individuals face and occasionally results in emergent issues.
Constipation can be classified as a primary disorder or secondary to many potential causes.
Primary Constipation
Primary constipation is constipation that is not caused by an underlying medical condition, medication, or structural abnormality (8). Essentially, the problem arises from bowel functions rather than from a disease or physical obstruction. Primary constipation is also called idiopathic constipation (3). Causes of primary constipation include dietary, lifestyle, neuromuscular, and psychological factors.
Although primary constipation is not caused by an underlying medical condition, it can significantly affect quality of life. Understanding its types and causes is essential for effective management and improved patient outcomes.
Primary constipation can be considered as (1) functional constipation, in which stool appropriately passes through the colon at a normal rate, or (2) slow transit constipation, where stool passes through the colon at a prolonged, slow rate (3).
Anorectal dysfunction is the inefficient coordination of the pelvic musculature in the evacuation mechanism and is typically an acquired behavioral disorder.
Secondary Constipation
Secondary constipation is due to chronic diseases, certain medications, or anatomic abnormalities (3). The etiology will be further evaluated in an upcoming section.
Epidemiology
Constipation is a common symptom, impacting up to 10% to 20% of the general population (6). The exact prevalence is underestimated because studies show that most patients do not seek out medical care for constipation. The prevalence of chronic constipation is increasing due to changes in diet composition, accelerated pace of life, and the influence of complex social and psychological factors.
Epidemiological surveys have shown that the incidence of chronic constipation is between 14 and 30% worldwide, affecting individuals of all ages, races, socioeconomic status, and nationalities (10). However, certain populations are impacted at higher rates. The rates of constipation increase with age, affecting roughly one-third of individuals over 60 (6). Individuals residing in nursing homes are more commonly reported. Another risk factor is gender, as constipation affects women more than men (7). Recent studies have also noted a two-fold higher rate of constipation among African Americans and those with lower socioeconomic status (income <$20,000 per year) (6).
Social determinants of health (SDOH) are the non-medical factors that impact health outcomes, they encompass the environments in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age, as well as the systems and structures that shape these conditions (9). SDOH significantly impacts health, quality of life, and health disparities across different populations, and research shows a correlation with constipation. These include lifestyle, demographics, education, healthcare access, and adherence to medications (7).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How would you describe the difference between primary and secondary constipation?
- What populations are more impacted by constipation?
- How can lifestyle, demographics, and education impact overall health?
- Can you discuss the reasons that chronic constipation rates may be increasing?
Pathophysiology
The underlying pathophysiology of constipation varies among different individuals. There are basic mechanical pathophysiological functions, such as the changes in feces once it stays in the rectum for too long and changes in mucous membrane sensitivity and peristalsis if the urge is ignored.
The pathophysiology of constipation can be categorized based on the underlying causes and mechanisms. These categories help identify the specific factors contributing to constipation and guide appropriate interventions. The primary mechanisms are colonic sensorimotor dysfunction and microbiome alteration (10). Factors associated with these mechanisms include gastrointestinal motility and fluid transport, anorectal movement and sensory functions, and dietary and behavioral factors.
Constipation occurs when the fecal mass stays in the rectal cavity for an extended period that is either atypical for the patient or less than three times within a week (5). As the fecal material lingers in the rectum, additional water is absorbed, and the feces becomes smaller, firmer, drier, and more difficult (or painful) to pass.
Another pathophysiological process of constipation can be described by the common saying, “Use it or lose it!”. In this case, when the urge to defecate is ignored, it becomes less recognized. Laxation is the term used for the urge to have a bowel movement (8), so when the urge is ignored, the muscular and rectal mucous membranes become less sensitive to the presence of fecal matter in the rectum (8).
It is important to review gastrointestinal mobility.
Gastrointestinal Motility
Gastrointestinal (GI) motility is the coordinated contractions of the muscles in the gastrointestinal tract for the movement of food and waste products. This process is essential for digestion, absorption of nutrients, and the exit of stool.
Components of GI Motility:
- Peristalsis is the wave-like contractions that move food along the digestive tract.
- Segmental contractions are rhythmic contractions that mix food with digestive enzymes and promote absorption.
- Tonic contractions are sustained muscle contractions that maintain tone in certain areas, such as the sphincters.
Anorectal dyssynergy is a dysfunction of the coordination between the rectal and pelvic floor muscles during defecation. is a common cause of chronic constipation. Normally, defecation involves the relaxation of the anal sphincter and pelvic floor muscles, combined with an increase in intra-abdominal pressure. In anorectal dyssynergy, this process is disrupted, leading to difficulties in stool evacuation despite the presence of normal colonic transit.
Diagnosis is typically made using tests such as anorectal manometry or balloon expulsion tests, and treatment may involve biofeedback therapy, pelvic floor exercises, or other interventions aimed at strengthening the muscles for coordination during defecation.
One prospective study of patients with chronic constipation showed that there was an inability to coordinate the abdominal, rectal, and pelvic floor muscles during defecation. This inability includes impaired rectal contraction, paradoxical anal contraction, or inadequate anal relaxation.
(6)

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What happens to fecal material when it is stored in the rectum for an extended period?
- Can you describe anorectal dyssynergy?
- What are possible reasons the urge to defecate may be ignored?
- Can you explain why gastrointestinal mobility (peristalsis, contraction, etc.) is essential to digestion, absorption of nutrients, and the exit of stool?
Etiology
Constipation can result from a variety of interconnected factors that influence bowel function. Nurses should recognize how the etiology of primary and secondary constipation is different.
Underlying Causes of Primary Constipation
Remember – primary constipation results from irregular bowel functions, not an underlying medical condition or medication. This type of constipation is commonly the cause of daily lifestyle factors. These lifestyle factors can be grouped as dietary and functional.
- Dietary factors
- Low fiber intake
- Lack of nutrient-dense foods
- Inadequate fluid intake
- Irregular eating patterns
- Functional factors
- Low or minimal physical activity
- Ignoring the urge to defecate
- Pain or discomfort with defecation
- Weak abdominal muscles
- Environmental changes or time constraints
- Lack of privacy leads to avoidance of a bowel movement for extended periods.
Underlying Causes of Secondary Constipation
- Endocrine/metabolic disorders
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Diabetes mellitus
- Uremia
- Hypercalcemia
- Hypothyroidism
- Myopathic conditions
- Amyloidosis
- Myotonic dystrophy
- Scleroderma
- Neurologic diseases
- Autonomic neuropathy
- Cerebrovascular disease
- Hirschsprung’s disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Parkinson’s disease
- Spinal cord injury/tumor
- Psychological conditions
- Anxiety/depression
- Somatization
- Structural abnormalities
- Anal fissure/stricture or hemorrhoid
- Colonic stricture
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Obstructive colonic mass
- Rectal prolapse or rectocele
- Others
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Pregnancy
- Medications
- Antacids
- Anticholinergics
- Antidepressants
- Antihistamines
- Calcium channel blockers
- Clonidine
- Diuretics
- Iron
- Narcotics
- NSAIDS
- Opioids
- Psychotropics
- Sympathomimetics
(3)
Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptoms of constipation are abdominal distention and discomfort, indigestion, “rumbling” of the intestinal system, straining during bowel movements, sensation of incomplete emptying, and rectal pressure (8). The description of stool is a key factor in clinical symptomology. The stool will likely be dry, hard, fragmented, and difficult or painful to pass. There may be findings of fresh bleeding (bright red) around the rectum, or protrusions.
Patients may also report fatigue, decreased appetite, and headache (5). There may also be mood changes related to constipation, such as irritability or depression (4).
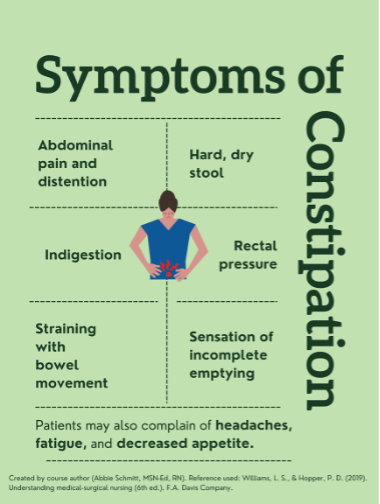
Pharmacological/Non-Pharmacological Treatment
Constipation management encompasses a harmonious blend of pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies. Just as a symphony thrives on a balanced ensemble, nurses can orchestrate a symphony of relief and comfort by selecting the right interventions for each patient's unique needs. Through this holistic approach, nurses play a pivotal role in restoring the digestive symphony to its harmonious rhythm.
Pharmacological
As nurses step into the realm of constipation management, they encounter a diverse array of strategies that can harmonize the digestive symphony. Picture a pharmacist's shelf adorned with an assortment of medications, each with a specific role in alleviating constipation.
Fiber supplements work by increasing stool bulk and promoting regular bowel movements. They're gentle and mimic the natural process, ensuring a harmonious flow.
Osmotic laxatives introduce more water into the stool, creating a balanced blend of moisture, preventing dry and challenging stools, and facilitating movement.
Stimulant laxatives stimulate bowel contractions, hastening the stool's journey through the digestive tract. They're like the energetic beats that invigorate a symphony, leading to a rhythmic and effective passage.
Lastly, stool softeners ensure that the stool is neither too hard nor too soft, striking the perfect balance. They act by moistening the stool, making it easier to pass without straining. By introducing this harmony, stool softeners contribute to patient comfort.
Non-pharmacological
Beyond the realm of medications lies an equally vital avenue: non-pharmacological interventions. Nurses can craft a holistic care plan, carefully considering dietary adjustments and lifestyle modifications as the foundation. Examples of non-pharmacological interventions include the following:
A diet rich in fiber guides the stool's journey with ease. Nurses can educate patients on incorporating fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, ensuring a harmonious flow through the intestines.
Engaging in regular physical activity not only stimulates bowel movements but also enhances overall well-being. Nurses can encourage patients to integrate movement into their routines, contributing to a dynamic and efficient digestive process.
Relaxation techniques play a vital role in constipation management. Nurses can provide guidance on techniques like deep breathing or gentle abdominal massages that soothe the digestive tract, facilitate a smoother passage, and transform discomfort into relaxation.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are the most common symptoms of constipation?
- Can you think of words patients may use to describe abdominal discomfort or indigestion?
- Are you familiar with ways of assessing rectal bleeding?
- What are mood changes that may correlate with constipation?
Assessment
A thorough history and physical examination are essential. Patients may feel uncomfortable or self-conscious when discussing bowel habits. It is important to establish a trusting and comfortable rapport before asking these questions. Providing privacy is meaningful.
Data Collection
- Onset, nature, duration of constipation.
- Past bowel movement patterns
- Current bowel patterns
- Occupation
- Lifestyle habits (nutrition, exercise, stress, coping, support)
- History of laxative or enema use
- Current medication regimen
(8)
Focused Assessment
- Inspect the abdomen for distention and symmetry
- Palpate the abdomen to assess for tenderness or distention.
- Rectal examination may identify anal fissures and hemorrhoids, which can contribute to painful bowel movements.
- Assessment of the anal sphincter tone can provide clues of neurological disorders which may impair sphincter function.
- A digital rectal exam may also reveal a rectal mass or retained stool.
(8)
Labs
- CBC
- BMP: calcium and creatinine levels
- TSH
Endoscopy
- Colonoscopy procedures should follow current guidelines.
- Patients with constipation and “red flag” symptoms of rectal bleeding, heme-positive stool, iron deficiency anemia, weight loss of >10 lbs., obstructive symptoms, or family history of colorectal cancer (3).
Radiography imaging is not especially helpful in underlying etiology, but it may detect stool retention. Barium radiographs may help detect Hirschsprung’s disease. Secondary tests such as anorectal manometry and colonic transit studies can be used to evaluate patients whose constipation is refractory (3).
Diagnosis Criteria
Chronic constipation is usually outlined by clinical symptoms known as the Rome criteria. The Rome IV diagnostic criteria define functional constipation as two or more of the following findings occurring in at least 25% of defecations
- Straining during the bowel movement
- Lumpy or hard stool
- A sensation of incomplete evacuation
- A sensation of anorectal obstruction/blockage
- The use of manual maneuvers to facilitate defecation.
- Loose stools are rare without the use of laxatives
- Having fewer than three spontaneous defecations per week.
The criteria also require these findings to be present for longer than 3 months, with an initial symptom onset of longer than 6 months.
(2,3)

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Can you describe the Roma IV diagnostic criteria for constipation?
- Why are bowel patterns and history important to the assessment of constipation?
Treatment
Nonpharmacologic Treatments
- Bowel training – Encourage patients to attempt a bowel movement in the morning, shortly after awakening, when the bowels are more active, and 30 min after meals to encourage gastrocolic reflex.
- Increase dietary fiber intake
- The recommended intake is 20–35 g daily and an increase of 5 g daily until the recommended daily intake is reached. Increase fiber-rich foods: bran, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and prune juice.
- Psyllium and methylcellulose are the most effective forms of fiber replacement.
- Increase fluid intake – decreased intake may result in fecal impaction
- Regular exercise
- Biofeedback/ pelvic floor retraining – useful for anorectal dysfunction.
(3)
Pharmacologic Treatment
A clinical practice guideline jointly developed by the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) and the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) provides evidence-based recommendations for the pharmacological treatment of chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) in adults (1).
The guidelines provide strong recommendations for the use of polyethylene glycol, sodium picosulfate, linaclotide, plecanatide, and prucalopride based on evidence for effectiveness. Conditional recommendations were given for the use of fiber, lactulose, senna, magnesium oxide, and lubiprostone, emphasizing the need for individualized treatment approaches. The guidelines highlight an individualized approach that considers patient preferences, lifestyle, costs, and medication availability (2).
Types of pharmacological treatments:
- Bulk laxatives – Citrucel and Metamucil absorb water from the intestinal lumen to increase stool mass and soften stool consistency.
- Recommended for patients with functional normal transit constipation.
- Side effects include bloating and increased gas production.
- Emollient laxatives—stool softeners: docusate lowers surface tension, thereby allowing water to more easily enter the bowel.
- Not as effective as bulk laxatives but useful in patients with painful defecation conditions such as hemorrhoids or anal fissures.
- Osmotic laxatives
- Milk of magnesia, magnesium citrate, MiraLAX, and lactulose hyperosmolar agents use osmotic activity to result in the secretion of water into the intestinal lumen.
Precautions:
- Monitor for electrolyte imbalances such as hypokalemia and hypermagnesemia.
- Use with caution in congestive heart failure and chronic renal insufficiency patients.
- Stimulant laxatives: Dulcolax, senna, tegaserod, castor oil, and bisacodyl increase intestinal motility and secretion of water into the bowel.
- Common side effects include abdominal discomfort and cramping as a result of increased peristalsis.
- Contraindicated for patients with suspected bowel obstruction.
(3)
Complications and Negative Impacts on Quality of Life
The most common complications associated with constipation are discomfort and irritation that can lead to:
- Hemorrhoids
- Rectal bleeding
- Anal fissures
Sometimes, the difficulty passing a bowel movement can cause more serious complications, such as:
- Rectal prolapse (the large intestine detaches inside the body and pushes out of the rectum)
- Fecal impaction (hard, dry stool is stuck in the body and unable to be expelled naturally)
Constipation significantly impacts quality of life (QOL), affecting both physical and emotional well-being. Patients with constipation may experience more negative QOL. Studies reported that chronic constipation also causes greater school and work absenteeism and loss of productivity (4).
Nursing Implications and Patient Education
Patient education is an important component of effective constipation management.
Assessment of Knowledge and Baseline Habits
- Assess the patient’s current understanding of constipation and its causes.
- Evaluate dietary habits, fluid intake, physical activity, and medication use that may contribute to constipation.
Provide education on the following:
- Causes and Risk Factors
- Risk factors include low fiber intake, inadequate hydration, lack of physical activity, and certain medications (e.g., opioids, and iron supplements).
- Discuss specific risk factors such as age, medical conditions (e.g., diabetes, hypothyroidism), or recent surgeries.
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary Changes
- Hydration
- Physical Activity
- Healthy Bowel Habits
- Encourage patients to respond promptly to the urge to defecate to avoid hardening of stools and reduced sensitivity.
- Recommend a regular bowel routine, such as attempting bowel movements after meals to take advantage of the gastrocolic reflex.
- Discuss Medication Use
- Advise patients on the appropriate use of laxatives, stool softeners, and other medications for short-term relief.
- Discourage routine use of laxatives and enemas to avoid trauma to the intestinal mucosa, dehydration, and eventual failure of defecation stimulus. (Bulk-adding laxatives are not irritating and are usually permitted.)
- Address Psychological Factors
- Tailor Education to Special Populations
- Encourage Self-Monitoring Log
- Teach patients to track their bowel habits, dietary intake, and hydration levels to identify patterns and triggers.
- Provide Written Materials and Resources
- Offer brochures, handouts, or trusted websites for additional information.
In the inpatient settings, nursing interventions should include:
- Record intake and output accurately to ensure correct fluid replacement therapy.
- Note the color and consistency of stool and frequency of bowel movements to form the basis of an effective treatment plan.
- Promote ample fluid intake, if appropriate, to minimize constipation with increased intestinal fluid content.
- Encourage the patient to increase dietary intake of fiber to improve intestinal muscle tone and promote comfortable elimination.
- Encourage the patient to walk and exercise as much as possible to stimulate intestinal activity.
(Lip)

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Why is it important to discourage patients from overusing laxatives and enemas?
- How can nurses encourage bowel training routines?
- Can you name the major lifestyle modifications that are important in constipation management?
- Are you familiar with fiber-rich foods?
Conclusion
Constipation is a common but complex condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and overall health. Nurses play a meaningful role in identifying, preventing, and managing constipation through comprehensive assessment, evidence-based interventions, and patient education. Understanding the underlying causes and employing tailored strategies can empower patients to take control of their bowel health. This course has provided learners with the knowledge and tools to approach constipation with confidence, compassion, and clinical expertise. Remember that even small changes in habits can lead to meaningful improvements in well-being.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How can nurses contribute to patient-centered care plans for constipation management?
- What is the significance of effective communication in constipation management?
- Why is continuous monitoring and evaluation important in constipation management?
Conclusion
Constipation is a significant concern that impacts the comfort and well-being of hospitalized and long-term care patients. Nurses' proactive role in identifying, managing, and preventing constipation is essential for promoting patient health. By employing a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, nurses can significantly enhance patient comfort and quality of life.
Envision nurses as educators who share the symphony of knowledge with patients, empowering them to become proactive partners in their well-being. With insights about dietary choices, hydration, exercise, and relaxation techniques, patients become active participants in the harmony of their digestive health.
Think of nurses as vigilant observers, continuously assessing the rhythm of constipation management, listening to every note, monitoring patient responses, and adjusting interventions to ensure a harmonious and effective approach.
Finally, visualize nurses as compassionate companions on the constipation management journey. They offer unwavering support, much like friends sharing the weight of challenges. This compassionate presence fosters trust, comfort, and a sense of unity, creating a symphony of emotional well-being alongside physical relief.
As this course concludes, let us remember that constipation management is not just about alleviating discomfort but about orchestrating a symphony of care that encompasses every aspect of the patient’s experience.
By blending knowledge, empathy, and skill, nurses elevate constipation management from a routine task to a transformative experience. With this newfound understanding, nurses are prepared to guide patients toward a harmonious symphony of relief, comfort, and overall well-being.
Spinal Cord Injury: Bowel and Bladder Management
Introduction
Imagine one day you are able to walk and take care of your own needs. Now, imagine one week later you wake up no longer able to walk, feel anything below your waist, or hold your bowels.
This is a reality for many people who sustain spinal cord injuries. Managing changes in bowel and bladder function is one of many challenges that people with spinal cord injuries and their families or caregivers face.
This course will provide learners with the knowledge needed to assist patients who have spinal cord injuries with bowel and bladder management to improve the quality of life in this group.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are some societal misconceptions or stereotypes about people with spinal cord injuries?
- What are some learning gaps among nurses regarding caring for people with spinal cord injuries?
- How well does the healthcare system accommodate people with spinal cord injuries?
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics
Spinal Cord Function
Before defining a spinal cord injury, it is important to understand the function of the spinal cord itself. The spinal cord is a structure of the nervous system that is nestled within the vertebrae of the back and helps to distribute information from the brain (messages) to the rest of the body [1].
These messages result in sensation and other neurological functions. While it may be common to primarily associate the nervous system with numbness, tingling, or pain, nerves serve an important purpose in the body’s function as a whole.
Spinal Cord Injury Definition
When the spinal cord is injured, messages from the brain may be limited or entirely blocked from reaching the rest of the body. Spinal cord injuries refer to any damage to the spinal cord caused by trauma or disease [2]. Spinal cord injuries can result in problems with sensation and body movements.
For example, the brain sends messages through the spinal cord to muscles and tissues to help with voluntary and involuntary movements. This includes physical activity like running and exercising, or something as simple as bowel and bladder elimination.
Spinal Cord Injury Causes
Spinal cord injuries occur when the spinal cord or its vertebrae, ligaments, or disks are damaged [3]. While trauma is the most common cause of spinal cord injuries in the U.S., medical conditions are the primary causes in low-income countries [4] [2].
Trauma
- Vehicle accidents: Accounts for 40% of all cases [2]
- Falls: Accounts for 32% of all cases [2]
- Violence: Includes gun violence and assaults; accounts for 13% of all cases [2] [5]
- Sport-related accidents: Accounts for 8% of all cases [2]
Medical Conditions
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Damage to the myelin (or insulating cover) of the nerve fibers [1]
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): Lou Gehrig’s disease, damage to the nerve cells that control voluntary muscle movements [1]
- Post-Polio: Damage to the central nervous system caused by a virus [1]
- Spina Bifida: Congenital defect of the neural tube (structure in utero that eventually forms the central nervous system) [1]
- Transverse Myelitis (TM): Inflammation of the spinal cord caused by viruses and bacteria [1]
- Syringomyelia: Cysts within the spinal cord often caused by a congenital brain abnormality [1]
- Brown-Sequard Syndrome (BSS): Lesions in the spinal cord that causes weakness or paralysis on one side of the body and loss of sensation on the other [1]
- Cauda Equina Syndrome: Compression of the nerves in the lower spinal region [1]
Spinal Cord Injury Statistics
According to the World Health Organization, between 250,000 and 500,000 people worldwide are living with spinal cord injuries [4]. In the U.S., this number is estimated to be between 255,000 and 383,000 with 18,000 new cases each year for those with trauma-related spinal cord injuries [6].
Age/Gender
Globally, young adult males (age 20 to 29) and males over the age of 70 are most at risk. In the U.S., males are also at highest risk, and of this group, 43 is the average age [2].
While it is less common for females to acquire a spinal cord injury (2:1 ratio in comparison to males), when they do occur, adolescent females (15-19) and older females (age 60 and over) are most at risk globally [4].
Race/Ethnicity
In the U.S. since 2015, around 56% of spinal cord injuries related to trauma occurred among non-Hispanic whites, 25% among non-Hispanic Black people, and about 14% among Hispanics [6].
Mortality
People with spinal cord injuries are 2 to 5 times more likely to die prematurely than those without these injuries (WHO, 2013). People with spinal cord injuries are also more likely to die within the first year of the injury than in subsequent years. In the U.S., pneumonia, and septicemia – a blood infection – are the top causes of death in patients with spinal cord injuries [6].
Financial Impact
Spinal cord injuries cost the U.S. healthcare system billions each year [6]. Depending on the type, spinal cord injuries can cost from around $430,000 to $1,300,000 in the first year and between $52,000 and $228,000 each subsequent year [6].
These numbers do not account for the extra costs associated with loss of wages and productivity which can reach approximately $89,000 each year [6].

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What is one function of the spinal cord?
- What is one way to prevent spinal cord injuries in any group?
- Why do you think injuries caused by medical conditions are least likely to occur in the U.S.?
- Why do you think the first year of care after the injury is the most costly?
Think about someone you know (or cared for) who had a spinal cord injury.
- Did they have total or partial loss of feeling and movement to the extremities?
- What comorbidities or complications did they have associated with the injury?
- In what ways did the injury affect their overall quality of life?
Spinal Cord Injuries: Types and Complications
Four Levels of the Spinal Cord
- Cervical (vertebrae C1 – C8): Neck; controls the back of the head down to the arms, hands, and diaphragm
- Thoracic (vertebrae T1 – T12): Upper mid-back; controls the chest muscles, many organs, some back muscles, and parts of the abdomen
- Lumbar (vertebrae L1 – L5): Lower back; controls parts of the lower abdomen, lower back, parts of the leg, buttocks, and some of the external genital organs
- Sacral (vertebrae S1 – S5): Lower back; controls the thighs down to the feet, anus, and most of the external genital organs
Types of Spinal Cord Injuries
Spinal cord injuries may be classified by level and degree of impairment. There are four types of spinal cord injuries [5].
Injury Level
- Tetraplegia or Quadriplegia: Injury at the cervical level; loss of feeling or movement to the head, neck, and down. People with this type of spinal cord injury have the most impairment.
- Paraplegia: Injury at the thoracic level or below; limited or complete loss of feeling or movement to the lower part of the body.
Impairment
- Incomplete spinal cord injury: Some sensation and mobility below the level of injury as the spinal cord can still transmit some messages from the brain.
- Complete spinal cord injury: Total loss of all sensation and mobility below the level of injury. Spinal cord injuries of this type have the greatest functional loss.

Spinal Cord Injury Complications
Complications from spinal cord injuries can be physical, mental, or social, and can impact overall quality of life. There are six common complications of spinal cord injuries [2].
Depression
Studies show that 32.9% of adults with disabilities experience frequent mental distress [7]. Mental distress may be related to functional limitations, chronic disease, and the increased need for healthcare services. Up to 37% of people with spinal cord injuries develop depression [2].
Pressure injuries
People with spinal cord injuries may have problems with circulation and skin sensation– both risk factors for pressure injuries. Some may be bedridden or wheelchair-bound which also places them at risk for pressure injuries. Up to 80% of people with spinal cord injuries will have a pressure injury during their lifetime and 30% will have more than one [2].
Spasticity
Around 65% - 78% of people with spinal cord injuries have spasticity [2]. Spasticity is uncontrolled muscle tightening or contraction. The damage from spinal cord injuries causes misfires in the nervous system leading to twitching, jerking, or stiffening of muscles.
Autonomic dysreflexia
In some people with spinal cord injuries, a full bladder or bowel distention can cause a potentially dangerous condition called autonomic dysreflexia. The full bladder or bowel triggers a sudden exaggerated reflex that causes an increase in blood pressure. This condition is also associated with a severe headache, low heart rate, cold skin, and sweating in the lower body [8].
Respiratory problems
If the diaphragm function is affected, as with cervical spinal cord injuries, there may be breathing difficulties. People with lumbar spinal cord injuries can even have respiratory problems as the abdominal muscles are used to breathe.
Sexual problems
Due to changes in muscle function and depending on the degree of damage, people with spinal cord injuries may have problems with arousal and climax due to altered sensations and changes in sexual reflexes.
Changes in bowel and bladder function
Many people with spinal cord injuries lose bowel control. Bowel problems can include constipation, impaction, and incontinence. They may also have problems with urination, for example, urinary retention.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Why might a person with a disability experience mental distress?
- In what type of spinal cord injury does a person lose all sensation and mobility below the waist?
- Why are people with spinal cord injuries at risk for pressure injuries?
- How can spinal cord injuries affect a person’s personal relationships?
Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction in Spinal Cord Injuries
This section will cover the normal function of the bowel and bladder, and the types of bowel and bladder dysfunction that occurs in patients with spinal cord injuries.


Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
Think about a time you assisted with bowel or bladder management in someone with a spinal cord injury.
- What types of activities were included in their bowel or bladder regimen?
- What challenges did you encounter during bowel or bladder care?
- What difficulties did they express to you about managing their bowel or bladder program?
- In what ways did you assist them in managing their own bowel or bladder program?
Normal Bowel and Bladder Function
In normal bowel and bladder function, when the rectum or bladder fills with stool/urine and presses on area nerves (stimulation), the message is sent to the spinal cord which sends it to the brain. The brain gives the person the “urge” feeling, allowing an option to control the elimination or not.
Whatever decision the person makes, the brain sends the message back to the spinal cord, which in turn sends a message to the elimination muscles (anal and bladder sphincters) to either relax or stay closed until the person is ready. In people with spinal cord injuries, the messages are limited or blocked, leading to problems with bowel and bladder control [9] [10].
Bowel Dysfunction with Spinal Cord Injuries
Reflex hypertonic neurogenic bowel occurs when a rectum full of stool presses against area nerves sending a message to the spinal cord, but it stops there. The message never makes it to the brain, so the person never gets the urge.
As a result, a reflex is set off, prompting the spinal cord to send a message to the anal muscle (sphincter) instead, causing it to relax and release the stool. This condition leads to bowel incontinence and usually occurs in spinal injuries at the cervical and thoracic levels [9] [10].
Flaccid hypotonic bowel occurs when area nerves are also stimulated by a full rectum, but the message does not even reach the spinal cord, so there is no reflex. The anal sphincter is always in a relaxed state.
As a result, the bowels simply empty when they are full, and this can occur at any time without the person having the ability to control it. This condition results in bowel incontinence and can lead to constipation as the patient does not have the urge and may not have the ability to push. This condition usually occurs in spinal injuries at the lumbar level [9] [10].
Bladder Dysfunction with Spinal Cord Injuries
Reflex neurogenic bladder occurs when the bladder automatically starts to contract after filling with a certain amount of urine. The person has no urge to go as the messages are either limited or blocked from reaching the brain, therefore leading to loss of bladder control. Similar to reflex hypertonic neurogenic bowel, the full bladder triggers are nerves that set off a reflex, prompting the spinal cord to send messages to the bladder releasing urine outside of the person’s control [9] [10].
Acontractile bladder occurs when the bladder loses muscle tone after a spinal cord injury, lessening its ability to contract, leading to bladder distention, and dribbling of urine. People with this condition need to use urinary catheters to help empty the bladder [9].


Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What is one role of the brain in bowel and bladder function?
- Which type of bowel dysfunction occurs in thoracic-level spinal cord injuries?
- In which type of bowel dysfunction might a suppository be most effective?
- In which type of bladder dysfunction does the bladder lose muscle tone?
The Nurse’s Role in Bowel and Bladder Management
This section will cover how nurses can assess, intervene, and teach when caring for patients with spinal cord injuries who have bowel and bladder dysfunction.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
Think about your experiences with patients with spinal cord injuries and their family or caregivers.
-
- How knowledgeable was the patient about their bowel or bladder care?
- In what ways were the family or caregiver involved in the plan of care?
- Did the family or caregiver have any learning gaps that needed to be addressed?
- What difficulties did the family or caregiver express to you about their role?
Nurse Assessments
When caring for patients with spinal cord injuries, nurses should obtain a detailed bowel and bladder history including diet, fluid intake, medications, and elimination patterns/habits [11]. Many of these patients may already manage their own bowel and bladder care at home.
If so, the nurse should obtain the patient’s current regimen and communicate the information to the physician. The physician may choose to continue the regimen or adjust as needed based on the patient’s current illness/condition.
Questions the nurse can ask the patient:
- What does your typical diet consist of?
- How much fluid do you drink on a daily basis?
- How often do you have a bowel movement or urinate?
- Do you schedule your bowel movements with assistance from medications?
- Are there certain body positions or things you do to help you pass stool more easily?
- How often do you use an intermittent urinary catheter for bladder relief?
- How much time do you spend on your bowel and bladder regimens?
- Do you care for all of your elimination needs or does someone help you?
- How does your bowel and bladder dysfunction affect your quality of life?
Some assessments may be observed. For example, nurses may notice that the patient has a surgically placed permanent suprapubic urinary catheter or colostomy (when the bowel is cut somewhere above the level of the rectum and diverted to the outside of the abdomen).
Nurse Interventions
Since many patients with spinal cord injuries have problems with bowel and bladder function, elimination must be scheduled. Nurses can help by implementing bowel and bladder programs and providing education and support to patients, families, or caregivers.
Regimens
Follow the patient’s home bowel and bladder regimen (as ordered). This may include maintaining intermittent catheterization every few hours or administering suppositories daily.
For patients who do not have a regimen already or wish to modify their current one, encourage them to pay attention to how often they urinate and pass stools, elimination problems, foods that alleviate or worsen the problem, and medications or other things that help. This can be done through a diary.
Dietary Considerations
Educate patients on the importance of a fiber-rich diet to avoid constipation. Patients should also be made aware that high-fat foods, spicy foods, and caffeine can alter gut dynamics and lead to bowel incontinence episodes [12].
Fluid Intake
Some patients may avoid drinking enough water to avoid bladder complications (e.g., frequent incontinent episodes) [12]. However, nurses should educate patients on the importance of adequate fluid intake to prevent constipation. Patients should be made aware that bladder and bowel elimination regimens go hand in hand.
Bladder Elimination
For bladder dysfunction, help patients perform intermittent urinary catheterization as needed or place a temporary urinary catheter (as ordered).
Bowel Elimination
For bowel dysfunction, administer ordered suppositories and laxatives to help the bowels move (use suppositories in conjunction with the level of sensation the patient has near the anus/rectum) [9]. Changes in body position may help as well.
While many of these interventions may not work in some patients with spinal cord injuries, bowel irrigation (water enemas) may be helpful [11]. Surgical placement of a colostomy may be indicated if all other measures have failed [11].
Emotional Support
Ensure privacy and sensitivity during all elimination care as patients may experience embarrassment or frustration.
Education for Families or Caregivers
Provide education to families or caregivers on the importance of helping patients stay consistent with their elimination regimen, follow diet and fluid intake recommendations, and comply with medication orders.
Referrals
Inform the physician if interventions are not effective or if the patient, family, or caregiver has a special need (e.g., counselor or dietician). Refer patients and families or caregivers to support groups as needed.
Support Groups and Resources
Christopher and Dana Reeve Foundation
Christopher Reeve – an actor who was left paralyzed after an equestrian accident – and his wife Dana’s legacy lives on through their foundation, an organization that advocates for people living with paralysis [13].
Miami Project to Cure Paralysis
In response to his son, who acquired a spinal cord injury during college football, NFL Hall of Famer Nick Buoniconti and world-renowned neurosurgeon Barth A. Green, M.D. started a research program aimed at finding a cure for paralysis and discovering new treatments for many other neurological injuries and disorders [14].
National Institute on Disability, Independent Living, and Rehabilitation Research (NIDILRR)
The National Institute on Disability, Independent Living, and Rehabilitation Research, a part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ Administration for Community Living, helps people with disabilities integrate into society, employment, and independent living [15].
Paralyzed Veterans of America (PVA)
A group of World War II veterans who returned home with spinal cord injuries, started this organization to support those with spinal cord injuries and dysfunction. Today, the organization focuses on quality health care, research and education, benefits, and civil rights to affected veterans [16].
The United Spinal Association supports people with spinal cord injuries and those in wheelchairs. The organization advocates for disability rights like access to healthcare, mobility equipment, public transportation, and community support. Support groups can be found on their website [17).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What is one question a nurse can ask a patient to obtain a bowel and bladder history?
- How can nurses help patients with spinal cord injuries start or modify a bowel or bladder regimen?
- When might a colostomy be indicated for a patient with a spinal cord injury?
- What type of referral might be ordered for a patient with a spinal cord injury who has bowel or bladder dysfunction?
Conclusion
Spinal cord injuries can have devastating effects on patients and their families. Management of basic bodily functions like bowel and bladder elimination should be made as easy as possible for these patients.
When nurses learn how to effectively help patients with spinal cord injuries better manage their own bowel and bladder regimens, quality of life and health outcomes may be improved for this group.
Pressure Injury Prevention, Staging and Treatment
Introduction
When hearing the term HAPI, what comes to mind? The fact is, HAPI may not necessarily generate happy thoughts. Hospital-acquired pressure injuries (HAPIs) are a significant problem in the U.S. today. In fact, pressure injuries in general – whether acquired in a hospital or not – are a global problem.
Many articles have noted that staging and differentiating pressure injuries can be overwhelming for nurses [9]. The purpose of this course is to equip learners with the knowledge needed to reduce pressure injuries, resulting complications, financial risk, and associated death. The information in this course will serve as a valuable resource to nurses from all specialties and backgrounds.
What is a pressure injury?
The National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel (NPIAH) defines pressure injuries as “localized damage to the skin and underlying soft tissue usually over a bony prominence or related to a medical or other device” [17]. Pressure injuries can present as intact or opened skin and can be shallow or deep. Pressure injuries can be quite painful for patients and may require extensive treatment.
Prior to 2016, pressure injuries were termed “pressure ulcers.” However, since ulcer implies “open skin,” the NPIAH changed it to “pressure injury” as the skin is not always open with some of these injuries [22][25].
What causes a pressure injury to develop?
Pressure
Intense and/or prolonged pressure on the patient’s skin and/or tissue can cause compromised blood flow and decreased sensation [7]. This can occur when patients lay or sit on a bony prominence for an extended period of time [16].
Bony prominences are areas where you can easily feel a bone underneath the skin or tissue when palpating. These can include the heels, hips, elbows, and tailbone. Approximately two-thirds of all pressure injuries occur on the hip and buttocks area [7].
Friction and Shear
Friction and shear often happen when patients slide down in bed, for example, when the head of the bed is raised. Although “friction and shear” are often used together, there is actually a difference between the two.
While friction occurs when skin is dragged across a coarse surface (leading to surface-level injuries), shearing occurs when internal bodily structures and skin tissue move in opposite directions (leading to deep-level injuries) [10]. Shearing is often associated with a type of pressure injury called deep tissue injury (occurring in the deeper tissue layers rather than on the skin’s surface) [10].

[24]
What are risk factors for developing a pressure injury?
There are numerous risk factors for pressure injuries – some of which may not be directly related to the skin. These risk factors can be categorized as either intrinsic factors (occurring from within the body) or extrinsic (occurring from outside of the body) [2][13].
Intrinsic Risk Factors
- Poor skin perfusion (e.g., peripheral vascular disease or smoking)
- Sensation deficits (e.g., diabetic neuropathy or spinal cord injuries)
- Moist skin (e.g., urinary incontinence or excessive sweating)
- Inadequate nutrition (particularly poor protein intake)
- Poor skin elasticity (e.g., normal age-related skin changes)
- End of life/palliative (leads to organ failure including the skin)
- Limited mobility (i.e., bedridden, or wheelchair-bound)
Extrinsic Risk Factors
- Physical and chemical restraints (leads to limited mobility)
- Undergoing a procedure (laying down for extended periods of time)
- Length of hospital stay (for HAPIs)
- Medical devices (can lead to medical device-related pressure injuries)

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are the most common areas for pressure injuries to develop?
- What is the major difference between friction and shear?
- What is one reason why elderly adults are at an increased risk for developing a pressure injury?
Statistical Evidence
This section will cover pressure injury statistics both globally and nationally. This section will also cover the impact pressure injuries have on healthcare.
What is happening on a global scale?
In a global study, researchers found that the prevalence (all cases) and incidence (new cases) of pressure injuries in 2019 were 0.85 million and 3.17 million, respectively – numbers that have decreased over time [23][25]. Numbers were disproportionately high in high-income North America, Central Latin America, and Tropic Latin America [25]. Numbers were lowest in Central Asia and Southeast Asia. The report revealed that although numbers are high overall, they are much lower than what they were predicted to be, which may be attributed to better prevention and treatment initiatives.
What is happening nationally?
In the U.S., 2.5 million people develop pressure injuries each year [1]. This number does not account for the many people trying to manage pressure injuries on their own at home (i.e., when family acts as the caregiver).
HAPIs in particular are a growing problem. The most recent data on hospital-acquired conditions in the U.S. shows that from 2014 to 2017, HAPIs increased by 6% (647,000 cases in 2014 to 683,000 in 2017) [6]. Each year 60,000 patients in the U.S. die as a direct result of pressure injuries [1].
How do pressure injuries impact healthcare?
Pressure injuries can be quite costly to the healthcare system. These injuries can lead to persistent pain, prolonged infections, long-term disability, increased healthcare costs, and increased mortality [1].
In the U.S., pressure injuries cost between $9.1 - $11.6 billion per year [1]. These injuries are complex and can be difficult to treat [7]. Often requiring an interdisciplinary approach to care, the costs of one pressure injury admission can be substantial. Individual care for patients with pressure injuries ranges from $20,900 to $151,700 per injury [1]. Not to mention, more than 17,000 lawsuits are related to pressure injuries every year [1].
Due to the significant impact that these injuries have on healthcare, prevention and accurate diagnosis is imperative.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are possible contributing factors to the increase in HAPIs in the U.S.?
- What are some factors that may contribute to the high costs of pressure injuries in healthcare settings?
Staging and Diagnosis
The section will cover the staging, varying types, and diagnosis of pressure injuries.
What is the difference between wound assessment and staging?
Pressure injury staging is more than a basic wound assessment. Wound assessment includes visualizing the wound, measuring the size of the wound, paying attention to odors coming from the wound, and lightly palpating the area on and/or around the wound for abnormalities. Pressure injury staging, however, involves determining the specific cause of injury, depth of skin or tissue damage, and progression of the disease.
What are the six stages of pressure injuries?
According to NPIAP guidelines, there are six types of pressure injuries – four of which are stageable [14].

[16]
Stage 1
In Stage 1 pressure injuries, there is intact skin with a localized area of non-blanchable erythema (pink or red in color), which may appear differently in darkly pigmented skin. Before visual changes are noted, there may be the presence of blanchable erythema or changes in sensation, temperature, or firmness. Stage 1 pressure injuries do not have a purple or maroon discoloration (this can indicate a deep tissue pressure injury).
Stage 2
In Stage 2 pressure injuries, there is partial-thickness loss of skin with exposed dermis. The wound bed is viable, pink or red, moist, and may represent an intact or opened serum-filled blister. Fat (adipose) and deeper tissues are not visible. Granulation tissue, slough (soft moist material, typically yellow or white), and eschar (hard necrotic tissue, typically black in color) are not present. Stage 2 injuries cannot be used to describe wounds associated with moisture-only, skin chaffing, medical adhesives, or trauma.
Stage 3
In Stage 3 pressure injuries, there is full-thickness loss of skin, in which fat is visible in the injury, and granulation tissue and rolled wound edges are often present. Slough and/or eschar may be noted. The depth of tissue damage is dependent on the area of the wound. Areas with a significant amount of fat can develop deep wounds.
Undermining (burrowing in one or more directions, may be wide) and tunneling (burrowing in one direction) may be present. Fascia, muscle, tendon, ligament, cartilage, and/or bone are not exposed. If slough or eschar covers the extent of tissue loss, this would be considered an unstageable pressure injury, not a Stage 3.
Stage 4
In Stage 4 pressure injuries, there is full-thickness skin and tissue loss with exposed or directly palpable fascia, muscle, tendon, ligament, cartilage, or bone in the wound. Slough and/or eschar may be visible. Rolled wound edges, undermining, and/or tunneling are often present. The area where the wound is present will determine the depth. As with stage 3 pressure injuries, if slough or eschar covers the extent of tissue loss, this would be considered an unstageable pressure injury.
Unstageable
In unstageable pressure injuries, there is full-thickness skin and tissue loss in which the extent of tissue damage within the wound cannot be confirmed because it is covered by slough or eschar. If the slough or eschar is removed, a Stage 3 or Stage 4 pressure injury will be revealed. Stable eschar (i.e., dry, adherent, intact without erythema or fluctuance) on an ischemic limb or the heel(s) should not be removed.
Deep Tissue Injury
In deep tissue pressure injuries (also termed: deep tissue injuries or DTIs), there is intact or non-intact skin with localized area or persistent non-blanchable deep red, maroon, purple discoloration, or epidermal separation revealing a dark wound bed or blood-filled blister.
Pain and temperature changes often precede skin color changes. Discoloration may appear differently in darker-pigmented skin. The injury may resolve without tissue loss or may worsen quickly and open up, revealing the actual extent of tissue injury. Deep tissue pressure injuries should not be used to describe vascular, traumatic, neuropathic, or dermatologic conditions.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How do basic wound assessments differ from pressure injury staging?
- What is the main difference between a Stage 1 pressure injury and deep tissue injury?
- What is one structure you might see in a Stage 4 pressure injury wound bed that you would not see in any other pressure injury?
What are other types of pressure injuries?
Mucosal Membrane Pressure Injury
Mucosal membrane pressure injuries are found on mucous membranes with a history of a medical device in use at the location of the injury. For example, a wound on the inside of a nostril from a nasogastric tube would be considered a mucosal membrane pressure injury. Due to the anatomy of the tissue, mucosal membrane pressure injuries cannot be staged [18].
Medical Device-Related Pressure Injury
Medical device-related pressure injuries, often associated with healthcare facilities, resulting from the use of devices designed and applied for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes [15]. The resulting pressure injury typically conforms to the pattern or shape of the device which makes identification easier. The injury should be staged using the staging system.
Hospital Acquired Pressure Injury (HAPI)
While the general hospital setting places patients at a 5% to 15% increased risk of developing a pressure injury (HAPI), patients in the intensive (or critical) care unit in particular have an even higher risk [17]. Critical care patients typically have serious illnesses and conditions that may cause temporary or permanent functional decline. There is also evidence that pressure injuries in this setting can actually be unavoidable.
The NPIAP defines “unavoidable” pressure injuries as those that still develop after several measures by the health provider have been taken. These measures include when the provider has (a) evaluated the patient’s condition and pressure injury risk factors, (b) defined and implemented interventions consistent with standards of practice and the patient’s needs and goals, and (c) monitored and evaluated the impact of interventions [20]. There are certain situations in which a critical care patient may have a higher risk of developing unavoidable pressure injuries.
In one study of 154 critical care patients, researchers found that 41% of HAPIs were unavoidable and those who had a pressure injury in the past were five times more likely to develop an unavoidable pressure injury during their stay [20]. The study also found that the chance of developing an unavoidable HAPI increased the longer patients stayed in the hospital – a 4% risk increase each day.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What type of pressure injury can be caused by nasogastric tube use?
- What is it about critical care patients that places them at a high risk for HAPIs?
- In what situation is a pressure injury considered unavoidable?
How are pressure injuries diagnosed?
Diagnosing a pressure injury is done by simply staging the injury. The health provider may stage the injury or rely on the nurse’s staging assessment before giving the final diagnosis and initiating treatment. There are tests that may be ordered to help identify the early stages of a developing injury.
For example, subepidermal moisture assessment (SEM) scanners may help to identify tissue changes early on in patients with darker skin tones [8]. Tests may also be ordered to determine the extent of the damage, disease, or infection caused by a pressure injury. A magnetic resonance imaging test (MRI) can be used to determine if the infection in a stage 4 pressure injury has spread to the bone.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are some problems that can occur if a pressure injury is not staged correctly?
- What is one reason a provider would order an MRI of a pressure injury?
Prevention and Treatment
This section will cover various strategies that can be used to prevent and treat pressure injuries.
What are some ways to prevent pressure injuries?
Preventing pressure injuries takes more than just one nurse repositioning a patient every two hours. It involves a combination of strategies, protocols, and guidelines that facilities can implement across various departments, specialties, and care team members. The NIAPH recommends the following prevention strategies [19].
Risk assessment
Facilities should use a standardized risk assessment tool to help identify patients at risk for pressure injuries (i.e., the Braden or Norton Scale). Rather than using the tool as the only risk assessment strategy, risk factors should be identified by other means (for example, by gathering a detailed patient history).
Risk assessments should be performed on a regular basis and updated as needed based on changes in the patient’s condition. Care plans should include risk assessment findings to address needs.
Skin Care
Monitoring and protecting the patient’s skin is vital for pressure injury prevention. Stage 1 pressure injuries should be identified early to prevent the progress of disease. These include looking at pressure points, temperature, and the skin beneath medical devices.
The frequency of assessments may change depending on the department. Ideally, assessments should be performed upon admission and at least once daily. Skin should also be cleaned promptly after incontinence episodes.
Nutritional Care
Tools should be used that help to identify patients at risk for malnutrition. Patients at risk should be referred to a registered dietician or nutritionist. Patients at risk should be weighed daily and monitored for any barriers to adequate nutritional intake. These may include swallowing difficulties, clogged feeding tubes, or delays in intravenous nutrition infusions.
Positioning and mobilization
Immobility can be related to age, general poor health, sedation, and more. Using offloading pressure activities and keeping patients mobile overall can prevent pressure injuries. Patients at risk should be assisted in turning and repositioning on a schedule. Pressure-relieving devices may be used as well. Patients should not be positioned on an area of previous pressure injury.
Monitoring, training, and leadership
Current and new cases of pressure injuries should be documented appropriately and reported. All care team members should be educated on pressure injury prevention and the importance of up-to-date care plans and documentation.
All care team members should be provided with appropriate resources to carry out all strategies outlined. Leadership should be available to all care team members for support (this may include a specialized wound care nurse or wound care provider).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What is one reason why a patient at risk for pressure injuries would be weighed daily?
- What are two ways to prevent pressure injuries in a patient with limited mobility?
How are pressure injuries treated?
There is no one way to treat a pressure injury. Management of pressure injuries involves a specialized team of care providers and a combination of therapies that aim to target underlying factors and prevent complications [7]. Depending on the stage of the wound and skin risk factors, providers may order specific types of treatments.
Some pressure injury treatments may include the following [7].
- Wound debridement – a procedure in which necrotic tissue is removed from a wound bed to prevent the growth of pathogens in the wound, allowing for healing
- Antibiotic therapy (topical or systemic)
- Medicated ointments applied to the wound bed (e.g., hydrogels, hydrocolloids, or saline-moistened gauze to enable granulation tissue to grow and the wound to heal)
- Nutritional therapies (e.g., referrals to dieticians)
- Disease management (e.g., controlling blood sugar in diabetes)
- Pain medications
- Physical therapy (to keep the patient active)

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- In what way does debridement help to heal a pressure injury?
- What non-nursing care team member may be consulted for a patient with a pressure injury?
The Nurse’s Role
The section will cover the nurse’s role in preventing pressure injuries and the progression of disease.
What is the nurse’s role in pressure injury prevention?
Based on NPIAH guidelines, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) – an agency that monitors pressure injury data for the U.S. – breaks down quality initiatives for preventing pressure injuries in a three-component care bundle [2].
A care bundle is a combination of best practices that when used together, can lead to better patient outcomes [2]. The care bundle includes skin assessments, risk assessments, and care planning. Nurses should follow the guidelines listed under each component.
Standardized pressure injury risk assessment
- Use risk assessment tools and processes to identify patients at risk
- Do not rely on tools only, use your own judgment as well (tools are meant to guide the assessment)
- Update risk scores at least once daily and if patient’s condition changes
- Document findings in the medical record
- Communicate findings to other staff involved for continuity of care (e.g., informing another nurse during patient handoff reporting)
Comprehensive skin assessment
- Identify any pressure injuries that may be present
- Determine whether there are other areas of skin breakdown or factors that may predispose the patient to develop a pressure injury (e.g., moist skin)
- Identify other skin issues
- Perform assessments at regular intervals
- Document findings in the medical record
- Communicate findings to other staff involved in care so that appropriate changes can be reported (e.g., informing the nursing assistant)
- Ask colleague to confirm findings for accuracy (i.e., two-nurse skin checks)
Care planning and implementation to address areas of risk
- Create care plans that include each skin risk factor (e.g., nutrition, mobility, and moisture)
- Update care plans as often as needed if there are any changes in the patient’s condition
- Evaluate whether care plan was effective by assessing patient response to interventions
- Individualize care plans for each patient based on risk assessment scores and other observed risks
- Identify patient learning needs and implement teaching as needed
- Document care plan in the medical record
- Communicate care plan to other staff involved for continuity of care (e.g., informing another nurse during patient handoff reporting)

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Why should nurses avoid relying solely on standardized assessment tools?
- Why is documentation important when performing a skin assessment?
- What pressure injury information should nurses communicate during handoff report?
How can nurses prevent medical device-related pressure injuries?
The NPIAP outlined best practices to prevent medical device-related pressure injuries in various settings including general care, long-term care, critical care, and pediatric care [20]. The following strategies apply across all settings.
- Choose the correct size of medical device for the individual.
- Cushion and protect the skin with dressings in high-risk areas (e.g., nasal bridge).
- Inspect the skin under and around the device at least daily (if not medically contraindicated).
- Rotate sites of oximetry probes.
- Rotate between O2 mask and prongs (if feasible).
- Reposition devices (if feasible).
- Avoid placement of device over sites of prior or existing pressure injury OR directly under the patient.
- Be aware of edema under the device and the potential for skin breakdown.
- Change rigid C-collar to softer collar when medically cleared (for critical care settings).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How can nurses prevent a pressure injury from developing on the ear of a patient who wears a nasal cannula?
How can nurses identify pressure injuries in patients with darker skin tones?
Research suggests that it may be difficult to note early changes that can lead to the development of a pressure injury in patients with darker skin tones – for one, blanching may not be as visible [8]. This places the patient at a greater risk for the advancement of disease as early identification may be challenging.
In order to appropriately identify pressure injuries in patients with darker skin tones, nurses should use unique strategies. The NIPAH offers these recommendations for nurses to help accurately identify pressure injuries in this group [8].
Identification tips
- Clean the suspected area beforehand
- Compare the area to surrounding unaffected areas
- Compare the area to the opposite laterality if possible (i.e., right versus left elbow)
- Compare the area to unaffected areas in a different location (i.e., upper back versus chest)
- Look for differences in skin tautness
- Look for shining skin changes
- Palpate for changes in skin temperature

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What is one way to identify pressure injuries in patients with darker skin tones?
How can nurses quickly differentiate between pressure injury stages?
Correct staging of pressure injuries is vital as treatment is determined by the extent of damage, disease, or infection. First and foremost, wounds should be gently cleaned prior to staging as drainage or debris can be mistaken for fat or bone within the wound bed [14].
Nurses can quickly differentiate between stages by asking these simple easy-to-understand starter questions. A more detailed assessment should follow.
- Stage 1 versus Stage 2: Is the skin intact?
Rationale: The skin is always intact in Stage 1. The skin is always open in Stage 2 (or there may be an intact blister present).
- Stage 2 versus Stage 3: Is the wound bed pink or beefy red?
Rationale: The wound bed is pink or beefy red in Stage 2. In Stage 3, the wound bed has structures within that may be discolored.
- Stage 3 versus Stage 4: Does the wound bed contain soft or firm structures?
Rationale: The wound bed contains softer structures in Stage 3. The wound bed contains firmer structures in Stage 4.*
- Unstageable versus Stageable: Is any part of the wound bed hidden?
Rationale: The wound bed is not entirely exposed in an unstageable. The wound bed is exposed in a stageable that is open.
- Intact DTI versus Stage 1: Is the discoloration light or dark?
Rationale: The discoloration is dark in a DTI. The discoloration is much lighter in Stage 1.
- Open DTI versus Stage 2: Is the discoloration in or around the wound bed dark?
Rationale: There is dark discoloration in or around the wound bed in an open DTI. In stage 2, the discoloration is much lighter (if even present).
*Nurses should familiarize themselves with the appearance of the various structures that may be present in a wound like fat, fascia, bone, tendon, ligament, etc. Most importantly, nurses should consult the wound care team or health provider if a stage cannot be determined.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Why should nurses clean a wound prior to staging?
- What should nurses do if unsure how to stage a pressure injury?
What should patients know?
Facilities can use the NIAPH prevention strategies to devise teaching plans for patients [19]. Nurses should educate patients and families/caregivers on risk factors, signs and symptoms, prevention tips, and the importance of following through with treatment.
Nurses should also teach patients to advocate for their own health in order to avoid progression of disease. Here are important tips to teach at any point during the patient’s stay. These tips can apply to nurses working in a variety of settings.
- Tell the nurse or provider of your medical conditions (needed to identify risk factors)
- Tell the nurse or provider if you notice any numbness or tingling in your body (potential risk for sensory deficits)
- Tell the nurse or provider if you have a loss of appetite or trouble eating (potential risk for malnutrition)
- Clean yourself well after using the restroom (maintains skin integrity)
- Tell the nurse or provider if you need to use the restroom or need help with cleaning yourself (maintains skin integrity)
- Tell the nurse right away if you have an incontinence episode (maintains skin integrity)
- Take all prescribed medications (may include necessary antibiotics or wound-healing medications)
- Reposition yourself in bed often or tell the nurse if you need help doing so (reduces immobility risk)
- Tell the nurse or provider if you notice a new discolored area on your skin, or an open area (potential new or worsening pressure injury)
- Tell the nurse or provider if you notice any changes to your wound (potential worsening pressure injury)

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What is one pressure injury prevention tip nurses can teach hospitalized patients?
- What signs or symptoms should nurses teach the patient to report?
Quality Improvement
This section will cover the quality improvement measures in place to reduce pressure injuries.
What is a pressure injury quality improvement initiative?
Quality improvement involves setting goals (or initiatives) and standards of care. The goal of quality improvement is to improve patient outcomes at a systematic level where everyone involved is on the same page.
Although possibly unaware, all care team members are involved in quality improvement. Nursing leaders design, manage, and evaluate program initiatives. Staff nurses and other care team members follow protocols that are often developed from these initiatives.
The Pressure Injury Prevention Program is a guide designed by the AHRQ to help health facilities implement a structured pressure injury prevention initiative based on quality improvement [12]. Facilities can use the guide as a training toolkit to implement a new quality improvement program [5].
Initiative Goals:
- Reduced pressure injury rates
- Reduced adverse events related to pressure injuries
- Reduced costs associated with pressure injuries
- Reduced lawsuits related to pressure injuries
Ways facilities can implement a prevention program:
- Address the overall objectives of the prevention program
- Identify the needs for change and how to redesign practice
- Develop goals and plans for change
- Use the NIAPH pressure injury prevention recommended practices
- Establish comprehensive skin assessment protocols
- Standardize assessments of pressure injury risk factors
- Incorporate risk factors into individualized care planning
- Establish clear staff and leadership roles

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What is one reason why a health facility would start or update a pressure injury prevention program?
- When pressure injury rates are reduced, what else can health facilities expect to improve as well?
What are some pressure injury quality measures?
Quality measures are tools that measure a system’s healthcare goals and/or ability to provide high-quality care [11]. In simple terms, quality measures are specific ways that systems (governments, states, organizations, etc.) can show how they are making progress in meeting goals. The AHRQ highlights the following three ways the U.S. measures its progress.
Number of HAPIs
The AHRQ measures the number of HAPIs per year. The most recent data is from 2014 to 2017 [6].
| Year | Number of HAPIs |
| 2014 | 647,000 |
| 2015 | 700,000 |
| 2016 | 677,000 |
| 2017 | 683,000 |
Rate of HAPIs per admission
The AHRQ measures the number of HAPIs per admission related to age groups. The number is measured as a “rate,” meaning the number of HAPIs per 1,000 hospital admissions. The most recent evidence is from 2017 [4].
| Age group | Number of HAPIs per 1,000 admissions |
| 18 – 39 | 0.38 |
| 40 – 64 | 0.63 |
| 65 – 74 | 0.74 |
| 75 and over | 0.71 |
Costs of HAPIs
Another quality measure is HAPI costs. While the AHRQ does not measure costs of HAPIs every single year, the most recent data is from 2017 [3].
| Year | Cost of HAPIs per patient |
| 2017 | $8,573 – $21,075 |
Deaths related to HAPIs
Patient mortality rates related to HAPIs are a quality measure (calculated per 1,000 pressure injury cases). The most recent data is from 2017 [6].
| Year | Number of deaths per 1,000 pressure injury cases |
| 2017 | 2.42 – 5.06 |

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What is one way a health facility can show its progress in preventing pressure injuries?
- What patient age range do you think has the most pressure injury rates? Age 65 to 74 or age 75 and over?
Conclusion
Pressure injuries are complex conditions that can lead to poor patient outcomes and a burdened healthcare system. The best strategy in the care of patients with pressure injuries or those at risk is prevention.
However, preventing these injuries involves more than individual nurses taking specific steps. Prevention of pressure injuries involves a team effort from all members of the care team and a systemic plan for improvement.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (Wound Vac)
Introduction
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), also known as a wound vac, can be a powerful tool in combatting acute and chronic wounds. It relies on generating a negative pressure on the surface of a difficult wound to promote wound healing.
The goal of this course is to develop an understanding of mechanism of action of NPWT, discuss appropriate nursing assessment of these wounds, evaluate adjunct treatment options and troubleshooting support tips.
We will review basic concepts of the integumentary system and the normal wound healing process to support the rationale of NPWT.
Definition
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) is the application of sub-atmospheric pressure to help reduce inflammatory exudate and promote granulation tissue in an effort to enhance wound healing (4). The idea of applying negative pressure therapy is that once the pressure is lower around the wound, the gentle vacuum suction can lift fluid and debris away and give the wound a fighting chance to heal naturally.
NPWT has a long and interesting history. The idea of suctioning fluid from wounds as therapy is not a new concept. The process was first called “cupping” and was described in Ebers Papyrus around 500 BC; historians tell us that a form of wound suction was used around 1000 BC in China, 600 BC in Babylon and Assyria, and in 400 BC by Greeks who heated copper bowls over wounds to remove blood and fluids (5).
Modern medicine has built upon a very old concept. Thankfully, nurses have a slightly easier tool in NPWT devices than heating copper bowls.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Can you name the various methods of wound treatments that you have encountered?
- Do you recognize how negative pressure can create suction?
Indications for Use
Negative pressure wound therapy is widely used for the management of both acute and chronic wounds. This therapy is helpful for a broad range of wounds, from pressure ulcers to closed surgical incisions.
The system is now implemented routinely for open wounds, such as open fractures, fasciotomies, diabetic foot ulcers, and infected wounds. Delayed wound healing and difficult wounds are seen more commonly in elderly patients and those with comorbidities (1).
It’s important to review the basic anatomy of our integumentary system, types of wounds, and barriers to healing to understand the usefulness of NPWT.
Basic Anatomy of Integumentary System
Our integumentary system is considered the body’s largest organ. Our skin acts as a shield against heat, light, bacteria, infection, and injury. Other functions include body temperature regulation, storage of water and fat, sensory function, prevention of water loss, and a basic storage compartment for the organs (6).
The skin is made up of 3 layers. Each layer has unique functions:
- Epidermis
- Dermis
- Subcutaneous fat layer (hypodermis)
The epidermis is the thin outer layer of our skin, it contains squamous cells, basal cells, and melanocytes (gives skin its color). The dermis is the middle layer of skin, it contains blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, nerves, lymph vessels, fibroblasts, and sebaceous glands (6). It is important to remember that the dermis contains nerves and nerve receptors.
The subcutaneous fat layer is the deepest layer of skin and is made up of a network of collagen and fat cells; this layer conserves the body's heat and protects the body from injury by acting as a shock absorber (6).

This design was created on Canva.com on September 28, 2023. It is copyrighted by Abbie Schmitt, RN, MSN and may not be reproduced without permission from Nursing CE Central.
Types of Wounds
Negative pressure wound therapy is primarily used to treat complex wounds that are non-healing or at risk of non-healing. It is also indicated for acute wounds when the wound cannot be closed due to the risk of infection, active infection, skin tension, or swelling (7).
Closure or skin grafting of acute wounds, such as open fractures or burns, are at high risk for infection due to microorganisms becoming trapped in the soft tissue leading to abscess development.
Examples of possible wounds to apply NPWT (1):
- Diabetic foot ulcers
- Bed sores
- Skin graft fixation
- Burns
- Crush injuries
- Sternal/abdominal wound dehiscence
- Fasciotomy wounds
- Animal bites
- Frostbite
Barriers to Healing
Age
- Increased risk of tearing and shearing due to thinning of epidermis and decrease in elastin
- Phases of healing are prolonged
- Increased risk of dehiscence as the dermis has slower contractility
- Skin more susceptible to bacterial growth and infections as pH becomes more neutral with age
Co-morbidities
- Cardiopulmonary Disease
- Oxygen-transport pathways are affected
- O2 necessary for wound healing
- Diabetes Mellitus
- High glycemic levels predispose patients to infection
- Microvasculature and neuropathic components of DM increase the risk for impaired healing
- Poor glycemic control can increase the risk of ulceration and delayed healing
- Immune-suppressing conditions (Cancer, HIV, immunosuppressive therapy, immunosuppression syndrome)
- Inflammatory phase (immunology) is impaired
- Increased risk for infection
Impaired Perfusion and Oxygenation
- Peripheral Vascular Impairment
- Proper perfusion is required for growth of new tissue and immunological responses of the tissue.
- Arterial insufficiency (blood flow to extremities) leads to necrosis or lack of response to edema.
Neurological Impairment
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Complication related to DM, alcoholism, chemotherapy
- Loss of neuronal signaling and transmission
- Loss of the sensory ability to recognize and react to sensations of touch, pressure, temperature, pain. Example: patient leaving foot on hot surface because there was no pain sensation, leading to burn wound.
- Spinal cord injury

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Are you familiar with the layers and components that make up the integumentary system?
- Have you ever cared for a patient with a chronic wound?
- What are some ways the elderly population is at higher risk for prolonged wound healing?
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action is dependent on applying negative pressure, which is below atmospheric pressure, to the wound. This pressure allows the gentle vacuum suction to lift fluid and exudate away from the wound to enhance healing (3).
The vacuum is gentle because powerful suction would remove newly formed tissue as well. The mechanism of action is not only in removing fluid and debris from the tissue, but the pressure causes stimulation of the growth of granulation tissue at a macroscopic and microscopic level.
The porous foam shrinks in size with the application of negative pressure and exerts strain on the wound bed, which leads to macro- and micro-deformation of the wound (3). Microdeformation is simply a term used to describe microscopic tissue cell reactions. This reaction can be compared to a battery jump-start of a car; the stimulation causes the battery to engage.
NPWT systems consist of a sterile foam sponge, a semi-occlusive adhesive cover, a fluid collection system or canister, and a suction pump (1). The foam sponge is applied to the wound and covered. A fenestrated tube is embedded in the foam and the wound is sealed with adhesive tape to make it airtight, and the machine delivers continuous or intermittent suction, ranging from 50 to 125 mmHg (1).

This design was created on Canva.com on October 1, 2023. It is copyrighted by Abbie Schmitt, RN, MSN and may not be reproduced without permission from Nursing CE Central.
Proper application of the NPWT is important for the mechanism of action to be effective. Research supports that NPWT is effective at creating a stable wound environment, reduces inflammation and bacterial load, improves tissue perfusion, and stimulates granulation tissue and angiogenesis (1).
Imagine you want to plant a garden in a swampy location, you would first need to divert the water and algae from the land, cover it with a greenhouse with consistent heat and pressure, and cultivate the soil for optimal growth. Similarly, NPWT creates the most ideal conditions possible for tissue regeneration.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Can you name the components of NPWT?
- Have you ever applied a wound vac dressing?
- Are you familiar with the other semipermeable materials that serve as a filter?
Contraindications
NPWT would be contraindicated for the following:
- Wounds involving untreated osteomyelitis.
- Wounds that have exposed blood vessel
- Wounds with exposed nerves, anastomotic sites, or organs
- Wounds including open joint capsules
- Malignant wounds
- Wounds with necrotic tissue; it is recommended to excise first
The following wounds could benefit from NPWT, but caution should be given (5):
- Wounds with visible fistula
- Wounds with exposed bone or tendon
- The bone or tendon should be isolated from direct pressure
- Patient with clotting disorders or that are taking anticoagulants, due to an increased risk of bleeding.
- Compromised microvascular blood flow to the wound bed.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Can you think of reasons a malignant, cancerous wound should not have NPWT?
- Have you ever dressed a wound prior to or following debridement?
Assessment
A focused assessment should be done for patients with NPWT devices in place, both on the machine settings, the dressing, and the wound itself. Thorough documentation of the wound is essential to see the progression of wound healing.
Suction Device Settings:
- Continuous or intermittent
- Pressure Setting: Range of pressure settings from -40mmHg to -200mmHg, which can be tailored for different types of wounds (7). This is set by the medical provider.
Laboratory assessment is meaningful in wound care. Labs can be used to assess oxygenation or indicators of infection (6).
Dressing Assessment
The appearance of the NPWT and dressing should be clean, dry, intact, and sealed. The tubing should not be twisted or kinked, and the clear adhesive dressing should not be wrinkled or overlapping. Please see below an example of the appropriate appearance of a dressing.
Wound Assessment:
- Anatomic location
- Type of wound
- Degree of tissue damage
- Description of wound bed
- Wound size
- Wound edges and surrounding skin
- Signs of infection
- Pain
Anatomical Location
Anatomical terms and numbering should be used to make sure the location of each wound is documented. Patients often have more than one wound, so the treatment needs to be specified for each wound.
Wound Base
Assess the color of the wound base. Healthy granulation tissue appears pink and moist due to the new capillary formation. The appearance of slough (yellow) or eschar (black) in the wound base should be documented and communicated to the health care provider (1).
This tissue may need to be removed to optimize healing. If any discoloration or duskiness of the wound bed or wound edges are identified, the suction should initially be reduced or switched off (7).
Type and Amount of Exudate
Assess the color, thickness, and amount of exudate (drainage) The amount of drainage from wounds is categorized as scant, small/minimal, moderate, or large/copious.
Terms are used when describing exudate: sanguineous, serous, serosanguinous, and purulent (6).
- Sanguineous: fresh bleeding
- Serous: Clear, thin, watery plasma
- Serosanguinous: Serous drainage with small amounts of blood noted
- Purulent: Thick and opaque. The color can be tan, yellow, green, or brown. This is an abnormal finding and should be reported to a physician or wound care provider.
Wound Size
Wounds should be measured on admission, wound vac dressing changes, or as needed for abnormal events. Many healthcare facilities use disposable, clear plastic measurement tools to measure the area of a wound.
Consistent measurement is vital to the assessment of wound healing.
- Measure the greatest length, width, and depth of the wound in centimeters
- Examples of wound classification tools:
- NPUAP staging system for pressure injuries
- Payne-Martin classification system for skin tears
- CEAP (clinical, etiologic, anatomic, and pathophysiology) system for venous ulcers
Tunneling or Undermining
Tunneling is when a wound has moved underneath the skin, making a “tunnel.” The depth of tunneling can be measured by gently inserting a sterile, cotton-tipped applicator into the tunnel and noting the length from the wound base to the end of the tract (7). Undermining occurs when the tissue under the wound edges becomes eroded, resulting in a pocket beneath the skin at the wound’s edge.
Healing Process
It is important to recognize the entire process of normal wound healing. There are four phases of wound healing: hemostasis, inflammatory, proliferative, and maturation (6).
Hemostasis begins immediately after injury, involving platelet aggregation and activation of clotting factor (6). A platelet “plug” is formed as fibrinogen converts to fibrin and binds to itself. Vasoconstriction occurs at this time, decreasing blood loss and allowing clot formation.
The inflammatory phase begins right after the injury and the injured blood vessels leak and cause localized swelling. The swelling, warmth, pain, and redness present during this stage of wound healing are related to the release of white blood cells, growth factors, nutrients, and enzymes to help control bleeding and prevent infection (6).
The proliferative phase of wound healing involves “rebuilding” with new tissue made up of collagen and extracellular matrix; granulation tissue is built stronger with proper oxygen and nutrients.
Key nursing knowledge: Dark granulation tissue can indicate infection, ischemia, or poor perfusion. The maturation phase of wound healing is when collagen is remodeled, aligns along tension lines, water is reabsorbed so the collagen fibers can lie closer together and cross-link, and the wound fully closes (1).
There are three types of wound healing: primary intention, secondary intention, and tertiary intention.
Primary intention means that the wound healing is supported by sutures, staples, glue, or otherwise closed so the wound heals beneath the closure (6).
Secondary intention must happen when the edges of a wound cannot be approximated, or “brought together,” so the wound heals with the production of granulation tissue from the bottom up (6).
Wounds that heal by secondary intention are at higher risk for infection, so contamination prevention is essential. Pressure ulcers are an example of wounds that heal by secondary intention.
Tertiary intention refers to a wound that needs to remain open, often due to severe infection. Wounds with secondary and tertiary intention have longer healing times (2).

Alternatives when NPWT fails
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT):
- HBOT is a treatment in which the wound is exposed to pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber to enhance wound healing (3).
- Bioengineered Tissue:
- Skin grafting or bioengineered tissue to promote tissue growth and healing.
- Skin grafts are considered as a treatment option if a wound is so large that it can’t close on its own. In this procedure, skin is taken from another part of your body – usually your thigh – and transplanted onto the wound (2).
- Some grafts are made from human cell products and synthetic materials. Studies have shown that these increase the chances of poorly healing venous leg ulcers closing faster. (2)
- Electrical Stimulation Therapy:
- Electrical stimulation therapy applies electrical currents to stimulate wound healing and tissue generation (4). It may be used to treat chronic wounds or pressure ulcers.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Have you ever cared for a patient with a wound that was unable to be stitched or sutured?
- Can you describe the importance of thorough, descriptive documentation of multiple wounds?
- Can you think of barriers to the normal wound healing process?
Adjunct Treatment Options
When selecting an adjunctive therapy for wound management, the patient's medical history, overall health, co-morbidities, ambulation status, psychosocial aspects, environmental factors, and the specific needs of the wound should all be considered. Each patient is unique, and an individualized care plan is the goal.
Treatment of the underlying contributing disorder will be essential. For example, a patient with uncontrolled diabetes that has led to poor circulation can benefit from glycemic control.
Take a look at the larger, holistic picture. It can be helpful for the healthcare team to create a concept map of problems that contribute to the wound.
Topical Agents and Dressings
Various creams, ointments, or dressings can promote wound healing and prevent infection. One example is silver-based products, which are commonly used in reducing bacterial burden and treating wound infection (4).
Nutrition Therapy for Wound Healing
Patients with wounds would benefit from nutrition consultation and ongoing support.
Nutrients from foods help the body build and repair tissue and fight infection. An increase in calories and protein is important, as well as blood sugar control for diabetics.
Vitamins C, D, B-6, B-12, folate, and others aid in repairing tissues (6). Minerals such as iron, magnesium, calcium, zinc, and others support the cardiovascular system making sure cells have enough oxygen, the nervous system, and immunological function (6).
Compression Therapy
Compression therapy uses pressure to reduce swelling and improve blood flow to the wound. There are common compression devices or stockings available. It is frequently used to treat venous leg ulcers (6).
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
HBOT can also be used as an adjunct treatment in which the patient breathes pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber to increase the amount of oxygen in the blood, which enhances wound healing (3).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Have you ever provided patient education on how nutrition impacts the immune system and wound healing?
Troubleshooting Tips
You may encounter complications with the wound dressing or the wound vac equipment. The most common complications associated with NPWT are pain, bleeding, and infection (7).
The wound therapy relies on an adequate seal similar to a regular vacuum, so a loss of suction can result in ineffective treatment. If loss of seal occurs, the nurse should assess the seal around the wound dressing and note if the transparent adhesive sealant tape has either been misapplied or has come off due to poor contact with the underlying skin.
A loss of suction could also result from incorrect placement of the suction drain tube, loss of battery power, blockage of the suction drain tube, or if the suction device is full of output (7). Sometimes the location of the wound leads to difficulty in keeping the dressing seal in place; for example, the abdomen or near joints, so movement can misplace the dressing and break the seal. Patient education is key to maintaining proper suction.
Troubleshooting Tips:
- Confirm the machine is on and set to the appropriate negative pressure.
- Make sure the foam is collapsed and the NPWT device is maintaining the prescribed therapy and pressure.
- Assess the negative pressure seal and check for leaks.
- Check for kinks in the tubing and make sure all clamps are open.
- Avoid getting the machine wet.
- Assess the drainage chamber to make sure it is filling correctly and does not need changing.
- Address alarm issues:
- Canister may be full
- Leak in the system
- Low/dead Battery
- The device should not be turned off for more than two hours without ordered discontinuation.
- If the device is off, apply a moist dressing and notify the provider immediately.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Can you name reasons the NPWT device may sound an alarm?
- Can you think of barriers to proper suction? (ex: kinks in tubing, full canister, etc.)
Case Study
Mr. Smith is a 59-year-old male presented to his primary care provider and referred to general surgery; diagnosed with lymphedema and multiple, copiously draining ulcerations on the left lower extremity.
The patient presented with lymphedema and multiple ulcerations on the left lower extremity with copious amounts of drainage. This is an ongoing, worsening issue for over 8 months and has failed to respond to compression, foam dressings, or hydrocolloid dressing.
The hospitalist has ordered surgical consultation, who scheduled debridement of the wounds and application of a wound vac following the procedure; Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) orders in place.
CHIEF COMPLAINT: "The sores on my feet are draining more and I can no longer go to work because my boots do not fit on my foot.” He also reports a loss of appetite, chills, and loss of sensation to his left lower extremity.
HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS: Patient is a 59-year-old truck driver who has previous medical history of DM Type II, hypertension requiring use of anti-hypertensive medication, and hyperlipidemia (non-compliant with medication regimen). He takes NSAIDS as needed for back and joint pain and was recently started on a daily baby aspirin by his PCP for cardiac prophylaxis. He denies alcohol intake. He reports smoking a pack of cigarettes per day.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: Examination reveals an alert and oriented 59-YO male. He appears anxious and irritated. Vital sips are as follows. Blood Pressure 155/90 mmHg, Heart Rate 120/min - HR Thready - Respiratory Rate - 20 /minute; Temperature 98.0
ENT/SKIN: Facial pallor and cool, moist skin are noted. No telangiectasia of the lips or oral cavity is noted. Wound: 3 cm x 2 cm x 1 cm wound to lateral LLE. Wound base is dark red with yellow-green drainage present. Removed 4 x 4 dressing has a 5 cm diameter ring of drainage present. The surrounding skin is red, warm, tender to palpation, and with a dusky appearance to the entire LLE.
CHEST: Lungs are clear to auscultation and percussion. The cardiac exam reveals a regular rhythm with an S4. No murmur is appreciated. Peripheral pulses are present but are rapid and weak. A positive Stemmer sign was noted and palpable pedal pulses with mild symptoms of venous insufficiency were noted.
ABDOMEN/RECTUM: The abdomen reveals a rounded abdomen. Bowel sounds are present.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Discuss abnormal findings noted during History & Physical Examination.
- Evaluate additional data to obtain possible diagnostic testing, treatment, nursing interventions, and care plans.
- Discuss how the patient’s comorbidities may be attributed to prolonged wound healing.
- What suction settings would the nurse expect to be ordered?
Conclusion
Hopefully, upon completion of this course, you feel empowered and curious about the use of negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT). Wound vacs can be a powerful tool in combatting acute and chronic wounds, it is a well-documented concept throughout history.
The nurse should be knowledgeable on the integumentary system makeup and types of wounds this therapy is indicated for. The mechanism of action of NPWT is critical knowledge when assessing the healing of a wound. Adjunct treatment options and troubleshooting support tips are also meaningful in the care of patients with NPWT.
Nutritional Interventions to Promote Wound Healing
Introduction
The medical field is an ever-evolving and constantly changing arena. Advances in technology and an increased understanding of how the body works have produced newer and better procedures and techniques in healing. These initiatives, as innovative as they may be, still depend on the body’s ability to heal itself as the foundation of the recovery process.
In turn, the body needs proper nutrition to support the healing process within itself. Nutrition is often overlooked by nurses even though it is arguably the most critical aspect of physical healing.
Factors That Impact Wound Healing
Wound healing is a complex process. There are a myriad of factors that impact the body’s ability to heal and recover from an injury. Comorbidities, genetic disorders, medications, and, in some cases, disease treatments (chemotherapy, radiation, steroids, etc.) can all have the potential to slow, change, or interfere with normal wound healing (2). For this course, we will discuss a few of the more common factors that nurses will undoubtedly come across during their practice.
Diabetes
It is estimated that this growing, global disease will impact forty million people by the year 2030. It has been proven that diabetes is responsible for more than one hundred changes in wound healing.
These alterations have been seen across all four phases of wound healing. Platelet activation, epithelialization, collagen deposition, and granulation tissue formation are among the alterations that take place with diabetes. Worsening renal function/failure and peripheral vascular disease as a result of diabetes also affect the wound-healing process (2).
Renal Failure
Though most patients who have chronic kidney disease or renal failure also have multiple comorbidities that cause the renal problem, renal failure does, independently, bring a risk of diminished wound healing. Tissue edema, delayed granulation, chronic inflammation, and decreased vessel formation are all ways that renal failure impacts wound healing.
Hemodialysis, a life-sustaining treatment of chronic renal failure, adds fuel to the fire when it comes to risks of diminished wound healing. Protein and water-soluble vitamins and nutrients are lost through the dialysis process. This includes zinc and iron and will lead to deficiencies in these needed nutrients. Further, patients on hemodialysis and patients who receive a kidney transplant as treatment for renal failure are both at higher risk for developing infections (2).
Smoking
Smoking causes multiple alterations within the body at the molecular level that affect normal wound healing. Vasoconstriction caused by smoking worsens wound ischemia. The highly documented negative impact that smoking has on wound healing has led physicians to decline some elective surgeries due to the risk of poor wound healing (2).
Infection
It is not fully understood how infection alters wound healing. It is believed to be a multifactorial process that has a range of properties that can be progressive in nature; infection-necrosis-sepsis-death. The bacteria create an environment where the collagen that repairs the injured tissue is destroyed (2).
Obesity
Obesity complicates virtually every disease process including normal wound healing. Wound healing complications due to obesity include increased rates of infection, hematomas, and dehiscence. Local hypoxia is also a complication that impacts wound healing (2).
Age
Aging also has an impact on wound healing. During the aging process, the skin loses elasticity, thickness, and water content. There is also a decrease in the skin’s blood vessels as it ages, reducing the capacity for oxygenation and nutrients. Wound closure becomes slower with aging; by age forty, the amount of time for an identical wound to heal doubles from age twenty. After the age of fifty, dermal collagen decreases by one percent per year (2).
Malnutrition
Malnutrition or undernutrition has a variety of effects on wound healing. Good nutrition is essential for proper wound healing and the overall recovery of the body after an injury.
Malnutrition can lead to the loss of immune function which will affect the body’s response to infection. With malnutrition, the skin becomes thin and frail thus more apt to develop wounds. Pressure wounds are also more likely as fat deposits over pressure points become depleted. The lack of energy during malnutrition leads to immobility, increasing the possibility of wounds. Collagen synthesis is also decreased (5).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Name three factors that can affect wound healing.
- How does age and aging impact wound healing?
- What are two ways that malnutrition impacts wound healing?
Phases of Wound Healing
Once again, wound healing is a complex process. From a simple pin prick to a stage-four decubitus ulcer, the wound healing process itself remains the same. The body will go through the four phases of wound healing to repair the damage.
Hemostasis
The first phase of wound healing is hemostasis. Whether by surgery or trauma, the body attempts to achieve hemostasis at the time of the injury. The intrinsic and extrinsic coagulation cascades are activated by the body.
Vasoconstriction takes place while platelet aggregation occurs to form a fibrin clot. This is all in an effort of the body to stop the bleeding to bring about hemostasis. As the platelets arrive at the site of injury, cytokines and growth factors are released by the platelets to initiate the inflammation process (3) (4) (5).
Inflammation
Inflammation is the second phase of wound healing. It starts once hemostasis has been re-established. During this phase, the previous vasoconstriction reverses and the vessels dilate.
This brings blood to the injury site along with neutrophils, macrophages, monocytes, and other inflammatory cells. Phagocytosis is initiated and the wound is cleansed by the removal of bacteria. The wound site will swell and there may be some restrictions in mobility to the affected area (3) (5).
Proliferation
Phase three is proliferation. In this phase, rebuilding of the wounded tissue begins. The number of fibroblasts increases and begins to build a collagen network and prepare the wound base for new granulation tissue.
At the same time, new blood vessels are created; a highway for oxygen and nutrients to be supplied to the site. By the end of this phase, the foundation will have been laid for full epithelialization (3) (5).
Remodeling
The final phase of wound healing is remodeling. Epithelialization is in full swing once granulation tissue has filled the wound. This process stimulates skin integrity restoration.
Scar tissue is formed as proteins such as collagen and elastin along with keratinocytes are produced. The wound closes and begins to strengthen and appear “normal”; it may take a couple of years for the site to return to its fully functional pre-injured status (3).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How many phases of wound healing are there?
- Name all the phases of wound healing in order.
- What happens during the proliferation phase of wound healing?
How Does Nutrition Impact Healing?
Nutrition is, perhaps, the most important underlying aspect of wound healing. The mechanism of wound healing and the role nutrition plays in that process is very complex.
Adding nutritional interventions to the wound healing care plan is generally low cost and will increase the probability of a full recovery. Nutrition is essential for all phases of the healing process. It is the foundation of wound healing.
The malnourished patient will have difficulty progressing through the wound healing phases. Proper nutrition will also help prevent wounds such as pressure ulcers from developing in the first place.
Understanding which nutrients are needed through the phases of wound healing will help to devise a nutritional plan of care. Energy is required in all the phases of wound healing and is only made possible through proper nutrition (3).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- In what phase of wound healing is proper nutrition essential?
Common Deficiencies
Nutrients and proteins are the building blocks of life. They are needed for growth, maintenance, and healing of the body. Many types of nutrient deficiencies greatly impact the healing process. Here, we will discuss some of the more common nutrient deficiencies.
Iron
Iron plays a key role in the synthesis of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin delivers oxygen throughout the body; oxygen is required through all phases of wound healing. Iron deficiencies can lead to anemia and decreased tissue perfusion. An iron deficiency will also affect protein synthesis, macrophage function, and overall wound strength (3) (6).
Vitamin A
When it comes to wound healing, vitamin A quickens collagen synthesis and the overall inflammatory phase. A deficiency in vitamin A decreases collagen production, epithelization, and tissue granulation (9).
Vitamin B
There are eight vitamins included in the vitamin B complex. Each of the eight vitamins has its own daily recommended intake. Vitamin B promotes cell proliferation and promotes normal metabolism. In the presence of a wound, some dietitians promote doubling the daily recommended intake of the B vitamins (3).
Vitamin C
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) assists with iron absorption. It is also essential in the process of collagen formation. Without vitamin C, the immune response cannot take place as needed. There are many sources of vitamin C readily available for everyday consumption (6).
Zinc
Zinc is used through all phases of the wound-healing process. It is used to initiate and modulate enzyme function throughout the wound healing phases. It affects immunity and assists in fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. It is also needed for granulation tissue formation (5) (6).
Amino Acids
Protein and amino acids are another set of nutrients that are highly essential in wound healing. The blood’s most abundant amino acid, glutamine, provides the body’s preferred energy source, glucose. Increased levels of glutamine have been shown to help with wound strength and increase the levels of mature collagen.
Generally, the body is able to produce enough glutamine for regular function. In times of stress on the body, such as a wound, glutamine is sought out in the diet. Arginine assists in modulating the collagen deposits, increases new vessel formation, and aids in wound contraction (3).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Name three common nutrient deficiencies that the nurse may encounter.
- What are two amino acids that play key roles in wound healing?
- An iron deficiency can lead to what issues?
- Which phases of wound healing require zinc to complete the phase?
Special Considerations
Tube Feedings
Patients who use tube feedings or enteral feedings are in a unique situation when it comes to wound healing and nutrition. Once a proper nutrition assessment has been performed, a tailor-made nutrition-rich diet can be formulated and administered directly into the gut.
Studies have shown that different formulas with supplemental nutrients have increased the ability of the body to heal faster than those without supplements. With tube feedings, patients don’t need to prefer the taste of one formula over another as it is delivered through the tube.
The amount of formula can also be adjusted as the patient’s needs change. Though some formulas may have side effects such as diarrhea, the overall benefits usually outweigh such side effects (8).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
-
What considerations are there for patients with tube feedings?
-
What is a pitfall when using tube feedings to deliver full nutrition?
Chronic and Terminal Illness
Autoimmune, inflammatory, and cancers are among the chronic and terminal diseases that are under special consideration when it comes to wound healing. These types of diseases can interrupt the immune/inflammatory response of the body thus prolonging the phases of wound healing.
When a wound develops on a patient who is immunocompromised, there is a higher incidence of wound infection which will delay wound healing. In many of these diseases, there may be circulatory issues that decrease the body’s ability to provide the affected area with nutrient-rich blood.
Chronic illnesses often decrease the patient’s energy levels. This can lead to immobility and increases the risk of wounds developing.
Further, for many of these types of issues, the treatment itself can have adverse effects on wound healing. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunosuppressants all decrease the body’s ability to heal and increase the rates of infection in wounds (2).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are three types of chronic or terminal diseases?
- What issue is an immunocompromised patient at risk for?
- What are two treatments for chronic illness that can affect wound healing?
Supplements
Nutritional supplements have been shown to improve wound healing and recovery outcomes. It is important that the supplements are given under the supervision of a provider as too much of some nutrients can have a detrimental effect on wound healing.
A proper nutrition screening should be performed on all patients with wounds so that the nutrition plan can be tailored to the individual patient. These improvements to wound healing with nutritional supplementation differ based on the type of wound and the overall health of the patient.
The patient should be monitored and reassessed regularly by a dietitian. Again, there is no cookie-cutter supplement regimen.
Another factor to consider with supplements is the ease of following the supplement regimen. Hard to swallow pills or foul-tasting food/liquids may have a negative impact on the patient’s ability to adhere to the supplement regimen.
Allowing the patient to choose (with the input of the provider) the method of supplement delivery along with a choice of flavors will help increase compliance with the prescribed regimen (1).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What should be done prior to starting dietary supplements?
- Who should assess and reassess a patient’s dietary status?
- Why is the method of supplement delivery important?
Patient Education
Throughout the entire wound healing process, patient education is a must. Not only is it important so that the patient can make an informed decision about their care, but the patient should understand what is going on with their bodies.
Education fuels compliance. A comprehensive nutrition assessment will not only provide a baseline of the patient’s nutritional status but will also help identify gaps in the patient’s understanding.
This is where the education can be focused to best help the patient meet their wound healing goals. Education must include which foods contain which nutrients, the amount of these foods to eat, and which foods will interact with the absorption processes of the nutrients.
Discussing normal daily requirements and the requirements needed during wound healing is also needed (1).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Why is education important when discussing nutrition and wound healing?
Conclusion
Nutrition plays a key role in wound healing. There are many factors that affect the body’s ability to acquire and use the needed nutrients. One of the most important considerations that we as healthcare providers need to put into practice is determining a patient’s nutritional status.
A nutritional assessment should be done on patients with wounds so that a proper plan of care can be developed. Often, nutrition is an afterthought when in reality it is the foundation on which other treatments should be built upon.
Once this has been established, the patient’s plan of care can be implemented and must include nutritional education. Needed supplements to increase the patient’s ability to heal can be added or removed as necessary when the reassessments have been completed.
Ostomy Management
Introduction
Newton's law of gravity states: what goes up, must come down; similarly, the normal human gastrointestinal system has a law that what goes in, must come out. When disease inhibits the normal process, ostomy procedures are a life-saving intervention.
There are around one million people living with an ostomy or continent diversion in the US, and approximately 100,000 ostomy surgeries are performed annually in the US (1). We will build a stronger understanding of various types of ostomies, indication for the need, site selection, stoma care, complications, and patient education.
Types of Ostomies
An ostomy is a surgically created opening that reroutes stool or urine from the abdomen to the outside of the body through an opening called a stoma (9). The term stoma refers to the portion of the bowel that is sutured into the abdomen (9).
When you look at a stoma, you are looking at the lining (the mucosa) of the intestine. The color is similar to the mucosa inside your mouth and cheek. Throughout various healthcare environments, you may hear the terms ostomy or stoma interchangeably. The purpose of an ostomy is to bypass a diseased portion of the gastrointestinal tract that is not functioning properly or has been removed (2).
Ostomies are placed proximal to the diseased area, comparable to building a dam in a river to stop the flow of fluid and divert it somewhere else. An ostomy can be temporary or permanent.
There are three most common types of ostomies: ileostomy, colostomy, and urostomy (9). We will discuss these types, but it is important to recognize that gastrostomy, jejunostomy, duodenostomy, and cecostomy procedures are also done.
- Ileostomy: A stoma is attached at the end of the small intestine (ileum) to bypass the colon, rectum, and anus.
- Colostomy: A stoma is attached to a portion of the colon to bypass the rectum and anus.
- Urostomy: A stoma is attached to the ureters (the tubes that carry urine from the kidney to the bladder) to bypass the bladder.
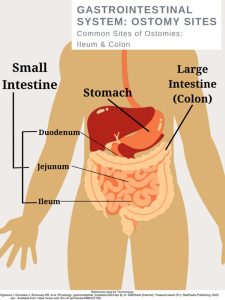
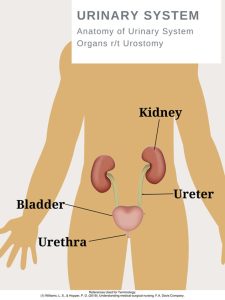
Ileostomy
The small intestine has three parts that are compact and folds over itself: the duodenum, jejunum, and the ileum. An ileostomy has a stoma attached and created from the ilium. The ileum is the final and longest segment of the small intestine (9).
The ileum terminates at the ileocecal valve, which controls the flow of digested material from the ileum into the large intestine and prevents the backup of bacteria into the small intestine (9). If a patient has this type of ostomy, the colon distal to the ostomy has a form of disease or disorder such as cancer. There are two main types of ileostomies, loop, and end ileostomy.
Loop ileostomy
In a loop ileostomy, a loop of the small bowel is lifted and held in place with a rod due to resection or repair to the distal bowel (Will). This ostomy is technically two stomas joined together (4). Loop ileostomies are typically temporary and will be closed or reversed through an operation in the future.
End ileostomy
In an end ileostomy, the ileum is surgically separated from the colon, the colon is removed or left to rest, and the end of the ileum is brought to the surface through the abdomen to form a stoma. Although end ileostomies are sometimes temporary and later rejoined, they are usually permanent (9).
Colostomy
A colostomy may be formed as an ascending, transverse, descending, or sigmoid colostomy (9). It is named according to the location of placement. An end colostomy is constructed from the ascending, transverse, descending, or sigmoid colon and has one opening for fecal elimination.
Loop Colostomy
The creation of a loop stoma takes a loop of the colon (usually the transverse colon) and pulls it to the outside of the abdominal wall (9). In this type of ostomy, the entire bowel is not dissected but left mostly intact.
End Colostomy
In end colostomies, the proximal end of the colon is dissected and pulled out of the abdominal cavity, which becomes the stoma (9). Additional procedures may involve repairing or removing portions of the distal colon or rectum.
Urostomy
Kidneys have an important job of filtering waste and excess fluid from your blood. This process creates urine, which then travels from the kidneys to the bladder through tubes called ureters (8). If the bladder is damaged or diseased, ostomies are a life-saving method of creating safe passage for the urine.
A urostomy is a surgical opening in the abdominal wall that redirects urine away from a bladder that’s diseased, has been injured, or isn't working properly (8). The bladder is either bypassed or removed (called a cystectomy) during surgery. Following the surgery, urine exits the body through a stoma.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Have you ever witnessed a GI or Urinary Surgery?
- Do you have experience with GI / Urinary procedures like a colonoscopy?
Indication for Ostomy Placement
Gastrointestinal Tract Ostomy
- Cancer
- Colorectal
- Rectal
- Trauma/ Injury
- Significant Disorders
- Crohn’s disease
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Diverticulitis
- Bowel perforation from a ruptured diverticulum or abscess
- Bowel obstruction
- Infection (9)
Urinary Tract Ostomy
- Bladder Cancer
- Neurogenic bladder disease (damage to the nerves that control the bladder)
- Birth defects
- Chronic inflammation of the bladder (9)

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Have you cared for a patient with a new ostomy?
- Can you list reasons a patient is a candidate for an ostomy?
Site Selection
Wound, ostomy, and continence nurses (WOCN) play a vital role in site selection. Patients should have a pre-operative consultation prior to surgery. During this consultation, the nurse acts as an advocate and educator to prepare these patients for the physical and emotional path ahead of them. A significant amount of time should be spent with the patient before surgery to determine a stoma incision site (exit of ostomy).
It is important to make the presence of the ostomy (and collection bag) as comfortable as possible, striving to reduce the hindrance to ease movements and ability to wear their typical clothing (9). Studies show that preoperative education and stoma site marking has been directly responsible for improving quality of life and decreasing peristomal skin and pouching complications (4).
Site Assessment:
Locate positions for a site within the rectus muscle (4).
Observe the abdomen in various positions sitting, standing, or lying down.
Ask the patient about the types of clothing they wear most often. Examples: Level of pants (low, high), use of belts, dresses, etc. (9)
Determine a location that is visible to the patient, as they will need to see the site well for stoma care.
Avoid skin or fat folds (folds increase chances of leakage)
Avoid scars, bony prominences, and the umbilicus (4).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Locate places on yourself that would be appropriate for an ostomy site
- Can you think of reasons patients need to be able to see the site?
- Do you have a wound care nurse at your past or present workplace?
Post-operative Care
Post-operative care following ostomy placement is vital. The post-operative nurse assigned to this patient should read the surgery documentation to determine the type of procedure performed, intraoperative findings, type of stoma created, any advanced diseases, and unexpected events during surgery (2).
The nurse should be aware of the level of invasiveness; was this a laparoscopic, robotic, or open surgery? This type of surgery can have an impact on the post-op care plan and length of stay (2). Teaching can begin as soon as they are able to comprehend and focus on understanding new skills.
The stoma will gradually decrease in size over the weeks following the surgery. For a patient with a new ostomy, postoperative assessments should be done per facility protocol and the stoma should be inspected at least every 8 hours (9).
Note the type of closure (staples, sutures, liquid bonding agent), presence of abdominal drains, and presence of urinary catheter (C2). Assess for pain and address accordingly with repositioning, cold/heat therapy, and ordered pain medications. Assess for bowel sounds. Palpate the abdomen and note firmness and tenderness levels. Document strict Intake and Output for these patients.
Stoma Assessment:
Note the Appearance/ Color: The stoma should be pink to red in color, moist, and firmly attached to the surrounding skin (9). If the stoma appears bluish, it indicates inadequate blood supply; if the stoma appears black, necrosis has occurred. Immediate notification is needed from the provider, as the need to return to surgery will be assessed.
- Note the Presence of edema.
- Note the Surrounding skin
- Note any Ostomy Discharge
- Amount
- Color / Consistency
- Note any Bleeding
- Monitor for rupture or leakage.
Diet
Once bowel sounds and activity return, the patient’s diet may resume (2). Typically, patients are offered clear liquids to determine their ability to tolerate fluids. Nurses should encourage the patient to chew thoroughly, eat small frequent meals, and ambulate frequently to assist in gas movement and peristalsis (2).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Do you have experience with post-operative abdominal surgery?
- Explain possible respiratory or cardiovascular assessments that would be helpful for these patients
Stoma Care
Nursing Consideration / Reminders
Ostomy pouching system needs to be changed every 4 to 7 days, depending on the patient and type of pouch.
Patients should be encouraged to participate in stoma care. Instruct the patient to empty the pouch when it is one-third to one-half full as they become heavy and more prone to spilling or leaks.
Table 1. Ostomy Change Procedure SAMPLE (Always check with your agency policy)
| Steps | PURPOSE |
| 1. Perform hand hygiene. | This prevents the spread of germs and microorganisms. |
| 2. Gather supplies. |
Supplies:
|
| 3 Create privacy. Lift bed to comfortable height. |
Attention to psychosocial needs is imperative. Proper body mechanics is important for nurse. |
| 4. Place waterproof pad under pouch. | The pad prevents the spilling of effluent on patient and bed sheets. |
|
5. Remove ostomy bag. Apply non-sterile gloves. Support / hold the skin firmly with your other hand, apply adhesive remover if needed. Measure and empty contents. Place old pouching system in a garbage bag.
|
The pouch and flange can be removed separately or as one. Gentle removal helps prevent skin tears. Remove flange by gently pulling it toward the stoma. |
| 6. Clean stoma gently by wiping with warm water. Do not use soap. |
Aggressive cleaning can cause bleeding. If removing stoma adhesive paste from skin, use a dry cloth first. Soaps can irritate the stoma. Clean stoma and peristomal skin |
| 7. Assess stoma and peristomal skin. |
Stoma skin should be pink or red in color, raised above skin level, and moist (2). Skin surrounding the stoma should be intact and free from wounds, rashes, or skin breakdown. |
|
8. Measure the stoma diameter using the pre-cut measuring tool (or tracing template). Trace diameter of the measuring guide onto the flange and cut the outside of the pen marking. |
The opening should match the size of stoma. If there is skin exposed between the stoma and edge of the flange with an ileostomy, the drainage contains enzymes that will break down the skin (9). Cut out size to fit stoma, assess fit once cut. |
|
9. Prepare skin.
|
Paste can be applied directly to the skin or flange. |
|
10. Apply Flange
|
Press gently around the periphery of the stoma to create a seal |
|
11. Apply the ostomy bag Close the end of the bag with clip (follow the manufacturer’s instructions) |
Involve patient with this process, understanding instructions. |
| 12. Apply pressure to ostomy pouch to help with adhering to skin. | Heat/ warmth from hand can activate some flanges. |
| 13. Clean us supplies, perform hand hygiene. | Remove trash as quickly as possible to reduce odor. |
| 14. Document Procedure |
Example: Date/time: flange change complete. Stoma pink, moist, warm. Peristomal skin intact. Patient instructed in cutting flange to correct size, verbalized understanding of frequency of change. See ostomy flowsheet. (Abbie S., RN) |
| Data Source: Carmel, Colwell, J., & Goldberg, M. (2021). Wound, ostomy and continence nurse’s society core curriculum: ostomy management (Second Edition). Wolters Kluwer Health. | |

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Are you familiar with your facility's ostomy care protocol (if appropriate)?
- How can the nurse implement safety measures with ostomy care?
- Do you feel comfortable with ostomy care documentation?
Complications
Ostomy Leakage
One of the most common and troublesome complications is leakage (4). Proper preoperative site selection (away from skin folds) is important. Patient education on proper techniques and supplies can aid in the prevention of leakage.
Educate patients on the risks of changing the ostomy too often. Frequent appliance changes lead to pain and frustration, as well as financial expenses on supplies (4). Leakage is more common in the early postoperative period but can also develop with weight changes later.
Interventions involve thickening the stool with antidiarrheals to form more solid excretion and pouching techniques to bolster the height of the stoma off of the peristomal skin (4). Helpful tips also include heating the appliance with a hair dryer before application, lying flat for several minutes following application, making sure the peristomal skin is dry before application, and the possible use of a fine dusting of stomal powder and skin sealant prior to application (4). Leakage is frustrating for patients, so support and encouragement is vital.
Mucocutaneous Separation
The stoma is sutured to the skin of the abdomen with absorbable sutures during surgery (4). Mucocutaneous separation is a complication that can occur if the sutures securing the stoma become too tight or if blood flow to the area is restricted (9). This complication requires appropriate treatment because the pouch leakage will occur from the open pocket.
The goal of treatment is to keep this open pocket covered properly until the wound heals on its own and closes. Appropriate covering of the opening can include an absorbent product such as an alginate, followed by a cover dressing such as a hydrocolloid, which is covered with the ostomy pouch (4).
Early High Ostomy Output
Early high ostomy output (HOO) is defined as ostomy output greater than fluid intake occurring within 3 weeks of stoma placement, which results in dehydration (4). This is more common with ileostomies (4). Strict Input and Output records are a vital nursing intervention. The most important treatment for this complication is hydration to prevent renal failure, which is typically done intravenously (4).
The site of a patient’s colostomy will impact the consistency and characteristics of the excretion. The natural digestive process of the colon involves the absorption of water, which causes waste from the descending colon to be more formed. Waste from an ileostomy or a colostomy placed in the anterior ascending colon will be a bit more loose or watery (2).
Peristomal Skin Issues
Irritant Contact Dermatitis (ICD) is the most common peristomal skin complication following ostomy placement (9). ICD is characterized by redness; loss of epidermal tissue; pain; and open, moist areas.
Newer and inexperienced patients and caregivers will increase the size of the pouching system opening to get a better seal and stop leakage (2) However, this only contributes to more skin breakdown and irritation. Patients may also develop a fungal rash, have allergic rashes to the ostomy appliance, or folliculitis (4).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Can you name measures to prevent leakage?
- Have you cared for a patient with Irritant Contact Dermatitis?
- Are you familiar with bulking agents for stool?
Patient Education
Patient education is a key aspect is caring for a patient with an ostomy, this process begins prior to surgery and remains constant throughout encounters. If you have not received specialized training on wound and ostomy care, you should reach out to the Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nurse (WON) within your healthcare setting to become involved if they are not already.
However, each nurse has a meaningful impact on discussing and managing expectations for life with an ostomy, including stoma care, complications, managing ostomy output, maintaining pouching appliances, and resources. Patients may feel inadequate and uneasy about caring for their stoma.
Nurses need to meet the unique learning needs of each patient and caregiver, providing education in verbal information, written pamphlets, online resources, videos, and demonstrations. The United Ostomy Associations of America, Inc. (UOAA), is a nonprofit organization that serves as an excellent resource for information, support, advocacy, and collaboration for those living with ostomies.
Nurses should be aware there is an “Ostomy and Continent Diversion Patient Bill of Rights” (PBOR) that outlines the best practices for providing high-quality ostomy care during all phases of the surgical experience (1). There are numerous national resources for patients, as well as community-based and online ostomy support groups.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Can you think of methods to assess patient knowledge on ostomy care?
- What are creative ways to involve an ostomy patient in care?
- Not all patients are savvy with online supply ordering, can you think of other ways to order supplies if they are not?
Promotion of Body Image and Self-Esteem
Ostomy surgery can have a major impact on how patients perceive themselves. A person’s body image is how they see themselves when they look in the mirror or how they picture themselves in their mind.
There are stigmas surrounding ostomies, such as being odorous, unhygienic, and unattractive due to the stoma, but the truth is that ostomies save lives and make life possible. Positivity should surround the conversation. Confirmations such as beauty, strength, celebration, and hope are meaningful.
Ways to become involved in celebrating ostomies:
- Become familiar with the United Ostomy Associations of America (UOAA) and their initiatives.
https://www.ostomy.org/ostomy-awareness-day/
National Ostomy Awareness Day on October 7, 2023
Worldwide Virtual Run for Resilience Ostomy 5k
- Social Media Sites
Celebrate Body Positivity for those with ostomies
Intimacy Encouragement
Conclusion
Ostomy care is an essential nursing skill. If you are caring for a patient with an ostomy, remember that this is a major life-altering event and condition. Reflect on ways to provide individualized care by understanding various types of ostomies, site selection, stoma care, complications, and patient education. Empower and encourage these ostomy patients’ confidence in themselves.
Diabetes Management Updates
Introduction
Diabetes Mellitus (DM), also known as diabetes, is a condition in which the body develops high levels of blood glucose due to the inability to produce insulin or for the cells to use insulin (1) effectively. If left untreated or mismanaged, it can lead to health complications such as heart disease, chronic kidney disease, blindness, nerve damage, oral and mental health problems (1)(15).
There are several classifications of DM, and the following will be discussed: T1DM, T2DM, gestational diabetes, and idiopathic diabetes.
Classifications of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM)
T1DM is formerly known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes and usually occurs in children and young adults (1). Although, it can also occur at any age and accounts for 5 – 10% of cases. T1DM develops when one’s own immune system attacks and destroys the beta cells that produce insulin in the pancreas (6).
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM)
T2DM, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes or non-insulin-dependent diabetes, develops because of the body's inability to use insulin effectively. It is the most common type of diabetes and mainly occurs in adults aged 30 years and older (1). However, it is also becoming common in children and young adults due to obesity. It accounts for 90% of the population diagnosed with diabetes (6).
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational Diabetes occurs during pregnancy and in women who have never had a previous diagnosis of diabetes. It is a result of pregnancy hormones that are produced by the placenta or because of the insufficient use of insulin by the cells (1). Gestational diabetes can be temporary or in some cases can become chronic. It is also likely that children whose mothers have gestational diabetes can develop diabetes later in life (6).
Prediabetes
Prediabetes, also referred to as impaired glucose tolerance, is a stage when a person is at risk of developing diabetes. If well managed through proper diet management and exercise, this can help with the prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes (1).
Other Forms of Diabetes
Other forms of diabetes include monogenic diabetes syndrome, diabetes from the removal of the pancreas or damage to the pancreas from disease processes such as pancreatitis or cystic fibrosis, and drugs or chemical-induced diabetes from glucocorticoids used to treat HIV/Aids or organ transplant (1) (6).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are the four named types of diabetes?
- What are the differences between T1DM and T2DM?
- What is the most common type of diabetes?
Statistical Evidence/Epidemiology
Diabetes is now ranked as the 8th leading cause of death in the United States (6). There is no known cure for diabetes. It is one of the fastest-growing chronic diseases and the most diagnosed noncommunicable disease. It is also one of the leading causes of chronic kidney disease, adult blindness, and lower limb amputations (6).
In 2019, it was estimated that 37.3 million American adults have diabetes, which equals 11.3% of the population (4). Of those, 41% were men and 32% were women. 28.7 million were diagnosed with diabetes, and 8.5 million were undiagnosed.
There are 96 million American adults who are prediabetic, which means they are at risk of developing diabetes, but their blood glucose levels are not high enough to be diagnosed with diabetes (5).
Most of the population that is pre-diabetic is 65 years old or older. Type 2 diabetes accounts for 90% to 95% of cases (5). The risk of developing diabetes increases with age.
The prevalence of diabetes is much higher in both black and Hispanic/Latino adult men and women. Men are more likely to develop diabetes compared to women. Due to the rise in obesity in younger adults, there has been an increase in the number of new cases of diabetes in black teens (4).
The figure below represents trends in incidence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents 2002–2018; results show the incidence of type 2 diabetes has significantly increased (4)
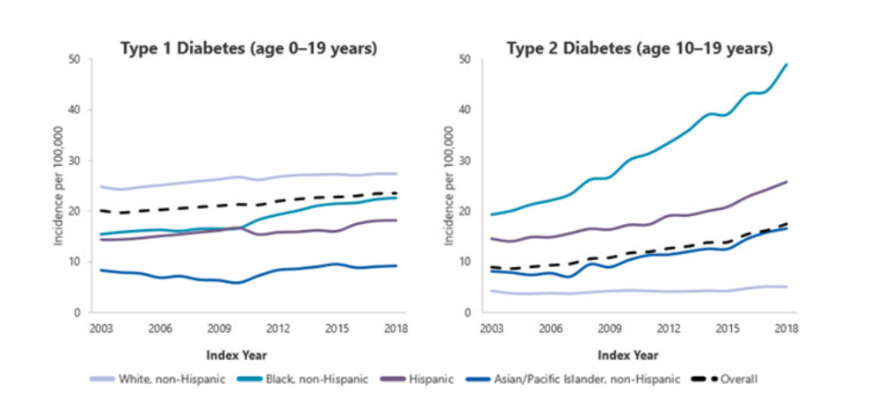

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What is one of the major comorbidities caused by diabetes?
- What age group is at risk for developing type 2 diabetes?
- What is a risk factor that is contributing to the rise of diabetes in younger adults?
Etiology and Pathophysiology
In normal glucose metabolism, blood glucose is regulated by the two hormones insulin and glucagon (11). Insulin is secreted by the beta cells in the Islet of Langerhans in the pancreas and glucagon is secreted by the alpha cells in the pancreas.
When there is an increase in blood glucose, the function of insulin is to reduce blood glucose by stimulating its uptake in the cells. Glucose is stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles or as fat in the adipose tissues. When blood glucose levels start to fall, glucagon promotes the release of glycogen from the liver, which is used as a source of energy in the body (8) (13).
When there is a deficiency of insulin or a decreased response of insulin on the targeted cells in the body, it leads to hyperglycemia (high blood glucose). Meaning that the glucose that remains in the blood is not able to get to the cells. Diabetes develops mainly because of lifestyle and genetic factors (13).
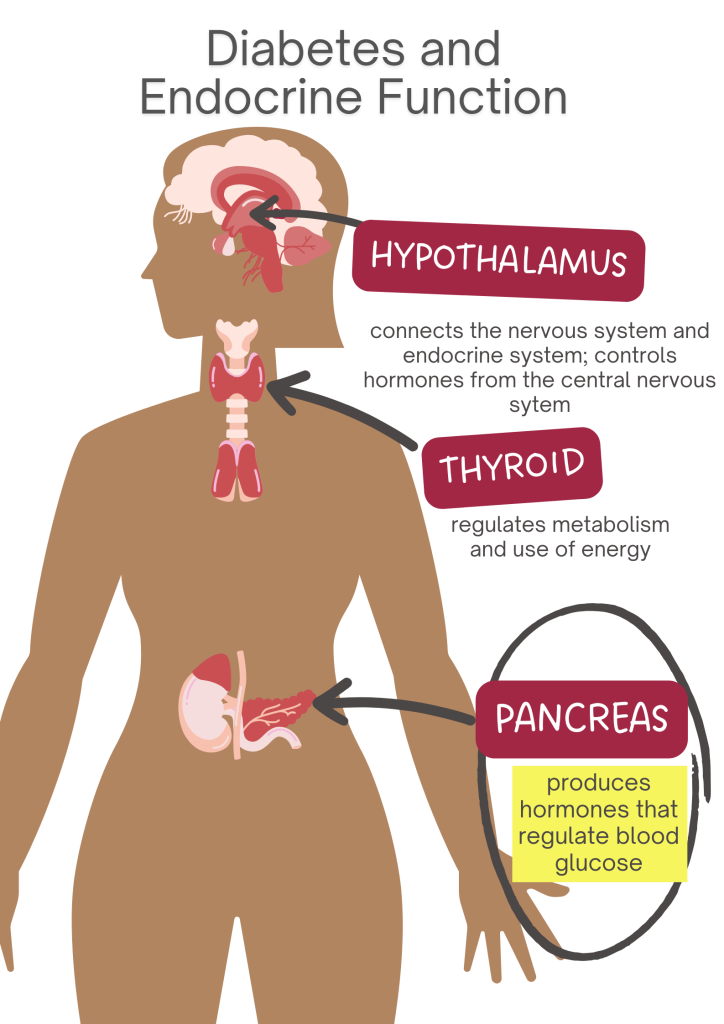
T1DM
The etiology is not well understood, though it is thought to be influenced by both environmental and genetic predispositions that are linked to specific HLA alleles. T1DM is considered an autoimmune disorder that is characterized by T-cell-mediated destruction of the pancreatic B-cells (13).
As a result, this leads to complete insulin deficiency and ultimately hyperglycemia, which requires exogenous insulin. The rate of destruction of the pancreatic B-cell-specific disorder is known to develop rapidly in infants and children or gradually in adults (8)(13).
T2DM
The etiology of T2DM is characterized by decreased sensitivity to insulin and decreased secretion of insulin. Insulin resistance occurs due to the disruption in the cellular pathways that result in a decreased response in the peripheral tissues, particularly the muscle, liver, and adipose tissue.
T2DM diabetes can progress slowly and asymptomatically over a period. Obesity and age can play a key role in the homeostatic regulation of systemic glucose because they influence the development of insulin resistance, which affects the sensitivity of tissues to insulin. Therefore, most patients with type 2 diabetes are overweight or obese 7) (8).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are the two hormones that are responsible for maintaining blood glucose levels in the body?
- Can you describe the etiologies of both T1DM and T2DM?
- What are some of the factors that contribute to T2DM?
Diagnostic and Screening tools
There are a variety of tests that are used to diagnose and monitor diabetes. These vary based on the type of symptoms that a patient may have. Diagnosis of DM requires at least two abnormal test results, which should include fasting glucose and A1C. The tests should be one of two from the same sample or two abnormal test results drawn on different days (3).
The recommended diagnosis guidelines for diabetes must be based on the following criteria:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) concentration with results greater than 126 mg/dL. This test involves measuring blood glucose at a single point. To have accurate results, the test should be conducted after one has had nothing to eat or drink for at least 8 hours (3).
- Glycated hemoglobin (Hb A1C) is indicative of the average levels of blood glucose in a period of two to three months. Results greater than 6.5% mean diagnosis of diabetes. This blood test does not require fasting. The A1C test is not suitable for pregnant women or those who have certain blood conditions (anemia) - NIDDK. This test should only be used for prediabetes screening (3).
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): prior to conducting this test, an FPG level needs to be measured. One must ingest 75 grams of glucose liquid. Thereafter, their glucose level is measured 2 hours after they have taken the liquid. Test results greater than 200 mg/dL are indicative of diabetes. This test is commonly used in pregnant women (3).
- Random plasma glucose of 200 mg/dL. This test is suitable when one has symptoms of hyperglycemia, which are polydipsia, polyuria, and polyphagia (3).
Screening
Screening is generally recommended for adults aged 45 or older regardless of present risk factors. The updated recommendation guidelines for prediabetes screening include adults 35 years and older who are overweight or obese (3).
Screening for Prediabetes
Prediabetes is associated with the impairment of blood glucose levels between 100 – 125 mg/dL. The diagnosis of prediabetes should be confirmed with glucose testing when there is impaired glucose tolerance with plasma levels between 140 – 199 mg/dL 2 hours after one has ingested 75g of oral glucose. A1C levels of prediabetes are between 5.7% to 6.4% (3).
Screening for Pregnant women
It is recommended that all pregnant women between 24 – 28 weeks be screened for gestational diabetes to avoid missing those that are at risk. A positive 3-hour OGTT test of greater than 140 mg/dL meets the criteria for diagnosis (3).
Medication Management
Monitoring of blood glucose levels in patients is useful in determining the effectiveness of antidiabetic medication. To achieve better patient outcomes, it is important to recognize individual needs (11).
It is recommended that the approach to medication management should be based on each patient's hyperglycemic index and should include the following: the presence of comorbidities, risk of hypoglycemia, vascular disease, life expectancy, and disease duration (3).
When the management of diabetes cannot be achieved through diet and exercise alone, oral antidiabetic agents are the preferred treatment (14). Oral antidiabetics can help maintain and achieve glycemic goals for patients who are diagnosed with T2DM) (10)(14).
Diabetes Education and patient engagement is essential to managing diabetes (11). There are several classes of anti-diabetic medication. Below are some of the most utilized antidiabetic medications (9)(14).
Biguanides
Metformin is the only medication in this category.
- It is considered the 1st line of treatment in patients with T2DM unless contraindicated.
- Metformin helps to decrease hepatic glucose production.
- Decreases intestinal absorption of glucose by improving insulin sensitivity. Must be titrated initially to minimize adverse effects.
- Avoided in clients with chronic kidney disease.
- Side effects: Lactic acidosis, hypoglycemia.
GLP 1- Receptor Agonists (RAs)
Mimics glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP -) hormone. Binds to GLP-1 receptors stimulate glucose-dependent insulin release and delay gastric emptying, which increases satiation.
- Known to have cardiovascular benefits.
- Can be taken orally or subcutaneously.
- Special considerations: Can cause weight loss, GI side effects such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, dehydration, increased satiation (fullness), acute pancreatitis, and reactions at the injection sites.
- Some labels may require renal dose adjustment.
- GLP - 1 RAs should be considered before starting clients on insulin to help reduce A1C then oral antihyperglycemic medications are not effective in treating diabetes.
Sulfonylureas 2nd generation
Stimulates insulin release in pancreatic beta cells.
- Risk for prolonged hypoglycemia. Therefore, it should be avoided with the concurrent use of insulin.
- Can cause weight gain.
- Can cause photosensitivity.
- Avoid use in clients with sulfa allergies and photosensitivity.
- Avoid use in clients with chronic kidney disease and liver disease.
Dipeptidyl Peptidase (DPP) - 4 inhibitors
Prevents DPP-4 enzymes from breaking down to GLP-1 hormone.
- Neutral weight.
- Monitor for acute pancreatitis, which can cause joint pain.
- May require renal dose adjustment with these brands: Saxagliptin (Onglyza), Sitagliptin (Januvia), and Alogliptin. Linagliptin does not require dose adjustment.
Sodium-Glucose transporter - 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors
Reduce the reabsorption of glucose by up to 90%, therefore promoting the exclusion of glucose from the body.
- Known to have cardiovascular benefits for clients with cardiovascular disease.
- Use with caution in clients with increased risk of fractures.
- Avoided in clients with diabetic ketoacidosis and those prone to have frequent urinary tract infections.
- This medication should be avoided in clients with pure poor kidney function due to volume depletion and hypotension.
- There’s also a risk for Fournier gangrene.
Thiazolidinediones
Pioglitazone and rosiglitazone can help reduce insulin resistance which promotes improved sensitivity to insulin. As a result, it can help reduce the A1C levels.
- Can cause weight gain.
- Potential risk for heart failure when taking thiazolidines (brands: pioglitazone, rosiglitazone).
- Generally, it is not recommended for clients with renal impairment as medication has the potential to cause fluid retention.
- Risk for bone fractures, bladder cancer, and increased LDL cholesterol (rosiglitazone).
- Thiazolidines do not cause hypoglycemia and can be used in combination with other antidiabetic medications including insulin.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Which class of antidiabetic medications are known to put patients at risk for bone fractures?
- Can you name a condition that thiazolidines and sulfonylureas 2nd generation are generally not recommended for?
- What is a common side effect in both thiazolidines and sulfonylureas?
- What class of medication is suitable for clients with insulin resistance?
- Can you name two antidiabetic medications that can be used in combination with other antidiabetics because it has the benefit of not causing hypoglycemia?
Insulin therapy
Insulin therapy is commonly recommended for patients with T1DM. It can be used to help prevent the development and progression of diabetes (2). The ideal insulin regimen should be tailored based on individual needs and glycemic targets to better contend with physiological insulin replacement to maintain normoglycemia. Insulin therapy is also recommended for patients with hemoglobin A1c of greater than 9% - 10% and when symptoms of hyperglycemia are present (3).
Other Diabetes Interventions
The automation of glucose monitoring devices and insulin delivery systems is revolutionizing glucose management mainly because it promotes lifestyle flexibility and improved glucose management (2).
- Glucose Monitoring Devices- these devices are ideal for clients who are on insulin regimens and may become the standard for assessing glycemic controls in clients with DM (7).
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)- devices that are inserted subcutaneously and measure interstitial blood glucose levels. CGMs are devices that are used to provide glucose readings, trends, and alerts to the user in real-time to inform diabetes treatment decisions. (2)(3)
- Importance- CGM is recommended for all patients with diabetes who receive treatment with intensive insulin therapy, defined as three or more insulin injections per day for all individuals with hypoglycemia (frequent, several, nocturnal) (3).
- Known to reduce hyperglycemia and A1C levels.
- Insulin Pump Therapy- also known as Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) has had notable advances over the years. CSII is recommended for those with type 1 diabetes, although in recent studies, conventional CSII is also recommended for use in T2DM patients (2)(3). CSII is a small computer that is programmed to deliver fast-acting insulin continuously to the body using mechanical force via a cannula that is inserted under the skin (2).
- It is more precise and flexible in insulin dosing.
- Known to improve glycemic control.
- Cheaper than using Multi-Dose Insulin.
- Automated Insulin Delivery Systems (AIDS) - This is a diabetes management system that utilizes an insulin pump in conjunction with an integrated CGM and computer software algorithm (3).
- Advantages: precision and flexibility with insulin dosing.
- Recommended for T1DM: Achieve glycemic targets with less burden.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What is the main type of insulin used in CSII pumps?
- What type of diabetes category is more suitable for using CSII?
Upcoming Research
Islet cell transplant has been a biological solution to help treat patients with T1DM due to poor graft survival rates. Future research will focus on manipulating the beta cells in the pancreas to make them more viable. Other treatments that have been recently made available include incretins and Amylin which improve the absorption of insulin in the body (1).
- The development of other types of insulin that can be administered by inhalation.
- The development of immunosuppressant drugs that will help treat T1DM.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Can you name two recently developed medications to help with insulin absorption in the body?
Conclusion
Diabetes is a complex disease that requires a multi-disciplinary and patient-centered approach to help with effective management. Regular and early screening are necessary for those at risk for developing diabetes. Most importantly, ease and access to choices of managing diabetes are necessary.
Hospice and Palliative Care: What’s the Difference?
Introduction
Hospice and palliative care are unique health concepts often incorrectly used interchangeably. During my career as a hospice and palliative care nurse, I often heard the question, "What's the difference between Hospice and Palliative Care?"
I usually answered with a common phrase the Hospice and Palliative Care community uses to explain the difference, "All Hospice is palliative care, but not all Palliative Care is hospice." The statement is accurate but still confusing.
This course aims to shed light on these topics and emphasize the importance of enhancing end-of-life care, but let's start with Merriam-Webster's dictionary definitions.
- Hospice: "a program designed to provide palliative care and emotional support to the terminally ill in a home or homelike setting so that quality of life is maintained, and family members may be active participants in care” (4).
- Palliative: "relieving or soothing the symptoms of a disease or disorder without effecting a cure” (4).
The Merriam-Webster definitions help to clarify the differences further: Hospice is a program, and palliative care is a practice. They are two distinct approaches to providing comprehensive medical care and support for patients with serious illnesses, and they have essential differences worth exploring.
This course aims to delve into the different types of care, their philosophy, eligibility criteria, duration of services, and common myths and misconceptions surrounding hospice and palliative care. Additionally, it highlights nurses' crucial role as advocates and resources in these specialized fields.

Hospice Care
The modern hospice movement originated in the late 1960s in the United Kingdom, primarily through the work of Dame Cicely Saunders. Saunders, a nurse, and social worker, recognized the need for specialized care for patients with terminal illnesses. She founded St. Christopher's Hospice in London in 1967, which became the model for modern hospice care (12).
Saunders emphasized care that was less focused on disease treatment and more focused on an individual's physical, emotional, social, and spiritual needs. This approach prioritized providing comfort, pain management, and dignity for patients nearing the end of life (12).
The concept of hospice care gained international recognition and spread to other countries. By 1974, the first hospice program in the US was formed in Connecticut, and the hospice movement expanded rapidly (11).
Hospice care was primarily provided by volunteers who went into families' homes to care for their loved ones when no curative care was available. These same volunteers helped write the federal regulations adopted as the Medicare Hospice Benefit (MHB) in 1982 (5).
It is essential to discuss the MHB because the US government benefit made hospice a fundamental part of comprehensive medical care. It is the benefit through which most patients nearing the end of life receive care, and it has defined how we provide hospice care throughout the United States.
An integral part of hospice care is visits from a nurse, social worker, chaplain, and nurse aides. In addition, the patient and family have access to a hospice physician specializing in Hospice and Palliative Care (5). Hospice care focuses on providing compassionate, holistic, patient-centered care for individuals with terminal illnesses. The primary goal is to enhance the quality of life for patients and their families by addressing physical, emotional, social, and spiritual needs (5).
The MHB covers 100% of the financial cost for hospice services, including medications, supplies, and treatments required due to a terminal illness. The medicines commonly covered under the hospice benefit are for treating pain, nausea, anxiety, and other distressful symptoms, such as constipation (5).
Who can receive this care?
The MHB was designed for patients who are terminally ill with a six-month life expectancy, as determined by a physician (5). Life expectancy is one of the critical differences between Palliative Care and Hospice Care.
Healthcare providers, unlike statisticians or actuaries, are unskilled at predicting a six-month or less life expectancy. As part of the hospice federal regulations, local coverage determinations set by government intermediaries help healthcare providers determine who meets the criteria and, therefore, is eligible for hospice.
Key indicators predicting the end of life due to a specific disease process have been defined so that we can compare each patient to determine their eligibility for hospice care. Some key indicators are activity level, the times the patient has sought emergent care or has been hospitalized in the past six months, weight loss, and neurological status.
Patients generally receive hospice care when curative care is no longer an option. This is another crucial difference between Hospice and Palliative Care. There are exceptions, commonly for children, where curative and hospice care are provided. This is termed "concurrent" care.
How long do they receive services?
The key indicators that hospice physicians use to determine eligibility are based on averages of patients who have died with the specifically defined disease process. However, the average time to death is unreliable when judging how long an individual may live.
Therefore, hospice care is provided for as long as the patient's condition remains terminal, according to local coverage determinations, and they choose to continue receiving this specialized type of palliative care. In fact, the MHB has no end date, and the duration of services may vary depending on the progression of the illness and the patient's preferences.
For example, patients with chronic illnesses, such as heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and Alzheimer's, tend to have a less predictable trajectory of terminal illness due to periods of exacerbation and stability, which are common. Patients with chronic diseases tend to have a longer stay in hospice care. A waxing and waning pattern of decline is less typical with cancer-related disease, and these patients generally use fewer days of hospice care.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What is your understanding of the philosophy behind hospice care?
- How do you determine the appropriate duration of services for a hospice patient?
Palliative Care
The long-held theory regarding palliation, or soothing symptoms as defined by Merriam-Webster, is that if the treatment causes suffering with the result of a cure, the benefit of the treatment outweighs the burden. In other words, a person should be able to tolerate suffering for a positive end result. On the other hand, if no cure is available, suffering is inhumane.
Palliative Care emerged as an integral part of hospice care, focusing on providing comfort and support to patients with terminal illnesses (14). However, for people without terminal illnesses, some treatments and symptoms of curable diseases are so intolerable that patients may be unable or unwilling to continue curative treatment. Why should patients and families not receive physical, psychosocial, or spiritual support simply because they are not at the end of life?
The need for Palliative Care beyond hospice was identified in other healthcare settings, such as hospitals and home care. Over time, the philosophy and principles of Palliative Care gained recognition beyond the hospice setting. This led to the development of specialized palliative care services that aimed to provide comprehensive support to patients with serious illnesses, regardless of their prognosis (14).
In 1990, the World Health Organization (WHO) formally defined palliative care, emphasizing its holistic approach. The WHO defines palliative care as improving the quality of life of patients and their families facing life-threatening illnesses by preventing and relieving suffering through early identification and treatment of pain and other physical, psychosocial, and spiritual problems (13).
The American Academy of Hospice and Palliative Medicine (AAHPM) was established to promote and advance Palliative Care, and it has now become a recognized medical specialty. Palliative care education programs, certifications, and fellowships have been established to ensure the development of skilled professionals who provide palliative care (14).
Palliative Care is an essential part of healthcare, aiming to improve the quality of life for patients with serious illnesses and their families. It focuses on relieving symptoms, addressing psychosocial and spiritual needs, and enhancing communication and decision-making throughout the illness trajectory.
Philosophy
Palliative care aims to improve the quality of life for patients who suffer regardless of life expectancy, a key differentiator from hospice care. Palliative care focuses on symptom management, pain relief, and addressing patients' and their families' physical, emotional, and psychosocial needs.
Who can receive this care?
In the modern healthcare system, "palliative" is often used to define comfort care for patients with "serious illnesses." Palliative Care is available to individuals of any age and at any stage of a serious illness, including those undergoing curative treatments. It can be provided concurrently with curative treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation, another differentiator from hospice care. Individuals with serious illnesses may receive palliative care during a hospitalization, at home, or office visits.
How long do they receive services?
Unlike Hospice Care, Palliative Care can be provided for an extended duration even if the patient's condition is not terminal. The duration of services varies based on the individual's needs.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How does Palliative Care differ from Hospice care in terms of philosophy and approach?
- Can you explain the eligibility criteria for receiving palliative care?
Common Myths and Misconceptions
| Myth |
Fact |
|
Hospice care hastens death. |
Studies show that patients with the same diagnosis and burden of illness live longer with hospice than without (2). |
|
Palliative care is only for people who are dying. |
Palliative care is available to people of any age and stage of serious illness. |
|
Hospice is a place. |
Hospice is a form of care provided to people wherever they reside. |
|
Palliative care is only available in hospitals. |
Palliative care is available in hospitals, at home, or in a doctor's office. This is dependent on the availability of practitioners in your area. |
|
Hospice is only for the last days of life. |
Hospice is for the terminally ill with a life expectancy of 6 months or less and continues as long as a person remains terminally ill (15). |
|
Palliative care is only for the elderly. |
Palliative care is for all individuals with a serious illness. |
|
Hospice is the same as Palliative Care. |
Hospice is palliative care for the terminally ill. Palliative care is for all patients receiving curative treatment no matter the stage of illness, depending on the Palliative Care team's defined practice. |
|
Hospice and Palliative Care mean you are giving up hope. |
Hospice and Palliative Care aim to manage symptoms and improve the quality of life. |
|
Hospice and Palliative Care are expensive and not covered by insurance. |
Hospice care is 100% covered by Medicare and most other insurance (15). Palliative care is covered as a medical practitioner's visit in most Palliative Care programs. |

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are common misconceptions you have encountered regarding hospice or palliative care?
- How did you resolve the misconceptions surrounding palliative and hospice care?
Handling Difficult Conversations
Conversations, especially regarding end-of-life, are difficult for the clinician, the patient, and the family. Sensitive conversations also take time, patience, and empathy. Often, more time than a general practitioner or clinician has available. In my experience, patients approaching the end of life are often referred to as Palliative Care practitioners because of the practitioner's experience with difficult conversations. I also believe this referral practice is part of the confusion in understanding the difference between Palliative and Hospice Care.
Palliative Care Practitioners are not the only ones with the time and the skill to broach difficult conversations. Nurses also play a critical role in facilitating difficult conversations about end-of-life decisions, goals of care, and advance care planning.
Nurses often spend more time with patients and families than other disciplines. The relationship and trust nurses build with patients and caregivers makes them especially adept at starting difficult conversations.
A nurse must take the following actions before, during, and after a difficult conversation (3).
- Build a strong relationship with the patient and their family through active listening, empathy, and creating a safe space for open communication.
- Assess the patient's and family's readiness and preferences to engage in discussions. Ask patients and families questions regarding the amount and detail of information they want and the personspeople that need to be involved in decision-making. This information helps to tailor the discussion.
- Use practical communication skills such as clear and concise language aimed at providing information in a way that is understandable and sensitive to the emotional needs of the patient and family.
- Begin the conversation by assessing the patient and family's understanding of the diagnosis and prognosis to address any misconceptions or gaps in knowledge and ensure everyone is on the same page.
- Engage in a collaborative discussion about the patient's goals and values. Exploring their priorities and preferences regarding treatment options, symptom management, and quality of life helps align the care plan with the patient's values and wishes.
- Acknowledge and validate emotions, offering support and empathy throughout the conversation. Referral to appropriate psychosocial or spiritual support services may be necessary.
- Document the discussion and decisions made in the patient's medical records. Follow-up conversations should be scheduled to address any further questions, concerns, or changes in the patient's condition or preferences (3).
Should you find yourself in a position to start a difficult conversation, the following practical framework may be of assistance (3):
- Set aside time and make a plan to minimize interruptions.
- Before the conversation, take a moment to center yourself and release stress.
- Acknowledge the family and offer support by inquiring about their immediate needs.
- Open the conversation by asking what the patient and family know about their condition.
- Repeating what they know, ask them how they want to experience the time they have left.
- Empathize and allow them time to discuss and consider what they want.
- Based on their desires, educate them about the options for care.
- Consult with the interdisciplinary team and make appropriate referrals.

Case Study
Emily is a registered nurse who works the day shift on a bustling med-surg floor. She has a reputation for excellent communication skills and the ability to handle difficult conversations with empathy and grace, but she admits she never feels comfortable doing so. When she must have a difficult conversation, she uses a structured format to guide her to maintain her composure and empathy. Emily needed to use this framework when the physician asked her to talk to the family of Mr. Johnson about hospice care.
Mr. Johnson was a 75-year-old man admitted with advanced pancreatic cancer. His condition was deteriorating rapidly, and it was clear that curative treatments were no longer effective. Mr. Johnson's wife, Judy, was consistently by his bedside, her worry and sadness evident in her eyes. Emily knew Mrs. Johnson needed a plan because the fear of not knowing can be far worse than the reality. Emily asked her co-workers to cover for her other patients for the next 20 minutes so she could have a conversation about hospice.
Emily approached the room; she stopped momentarily and took a deep, centering breath. She released the day's stress and gave herself space to focus on this task. Emily gathered her thoughts and reminded herself of the framework she would use. She knew this conversation would be challenging but discussing the next steps in Mr. Johnson's Care was necessary. She entered the room with a warm smile, acknowledging both Mr. and Mrs. Johnson.
Emily began by asking how Mr. Johnson was feeling, allowing him to express any concerns or symptoms he was experiencing. She listened attentively, validating his feelings, and reassuring him that his comfort was a top priority.
After addressing Mr. Johnson's immediate concerns, Emily asked, "Mr. Johnson, what has the doctor told you about your prognosis?" Mr. and Mrs. Johnson began to verbalize that they knew Mr. Johnson was not getting better and was worsening. Mr. Johnson offered that the doctor told them curative care was not an option and that his prognosis may be short. Emily noticed Mrs. Johnson's eyes welling up with tears as Mr. Johnson spoke. Sensing her emotional distress, Emily offered her a comforting hand.
Emily asked, "How do you see spending your remaining time?"
Mr. Johnson quickly stated, "I want to go home."
Mrs. Johnson had a worried look on her face. Emily turned to her, and Mrs. Johnson stated, "I don't know how I can care for him at home."
Emily reassured Mrs. Johnson that this was a fear expressed by many spouses experiencing similar circumstances. Then, Emily introduced the concept of hospice care, explaining that it could provide specialized support and comfort to Mr. Johnson in the comfort of his own home. She highlighted the benefits of hospice, such as nurse visits, pain management, emotional support, and assistance with daily activities by an aide.
Understanding the gravity of the situation, Mr. Johnson and his wife looked at each other, their love and concern evident. After a moment of silence, Mr. Johnson nodded, expressing his willingness to explore hospice care to enhance his quality of life during this challenging time.
Emily continued the conversation, outlining the next steps and assuring the couple that the hospice team would work closely with them to develop a customized care plan. She provided them with a referral to hospice and assured them that she would be available to answer any questions.
As the conversation came to a close, Emily thanked Mr. and Mrs. Johnson for their trust and assured them that their decision was an essential step towards ensuring Mr. Johnson's comfort and dignity. She could see more lightness in Mrs. Johnosn's eyes. She was standing taller and breathing easier.
Emily left the room, knowing that this difficult conversation had set the foundation for a new chapter of Care focused on providing the support and compassion that Mr. Johnson and his wife deserved.
Nurse Role as Advocate
Nurses are the center of the interdisciplinary team, often providing communication and updates from patients and families to other practitioners such as social workers and physicians. The focused time they spend with patients in guided conversations and daily assessments allows nurses to gain a more in-depth understanding of the patient, family dynamics, and care goals.
A particular time of vulnerability for patients and families is during a serious illness and at the end of life. Nurses are responsible for advocating for patients' rights, respecting their wishes, and facilitating open communication between healthcare providers, patients, and their families. They play a pivotal role in ensuring the patient's voice is heard, and their needs are met.
Here are some ways nurses advocate for patients:
- Patient-centered care: Nurses help guide decision-making processes and ensure care aligns with the patient's values and goals when they ensure patients' preferences, values, and goals are at the center of their care (18).
- Shared decision-making: Nurses facilitate shared decision-making between patients, families, and healthcare providers by acting as intermediaries, ensuring patients' voices are heard and respected during discussions about treatment options, advanced directives, and end-of-life care planning (19).
- Psychosocial and spiritual needs: Nurses advocate for patients by providing emotional support, facilitating discussions about fears and concerns, and connecting patients with appropriate resources (20).
- Pain and symptom management: Nurses advocate for optimal comfort by assessing and addressing patients' physical distress, collaborating with the healthcare team, and advocating for timely interventions (21).
- Patient autonomy: Nurses who involve patients in decision-making processes, including information about treatment options, risks, and benefits, support patients in making informed choices (24).
- Informed consent: Nurses ensure patients understand the nature of their treatment, potential risks, and alternatives serve to advocate for informed consent (23).
- Healthcare disparities: Nurses who identify and address healthcare disparities based on race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, or geographic location work toward eliminating inequitable healthcare (8,10).
By advocating for patients during these critical times, nurses can help ensure that patients’ wishes are respected, their quality of life is optimized, and they receive compassionate and patient-centered care.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How is advocacy different with hospice and palliative care patients than patients with non-serious illness?
- During your career, in what ways have you advocated for patients with serious illness?
Providing Resources
To provide comprehensive care, nurses must be knowledgeable regarding hospice and palliative care and what each provides. Educating families and patients about their options is a great way to provide emotional support and help them navigate complex medical decisions.
As part of the MHB and many other insurers, hospice care is funded 100%. As a result, hospices are required to provide a specific set of resources (15). Medicare and private insurers frequently cover the cost of a Palliative Care practitioner on a per-visit basis. Thus, Palliative Care resources can vary widely per program. Knowing what resources are available through your local palliative care program is essential. Below is a chart of common hospice and palliative care resources and their benefits.
| Resource | Hospice | Palliative | Benefits |
| MD | Yes | Yes | Palliate symptoms through medical assessment and treatment. |
| NP | Maybe | Often | Palliate symptoms through medical assessment and treatment. |
| Registered nurse | Yes | Maybe | Care coordination, assessment, monitoring, symptom management, education, and communication with interdisciplinary teams. |
| Social Work | Yes | Maybe | Assist with community resources, counseling, advance directives, and other support. |
| Chaplain | Yes | Maybe | Assist with spiritual support, counseling, and connecting patients with their church affiliation and practices. |
| C.N.A. | Yes | Rare | Assist patients with physical care such as bathing and dressing. This is often a great support to caregivers. |
| Dietician | Yes | Rare | Assist and support patient’s dietary needs. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Yes | No | Alleviate common symptoms. |
| Medical Supplies | Yes | No | Wound care, other treatments, continence, and cleanliness needs. |
| DME | Yes | Maybe | Supports a patient’s ability to be independent. |
| PT, OT, ST | Yes | Able to make referrals | Support to maintain function, non-pharmacological pain management, assistance with communication, swallowing, wound care, and ADL support. |

Self Quiz
Ask yourself…
- How do you advocate for patient’s rights and ensure their wishes are respected in your healthcare setting?
- How do you support patients and their families during difficult conversations about end-of-life decisions?
- How do you provide emotional support to patients and families in need?
- What strategies do you employ to ensure effective communication between patients, families, and the interdisciplinary team?
- How do you manage your emotional well-being when working with families and patients nearing the end of life?
Becoming a Hospice or Palliative Care Nurse
Even though Hospice and Palliative Care are different, the skills and qualities of successful hospice and palliative nurses are similar. As previously discussed, Hospice and Palliative Care payment differs, with Palliative Care primarily funded by payment to medical practitioners. Because of the funding, it is rare for Palliative Care practices to employ nurses to the same degree as hospice. Many Palliative Care programs do not have nurses in their daily practice but may have them for patient follow-up or coordination of care.
For this education, we are focused on the requirements of becoming a hospice and palliative care nurse, understanding that positions for Hospice nursing are more prolific than strictly Palliative Care nurses.
Educational Requirements
While many nurses can specialize in a specific area of care, for example, geriatric, cardiac, critical care, surgical, or emergency care, hospice, and palliative care nurses care for patients with a wide range of illnesses, ages, and abilities.
Hospice and palliative care nurses need to understand the ordinary course of numerous conditions in multi-aged patients to anticipate, prepare, and quickly palliate symptoms of the specific disease. They must be skilled in the assessment of patients and able to detect subtle changes in conditions that affect the patient’s plan of care.
Certain requirements need to be met to become a hospice and palliative care nurse (17). Here are the general requirements:
- Licensure: Current, unrestricted license as a registered nurse (RN) or licensed practical/vocational nurse (LPN/LVN) in the state where they practice. The specific licensure requirements may vary by state.
- Certification: Hospice nurses are often required to have specialized certifications related to hospice and palliative care. The most common certification for hospice nurses is the Certified Hospice and Palliative Nurse (CHPN) credential, offered by the Hospice and Palliative Credentialing Center (HPCC). This certification demonstrates expertise in providing care to patients with life-limiting illnesses. This certification requires two years of hospice experience for eligibility to take the certification test (16).
- Education and Experience: There are no specific education requirements for hospice nurses required by regulatory bodies. However, most hospice agencies prefer nurses with a bachelor’s degree in nursing (BSN) or higher. As written above, hospice and palliative care patients range in age and illness. Therefore, many agencies also prefer nurses with two years of experience in a medical-surgical healthcare setting (17).
- Training: Hospice nurses must receive comprehensive training in hospice care and be knowledgeable about the philosophy, principles, and practices of hospice and palliative care. The hospice agency typically provides this training and covers pain management, symptom control, psychosocial support, communication, and end-of-life care (17).

Self Quiz
Ask yourself…
- What is your experience with the importance of certification as perceived by patients and families?
- What is your experience with the importance of certification as perceived by healthcare professionals?
Skills and Qualities
Hospice and palliative care nurses must thrive on working independently since more than 80% of hospice and palliative care is provided in patient's homes. While hospice and palliative care are under the management of the physician, the hospice nurse is the primary assessor and at the patient's bedside.
Hospice nurses must be organized, have firm boundaries, and be able to systematize their practice to see multiple patients in one day, with the requirements of driving, documenting, communicating with the interdisciplinary team, and providing care according to the individual patient care plan. In addition, they must provide support and education to the patients and their families.
Nurses in hospice and palliative care settings require excellent communication, empathy, and the ability to navigate complex ethical dilemmas and difficult conversations.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How do you stay current on the latest research and best practices regarding caring for patients with serious illnesses or at the end of life?
- Can you describe a situation where you had to manage complex pain or symptoms?
- What additional training or education have you pursued to better manage patients with serious illnesses or near the end of life?
Conclusion
In conclusion, Hospice and Palliative Care represent two distinct but interconnected approaches to providing comprehensive medical care for individuals with serious illnesses. While hospice care focuses on terminal patients and aims to enhance their quality of life, Palliative Care addresses the needs of individuals at any stage of a serious illness.
Nurses are crucial in advocating for patients, facilitating difficult conversations, and providing resources to support patients and their families. By understanding the philosophy, eligibility criteria, and duration of hospice and palliative care services, nurses can contribute to the holistic well-being of patients in these specialized fields.
As society continues to recognize the importance of providing comprehensive end-of-life care and support for patients with serious illnesses, it is crucial to foster awareness, education, and support for hospice and palliative care services. By doing so, we can collectively work towards enhancing the experiences of those facing life-limiting illnesses, offering comfort, compassion, and dignity throughout their journey.
Navigating Difficult End of Life Conversations
Introduction
Talking about death is generally difficult for the average person. It is even considered taboo in some cultures or situations. For some nurses, having end of life conversations is a routine part of the profession. A hospice nurse, for example, carries the responsibility of managing care for a dying patient, and ultimately informing the patient’s family that death is imminent.
A lack of training, experience, or confidence in this area could result in poor delivery, unrealistic expectations, and an overall negative dying experience. Most people do not have experience or even a baseline when it comes to death and dying. This makes end of life conversations much more important in the delivery of patient care.
Perspectives About Dying and Death (Philosophical, Psychological, and Spiritual)
Philosophical
The human experience of death and dying is not one sided. On the contrary, there are many things to be considered to understand it fully. This goes beyond a scientific approach. An understanding of philosophical reasoning related to death is imperative to provide a thorough explication of the human dying experience. Historically, death has been an intrinsic part of life throughout various civilizations.
Ancient Egyptians spent much time preparing for the next life. Life was perceived as a dream that passed quickly. Death was viewed as eternal. Egyptians believed that the dead would make their way over to The Kingdom of Orisis, where they would spend eternity.
Ancient Greek civilization also viewed death in a particular light. According to San Filippo, “Greeks perceived death as a release of the soul from the body. The soul, which was considered to be part of the mind, was believed to be immortal. It was considered that the soul lived before the body and would live again in another life” (1).
Lastly, it has been noted that when it comes to fearing death, people create philosophies and theologies due to an inability to visualize our own death and afterlife.
Psychological
The psychological aspect of death is just as important as the physical. The thought of death alone has the potential to evoke various memories and feelings. You will typically find that a person either accepts or fears death (positive outlook vs negative outlook). This can be a fear of suffering, pain, or of the unknown. These views are typically formed based on past experiences with death.
Often, a person may have no underlying baseline when it comes to dying or death. That first experience with death can potentially shape someone’s entire perspective. Fearing death could be attributed to a fear of the unknown, lack of relatable experience, a negative experience, or a lack of communication regarding death, due to a cultural taboo, for example.
On the other hand, things like faith, positive experiences, and imminent death may cause someone to be more accepting of death. Often, someone facing imminent death may be forced to think about it and come to terms with it. In a study of terminally ill patients facing death, “The participants were afraid of death and earnestly desired to live but felt that death was imminent. To escape their distress, they attempted to accept the situation by thinking that all lives are finite, and death had to be accepted” (2). This is an example of coming to terms with an impending death and accepting it.
Spiritual
Spiritual perspectives on death should be considered when discussing views on dying. History shows that humans have long held beliefs that life does end when the body dies. Many tend to believe that once a person dies, their soul is then freed, and can go on to another life or be reincarnated into someone or something else. Religious ideologies contain a vast amount of knowledge and wisdom regarding death. “Religion and spirituality help individuals make sense of what awaits them near the end of life and help the dying cope with their terminal condition” (7).
What happens after death may vary from one religion to the next. Many religions also have a heaven or heaven like final place where the deceased can rest and be with other who have also died. One of the oldest ideologies of human history is the belief that there can be life after death.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Historically, how has death been viewed in different civilizations?
- Why might a patient fear death and dying?
- What causes patients to be more accepting of death?

Impact on Nurses
Imagine working as a hospice nurse. Your sole purpose is to provide end-of-life care for terminally ill patients. This includes providing information on what to expect at the end of life. At any given time, you have patients that could be imminently dying.
You are a source of knowledge and comfort for a patient and their family during this time. In the end, you will likely be there when the patient takes their last breath. How can one prepare to handle this scenario time and time again? Should a nurse feel sadness for a patient that was expected to die, or should they emotionally separate themselves?
The latter may prove hard to do. The reality is that nurses are frequently exposed to death and dying in a variety of settings. A patient’s dying process can be planned or not and this distinction may mean different things for different people. Typically, nurses are taught skills to help prevent death.
This may be a hard thought process to overcome when the goal is not curative, but comfort focused. These patient interactions help to shape a nurse’s feelings on death and dying. “Nurses are frequently exposed to dying patients and death in the course of their work. This experience makes individuals conscious of their own mortality, often giving rise to anxiety and unease.
Nurses who have a strong anxiety about death may be less comfortable providing nursing care for patients at the end of their life” (3). This ‘death’ anxiety could lead to disastrous outcomes for both the nurse and the patient. Nurses should be aware of their own thoughts and attitudes towards death, and how these could affect their ability to provide patient care.
Caring for the dying involves both skill and emotional support from nurses. Younger nurses and nurses with less experience with death may have greater difficulty caring for dying patients. End of life education and an introspective look at oneself are imperative when it comes to providing quality care. “Nurses’ professional experience is positively correlated with their position, professional level (rank), EOL care experience, competence in EOL, and another knowledge.
Nurses who have a positive attitude seem more likely to have more competence in dealing with patients’ symptoms at EOL and better knowledge of EOL care (3). The more palliative knowledge nurses had, the more competence they felt. Moreover, competence dealing with patients’ symptoms in EOL care was correlated with older nurses” (8). Positive conversations about death and dying usually lead to a positive dying experience.
To reach this point, nurses and other healthcare professionals need to know how to have these conversations. In a society that is so focused on the living, receiving education on death can be difficult. When death is perceived as a part of life, only then will people feel more comfortable talking about it.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What role do nurses play in death and dying?
- In what ways are nurses affected by death?
- How do previous experiences shape our views about death?
- What are some potential indicators of a nurse’s ability to provide quality care at EOL?
Communication Strategies
Many people are uncomfortable talking about death and dying and tend to shy away from such conversations. This may also be true for nurses. Talking about death should not be a formidable task. Nurses should be able to comfortably implement these conversations in their practice when needed. Effective communication is imperative throughout a patient’s trajectory.
Conversations about death and dying can impact patient care. “Research has shown that talking about and planning the EOL is important for how the final days in a patient’s life may play out and is associated with reduced costs as well as a higher quality of care in the final weeks of life” (4). In a society so focused on life, it may be difficult for nurses and other health professionals to obtain the skills needed to confidently speak with patients about death.
To effectively talk to patients about death, nurses should first be willing to initiate and discuss the topic. There are important strategies to remember when talking about the end of life. “Qualitative research on the end of life has revealed that medical personnel should consider the following strategies when conducting EOLD: open and honest conversation, setting treatment goals, and balancing hope with reality” (13).
Patients should also be encouraged to express their thoughts, fears, and to ask questions. It is also important to be honest and forward with patients. No “beating around the bush”. This means using words like “dying” and “death” while having these conversations.
One communication strategy, VALUE, “recommends to value and appreciate statements of family members, acknowledge their emotions, as well as to listen and ask questions to understand who the patient was as a person” (9). Nurses should keep the following in mind: a patient’s comfort level with death, goals of care, expectations, and cultural factors. Having this knowledge will help to guide the conversation.
Lastly, when a nurse feels confident and exhibits calmness while talking about death, a patient will more than likely feel the same way.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- How do conversations about death impact patient care?
- What can nurses do to effectively communicate with their patients about death?
- What strategies should be utilized when talking about death?
Stages of Grief
Nurses are not immune from experiencing grief or loss. We mourn personally and we mourn alongside our patients and their families. “Grief and loss are something that all people will experience in their lifetime. The loss may be actual or perceived and is the absence of something that was valued. An actual loss is recognized and verified by others while others cannot verify a perceived loss.
Both are real to the individual who has experienced the loss. Grief is the internal part of the loss; it is the emotions related to the loss” (4). Grief allows a person to begin to deal with the pain associated with loss and to heal. There are five stages of grief which were identified in Dr. Elisabeth Kübler-Ross in her book Death and Dying.
- Denial: This stage Is not necessarily about denying that the loss happened. Instead, it is more about denying the feelings associated with the loss. Denial lets us face our feelings of grief. “As an individual is able to accept that this loss is their reality, they will be able to move into the healing process and denial will begin to diminish” (5).
- Anger: A grieving person may feel anger towards a variety of people associated with the loss. This is a normal and a necessary part of the healing process. “Under the anger is the individual’s pain. Anger provides structure, and that is better than preceding numbness. It can be a challenge for some to feel the anger; sometimes it is easier to try and suppress the anger. Feeling anger and addressing anger is part of the grieving process” (5).
- Bargaining: Grieving people may begin to say things to themselves like, “If this__, then this __”, or “I will do anything if you take the hurt away” (5). This stage may occur at any point in the grief process. Once this step is reached, the person can begin to move through the stages in different ways.
- Depression: This stage involves a realization that the situation is real. “Empty feelings come forward, and one’s grief moves in on a deeper level than before. This type of depression is not a sign of mental illness; although reaching out for help may be the right step. It is an appropriate response to a great loss. An individual may withdraw from their daily life activities, and they may feel a fog of intense sadness” (4). Depression after a major loss is normal and necessary in the healing process.
- Acceptance: Entering this final stage does not mean one is completely okay with what has happened. In fact, one may never be as they once were prior to the loss. “Acceptance, as a stage, is about accepting that this is their new reality, and it is permanent. Life cannot go on as it once did, but through acceptance, life can and will go on” (5). Individuals in this stage must realize that change is necessary to adjust to the new normal.
Not everyone experiences grief in the same way. Grief is a very personal experience that affects people in different ways. Nurses should be familiar with the stages of grief to be able to offer optimal patient care to grieving patients and their families. This includes recognizing signs of depression and possible suicidal ideation, providing empathy, compassion, education, and resources to those in need.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are the stages of grief?
- Why should nurses be familiar with the stages of grief?
- What purpose does grief serve?
End of Life Process
Phases of Dying
Although everyone experiences death differently and on their own terms, there are two main pathways that most people take before dying. The dying process can be broken up into two phases: the transitioning phase, and the actively dying phase. The amount spent in each phase varies from person to person.
The transitioning phase usually begins 2-3 weeks prior to death. Major changes in function and the ability to do activities of daily life are observed during this time. Patients may even begin falling prior to entering this phase. Becoming bedbound is common as one will begin to spend most of their time sleeping.
This means decreased responsiveness, less interest in normal activities and hobbies, decreased interaction with family and friends, and an overall decline in one’s interest in external factors. It is possible to be roused during this phase, but this may only be possible in short intervals. It is not uncommon for transitioning patients to speak to or about loved ones that have already passed away. They may even report seeing deceased family in the room with them (11).
This should not be feared and is an important part of a person’s dying process. Incontinence may also begin during this time and briefs will be needed. Perhaps one of the most noticeable and difficult changes to witness, especially by friends and family, is changes in appetite. Patients will begin to show less interest in food and liquids. A greater difficulty swallowing will become apparent. “Refusal of food and fluid by a dying person is a common occurrence, particularly as the body slowly shuts down, and this may be the evidence signifying an actively dying process rather than starvation” (11).
Lastly, symptoms like restlessness, agitation, and pain may arise and detract from one’s comfort level. Although most patients will spend about two weeks transitioning, time can vary from days to weeks. The transitioning phase can also be skipped altogether, depending on the person.
Once the transitioning phase has concluded, the actively dying phase will begin. Actively dying immediately precedes death. This phase is usually short, lasting about 48 hours. Once actively dying, death is imminent, and a patient is expected to pass away at any moment. This phase is markedly different from the previous phase, and symptoms tend to become more apparent. “The following five changes constitute objective evidence of the end of life: diminished daily living performance, decreased food intake, changes in consciousness and increased sleep quantity, worsening of respiratory distress, and end-stage delirium” (12).
One key difference is one’s ability to response to tactile or verbal stimuli. The actively dying patient is obtunded and no longer responds to external forces. There could be slight reactions, but nothing meaningful. This is a comatose state.
There are many observable changes, including changes in vital signs. Blood pressure begins to drop, heart rate speeds up and eventually slow, respiratory rate picks up, and temperature may become elevated. Respiratory differences tend to be the most common observable changes. Cheyne-Stokes may occur, and the overall breathing pattern can be very irregular. Apnea is also common (11).
Many patients experience what is known as the “death rattle”. This very noticeable sound is due to an accumulation of secretions in the upper airway. This is a hallmark of the actively dying phase, but it is not experienced by everyone. “Death rattle is a strong predictor of imminent death, and nearly 80% of people die within 48 hours after its onset” (11).
Skin changes also occur. The body may become cool to touch, cyanosis may develop in the nail beds of fingers and toes, and mottling can occur usually beginning in the lower extremities and later spreading to other parts of the body. Skin may also become very pale. Urine output will decrease and become concentrated as evidenced by an amber color.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What are the dying phases?
- What changes are observed when someone is transitioning?
- What are some expected physical changes in the active dying phase?
- What education should a nurse provide to someone taking care of a patient that is actively dying?
Nursing Assessment and Care
Since there are so many drastic changes observed during the transitioning phase, proper education is crucial for caregivers. Nurses should reassure them that what the patient is experiencing is normal and to be expected. “At the end of life, most patients are in a state of lethargy, wherein their consciousness progressively declines, and sleep duration increases; therefore, it is necessary to provide appropriate explanations to patients and their families so that they can accept these symptoms as part of the natural end-of-life process” (12).
Family members usually try to wake the sleeping transitioning patient and have them attempt activities that could be done in the past. This is dangerous for the pt and can lead to injuries and more agitation. Becoming bedbound is a major change and puts the patient at risk for pressure injuries and increased pain. Fragile skin combined with new episodes of incontinence are topics that should be discussed, and proper supplies should be used.
Other potential barriers to a peaceful transitioning period are force feeding and aspiration. Nurses should provide education on what is acceptable and needed at this point. Patients will not die of hunger or lack of water. Allowing the patient to eat and drink small amounts is okay (12).
This amount will decrease as the body starts shutting down. Ice chips can be used while the patient is still alert. Utilizing mouth swabs with water is enough to hydrate the oral cavity and keep the patient comfortable until the end. During this time, symptoms can seemingly come out of the blue.
A once calm patient can become highly agitated in a short period of time. Medications should be added timely to ensure that the patient has a peaceful death. Information on medication and interventions to control uncomfortable end of life symptoms like pain, agitation, and restlessness should be provided to caregivers. Hospice patients, for example, have a comfort kit with various medications to use during this time.
Medications can be used as needed or scheduled to keep patients comfortable. (12). As the patient enters the actively dying phase and becomes less alert and aware, it is important that friends and family continue to talk to the patient and keep conversations positive around the patient. Hospice nurses, for example, are sure to tell caregivers that hearing is the last thing to go, so they should continue to speak to their loved one. Since vital signs start to become abnormal, reassurance is usually needed to keep family comfortable.
Not all vital signs need to be taken in the final stages. Taking blood pressure, for example, could cause discomfort. Death education related to respiratory changes is imperative. “Abnormal breathing patterns such as shallow breathing sound become increasingly common starting 1 week before death” (12).
Caregivers should be informed that breathing too fast or too slow at this point is not an emergency and there are things that can be done to promote comfort like applying oxygen, keeping the head of the bed upright, and keeping the room cool. Medications can also be given to decrease the death rattle. It should be noted that patients do not experience discomfort from the death rattle.
Lastly, not having a bowel movement or passing urine during the last few days of life is normal and interventions are not needed. Education and support are especially important during the final phases of life. With their peaceful words and deep knowledge base, nurses can be instrumental in facilitating a peaceful death.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- Is it reasonable to obtain vital signs every two hours? Why or why not?
- If the family expresses concern about changes in bowel or urinary habits, what can you say to reassure them?

Resources and Support
Planning, coordinating, and executing quality end of life care can be challenging for health care workers. This period can also be one of the most challenging times for both patients and their loved ones. There are available resources for health care workers, patients, and their loved ones that provide information on end-of-life care.
Hospice care is an invaluable resource and source of support. This is available to terminally ill patients with a life expectancy of 6 months or less.” Hospice care is the term given to the care provided when a patient is given a prognosis of death within 6 months, and they do not pursue curative treatments They focus on improving the quality of life which can mean many things” (10).
Care can be provided in any setting that a patient calls home. The hospice team includes a medical director, registered nurse, chaplain, social worker, home health aide, and often a nurse practitioner. Symptoms and care can be managed at home with the help of covered medications, supplies, and medical equipment. Hospice allows patients to reach their goal of dying peacefully at home. A bereavement team also provides support during the process. (10?)
Palliative care, another form of comfort care, can also be utilized to maintain comfort at the end of life. Unlike hospice, patients receiving palliative care do not need to have a life expectancy of 6 months or less. “Research found that timely EOL care discussions allowed family members to make use of hospice and palliative care services sooner and maximize their time with the patient” (6).
Nurses should be educated in other end of life resource topics such as advanced directives, POLST (Physician Orders for Life Sustaining Treatment), and Durable Medical Power of Attorney. Looking ahead and having meaningful discussions regarding end-of-life planning can help prevent the stress of needing to address these things when death is imminent.

Self Quiz
Ask yourself...
- What care options are there for patients at the end of life?
- What is the difference between palliative and hospice care?
- What tools can the nurse use to help patients in end-of-life planning?
Conclusion
End of life conversations have a profound impact on not only patient care, but also on the dying process itself. Research shows that when implemented appropriately, these conversations improve patient relationships with healthcare workers, lead to better outcomes, and allow for a more positive dying experience. Nurses play a critical role in end-of-life processes in many different settings. With education, practice, experience, and confidence, nurses can incorporate conversations about death and dying to provide quality care.
References + Disclaimer
- Agency for Healthcare Quality and Research. (2023). TeamSTEPPS program: Welcome guide for frontline providers. Retrieved from https://www.ahrq.gov/teamstepps-program/welcome-guides/frontline-providers.html
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (2022). Six domains of healthcare quality. Retrieved from https://www.ahrq.gov/talkingquality/measures/six-domains.html#_ftn1
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (2023). Talking quality: Measuring the quality of hospice care. Retrieved from https://www.ahrq.gov/talkingquality/measures/setting/long-term-care/hospice.html
- Agency of Healthcare Research and Quality. (2020). Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (CAHPS): Section 4: Ways to approach the quality improvement process (Page 2 of 2). https://www.ahrq.gov/cahps/quality-improvement/improvement-guide/4-approach-qi-process/sect4part2.html
- Alshammary, S. A., Abuzied, Y., & Ratnapalan, S. (2021). Enhancing palliative care occupancy and efficiency: A quality improvement project that uses a healthcare pathway for service integration and policy development. BMJ Open Quality, 10(4):e001391. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjoq-2021-001391
- American Society for Quality. (2023). The history of quality. Retrieved from https://asq.org/quality-resources/history-of-quality
- American Society for Quality. (2023). What are the five s’s (5s) of Lean. Retrieved from https://asq.org/quality-resources/lean/five-s-tutorial
- Anderson, J. E., Lavelle, M., & Reedy, G. (2021). Understanding adaptive teamwork in health care: Progress and future directions. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy, 26(3):208-214. Retrieved from https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1355819620978436
- Backhouse, A., & Ogunlayi, F. (2020). Quality improvement into practice. BMJ 2020, 368:m865. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m865
- BerryDunn. (2022). National healthcare at home best practices and future insights study: State of the industry and executive summary. Retrieved from https://advisors.berrydunn.com/hubfs/PDF_Downloads/Healthcare-at-Home-Study.pdf?gclid=LastTest
- Foxwell, A. M. (2022). Palliative and end-of-life care. In: Hinkle JL, Cheever KH, eds. Brunner & Suddarth’s Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing. 15th ed. Wolters Kluwer.
- Hines, K., Mouchtouris, N., Knightly, J.J., & Harrop, J. (2020). A brief history of quality improvement. Global Spine Journal, 10(1S):5S-9S. Retrieved from https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/2192568219853529
- Hussain, F.A. (2021). Psychological challenges for nurses working in palliative care and recommendations for self-care. British Journal of Nursing, 30(8). Retrieved from https://www.britishjournalofnursing.com/content/professional/psychological-challenges-for-nurses-working-in-palliative-care-and-recommendations-for-self-care/
- Institute for Healthcare Improvement. (2023). How to improve: Model for Improvement. https://www.ihi.org/resources/how-to-improve
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality of Health Care in America. (2001). Crossing the quality chasm: A new health system for the 21st Century. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US). Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK222265/
- Jones, B., Vaux, E., & Olsson-Brown, A. (2019). How to get started in quality improvement. BMJ, 364:k5408. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k5437
- Leiter, R.E., Pu, C.T., Mazzola, E., et al. (2020). Engaging hospices in quality measurement and improvement: Early experiences of a large integrated health care system. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, 60(4);P866-873.E4. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2020.05.027
- National Archives and Records Administration. (2023). Code of Federal regulations: Part 418 – hospice care. Retrieved from https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-42/chapter-IV/subchapter-B/part-418
- National Consensus Project for Quality Palliative Care. (2018). Clinical practice guidelines for quality palliative care, 4th edition. National Coalition for Hospice and Palliative Care. Retrieved from https://nationalcoalitionhpc.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/NCHPC-NCPGuidelines_4thED_web_FINAL.pdf
- National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. (2023). Hospice Item Set (HIS). Retrieved from https://www.nhpco.org/regulatory-and-quality/quality/hqrp-hospice-item-set-his/
- National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. (2022). Regulatory alerts: FY 2023 Medicaid hospice rates and state/county rate charts. Retrieved from https://www.nhpco.org/wp-content/uploads/NHPCO-Reg-Alert_FY-2023-Medicaid-Hospice-Rates.pdf
- National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. (2023). QAPI toolkit: Professional development and resource series. Retrieved from https://www.nhpco.org/regulatory-and-quality/quality/hospice-quality-updates-resources/qapi-toolkit/qapi-toolkit/
- Talevski, J., Wong Shee, A., Rasmussen, B., Kemp, G., & Beauchamp, A. (2020). Teach-back: A systematic review of implementation and impacts. PloS one, 15(4):e0231350. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0231350
- U.S. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2023). Hospital quality reporting program (HQRP): Current measures. Retrieved from https://www.cms.gov/medicare/quality/hospice/current-measures
- U.S. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2023). Hospice. Retrieved from https://www.cms.gov/medicare/payment/fee-for-service-providers/hospice
- U.S. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2023). Quality measures. Retrieved from https://www.cms.gov/medicare/quality/measures
- Arnetz, J. E. (2022, April). The Joint Commission’s new and revised Workplace violence prevention standards for hospitals: A major step forward toward improved quality and safety. Joint Commission journal on quality and patient safety. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8816837/
- American Nurses Association. (2019, January). Reporting incidents of Workplace Violence – Ana Enterprise. Reporting Incidents of Workplace Violence. https://www.nursingworld.org/~495349/globalassets/docs/ana/ethics/endabuse-issue-brief-final.pdf
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration. (n.d.). Healthcare – workplace violence. https://www.osha.gov/healthcare/workplace-violence/
- Minnesota Nurses Association. (2022, August 10). Hennepin Healthcare Nurses report rising violence against nurses and patients, cite under-staffing, unresponsive management as barriers in new survey. Minnesota Nurses Association. https://mnnurses.org/hennepin-healthcare-nurses-report-rising-violence-against-nurses-and-patients-cite-under-staffing-unresponsive-management-as-barriers-in-new-survey/
- ANA) Workplace violence. (2017). https://www.nursingworld.org/practice-policy/advocacy/state/workplace-violence2/
- Sahebi, A., Golitaleb, M., Moayedi, S., Torres, M., & Sheikhbardsiri, H. (2022, August 8). Prevalence of workplace violence against health care workers in hospital and pre-hospital settings: An umbrella review of meta-analyses. Frontiers in public health. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9393420/#:~:text=The%20overall%20prevalence%20of%20WPV,%2C%20and%2010.5%25%20(95%25
- Song, C., Wang, G., & Wu, H. (2020, December 3). Frequency and barriers of reporting workplace violence in nurses: An online survey in China. International Journal of Nursing Sciences. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7859538/
- Staff, A. (2022, November 4). End Nurse Abuse: 4 Actions You Can Take Today. Aorn.org. https://www.aorn.org/article/2021-12-03-End-Nurse-Abuse
- Fountain, D., Zankowski, D., & Arriola, J. (n.d.). Reporting incidents of Workplace Violence – Ana Enterprise. Reporting incidents of Workplace Violence. https://www.nursingworld.org/~495349/globalassets/docs/ana/ethics/endabuse-issue-brief-final.pdf
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (n.d.). Workplace violence in healthcare, 2018. U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. https://www.bls.gov/iif/factsheets/workplace-violence-healthcare-2018.htm
- Vincent-Höper, S., Stein, M., Nienhaus, A., & Schablon, A. (2020, May 1). Workplace aggression and burnout in nursing-the moderating role of follow-up counseling. International journal of environmental research and public health. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7246829/
- Creating a culture of safety in nursing. ANA. (2023, September 12). https://www.nursingworld.org/resources/individual/nurse-managers/safety-in-nursing/
- AlGhatrif, M., & Lindsay, J. (2012). A brief review: History to understand fundamentals of electrocardiography. Journal of Community Hospital Internal Medicine Perspectives, 2(1), 14383. https://doi.org/10.3402/jchimp.v2i1.14383
- Alila Medical Media. (2017). Cardiac action potential, animation. [YouTube Video]. In YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v7Q9BrNfIpQ
- American Heart Association. (2016). Ventricular fibrillation. Www.heart.org. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/arrhythmia/about-arrhythmia/ventricular-fibrillation
- Atkielski, A. (2023). PQRST segment. In StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551635/figure/article-20939.image.f1/?report=objectonly
- Benzoni, T., & Cascella, M. (2021). Procedural sedation. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551685/
- Bern Dibner. (2018). Luigi Galvani | Italian physician and physicist. In Encyclopædia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/biography/Luigi-Galvani
- Birnbaum, Y., Ye, Y., Smith, S. W., & Jneid, H. (2021). Rapid diagnosis of STEMI equivalent in patients with left bundle‐branch block: Is it feasible? Journal of the American Heart Association, 10(18). https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.121.023275
- Bracey, A. (2023). Posterior MI. In ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553168/figure/article-698.image.f1/?report=objectonly
- Burns, E., & Buttner, R. (2021). PVCs. In litfl.com. https://litfl.com/premature-ventricular-complex-pvc-ecg-library/
- Burns, E., & Buttner, R. (2023a). Anterior MI. In litfl.com. https://litfl.com/anterior-myocardial-infarction-ecg-library/)
- Burns, E., & Buttner, R. (2023b). Monomorphic vtach. In litfl.com. https://litfl.com/ventricular-tachycardia-monomorphic-ecg-library/
- Burns, E., & Buttner, R. (2023c). Torsades de Pointes. In litfl.com. https://litfl.com/polymorphic-vt-and-torsades-de-pointes-tdp/
- Cadogan, M. (2018, August 1). Delta wave. Life in the Fast Lane. https://litfl.com/delta-wave-ecg-library/
- Cadogan, M. (2022). Lead positioning. In litfl.com. https://litfl.com/ecg-lead-positioning/
- Cardiac Science. (2021). ECG graph paper. In cardiacsciencesmb.ca. https://cardiacsciencesmb.ca/ecg-graph-paper/
- Cardogan, M., & Buttner, R. (2021). Sgarbossa criteria. In litfl.com. https://litfl.com/sgarbossa-criteria-ecg-library
- Cascino, T., & Shea, M. (2022, September). Electrocardiography – cardiovascular disorders. MSD Manual Professional Edition. https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/cardiovascular-disorders/cardiovascular-tests-and-procedures/electrocardiography
- Center for Advanced Cardiac and Vascular Interventions. (2023). Mobile cardiac telemetry (MCT). Center for Advanced Cardiac and Vascular Interventions. https://cacvi.org/services/diagnostic-procedures/mobile-cardiac-telemetry/
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. (2021, January 8). FDA drug safety communication: New information regarding QT prolongation with ondansetron (zofran). FDA. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-drug-safety-communication-new-information-regarding-qt-prolongation-ondansetron-zofran
- Chruścik, A., Kauter, K., Windus, L., & Whiteside, E. (2021). 6.2 cardiac muscle and electrical activity. In usq.pressbooks.pub. University of Southern Queensland. https://usq.pressbooks.pub/anatomy/chapter/6-2-cardiac-muscle-and-electrical-activity/
- Cleveland Clinic. (2022a). Asystole. In my.clevelandclinic.org. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/22920-asystole
- Cleveland Clinic. (2022b, June 3). Pulseless electrical activity (PEA): Causes and treatment. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/23213-pulseless-electrical-activity
- Cleveland Clinic. (2022c, June 11). Cardiac event monitor: Types and uses. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/23272-cardiac-event-monitor
- Clip Art Library. (2023). EKG machine. In https://clipart-library.com/clipart/2049261.htm.
- Cohagan, B., & Dov Brandis. (2019, February 17). Torsade de Pointes. Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459388/
- Costa, C. (2016). Figure 2.1: A) basic cardiac anatomy and blood circulation through the… In ResearchGate. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-Basic-cardiac-anatomy-and-blood-circulation-through-the-hearts-cavities-and-valves_fig20_320411039
- de Jong, J. (2007a). 2nd AV block. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:Wenckebach2.png
- de Jong, J. (2007b). A fib. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:Afib_ecg.jpg
- de Jong, J. (2007c). Normal sinus rhythm. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:Nsr.jpg
- de Jong, J. (2008). SVT. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:Avrt_small.svg
- de Jong, J. (2009). A flutter. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:ECG000011.jpg
- de Jong, J. (2010a). 1st AV block. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:Rhythm_1stAVblock.png
- de Jong, J. (2010b). 3rd AV block. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:Rhythm_3rdAVblock.png
- de Jong, J. (2010c). A fib RVR. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:Afib_f_VR_ecg.jpg
- de Jong, J. (2010d). Bigeminy PVC. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:Rhythm_bigemini.png
- de Jong, J. (2010e). Idioventricular rhythm. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:Rhythm_idioventricular.png
- de Jong, J. (2010f). PAC. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:Rhythm_premature.png
- de Jong, J. (2010g). PVCs. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:Rhythm_ventricular_premature.png
- de Jong, J. (2010h). Ventricular fibrillation. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:Rhythm_ventricular_fibrillation.png
- de Jong, J. (2011a). Mobitz. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:Rhythm_Mobitz.png
- de Jong, J. (2011b, December 13). Normal tracing. En.ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=Normal_Tracing
- de Jong, J. (2011c). Sinus tachycardia. In ecgpedia.org. https://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=File:Rhythm_tachycardia.png
- Dmitriy Scherbak, & Hicks, G. J. (2019, April 7). Left bundle branch block (LBBB). Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482167/
- Douedi, S., & Douedi, H. (2020). P wave. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551635/
- Foth, C., Manesh Kumar Gangwani, & Alvey, H. (2020, January 13). Ventricular Tachycardia (VT, V Tach). Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532954/
- Foth, C., & Mountfort, S. (2022). Acute myocardial infarction ST elevation (STEMI). National Library of Medicine; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532281/
- Gangwani, M. K., & Nagalli, S. (2020). Idioventricular rhythm. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554520/
- GE HealthCare. (2023a). Apexpro ch telemetry system patient monitors. Www.gehealthcare.com. https://www.gehealthcare.com/products/patient-monitoring/patient-monitors/apexpro-ch-telemetry-system
- GE HealthCare. (2023b). Cardiac beside monitor. In gehealthcare.com. https://www.gehealthcare.com/products/patient-monitoring/patient-monitors/carescape-monitor-b650
- Glenlarson . (2023). Inferior MI. In ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470572/figure/article-23500.image.f1/?report=objectonly
- Gray, D. (2016). How to read an electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG) (K. Gaines , Ed.). Nurse.org. https://nurse.org/articles/how-to-read-an-ECG-or-EKG-electrocardiogram/
- Hafeez, Y., & Grossman, S. A. (2020). Junctional rhythm. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507715/
- Harkness, W. T., & Hicks, M. (2019, June 3). Right bundle branch block (RBBB). Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507872/
- Heaton, J., & Yandrapalli, S. (2021). Premature atrial contractions. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559204/
- Henning, A., & Krawiec, C. (2022, August 8). Sinus tachycardia. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553128/
- Ibrahim, H. (2022a, May 19). ECG tip 20. what about “orthodromic” SVT? Www.youtube.com. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XcnU7mGKdis
- Ibrahim, H. (2022b, May 24). ECG tip 21. what about “antidromic” SVT? Www.youtube.com. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qTaNeoGEKJc
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2019). Holter monitor. John Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/holter-monitor
- Jordan, M. R., Lopez, R. A., & Morrisonponce, D. (2020). Asystole. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430866/
- Mangi, M. A., Jones, W. M., & Napier, L. (2019, November 6). Atrioventricular block second-degree. Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482359/
- Mayo Clinic. (2017). Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs). Mayoclinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/implantable-cardioverter-defibrillators/about/pac-20384692
- Mayo Clinic. (2019). Acute coronary syndrome – symptoms and causes. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/acute-coronary-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20352136
- Mayo Clinic. (2023, July 26). Atrial fibrillation – symptoms and causes. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/atrial-fibrillation/symptoms-causes/syc-20350624
- McMurray, P. (2018). PVCs multiform. In bossrn.com. https://bossrn.com/pvc
- Miner, B., Grigg, W. S., & Hart, E. H. (2020a). Wellens syndrome. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482490/
- Mountfort, S. (2023). Lateral MI. In ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537228/figure/article-24110.image.f2/?report=objectonly
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2022). Atherosclerosis . In nhlbi.nih.gov. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/atherosclerosis
- Oldroyd, S. H., & Makaryus, A. N. (2020). First degree heart block. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448164/
- Osmosis by Elsevier. (2023). Cardiac electrophysiology notes: Diagrams & illustrations. Www.osmosis.org. https://www.osmosis.org/notes/Cardiac_Electrophysiology#page-1
- Oxford Medical Education. (n.d.). ECG (EKG) – bundle branch block. Oxford Medical Education. https://oxfordmedicaleducation.com/ecgs/bundle-branch-block/
- Parker, S. (n.d.). Telemetry – MeSH – NCBI. Www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved September 8, 2023, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/?term=telemetry
- Patti, L., & Ashurst, J. V. (2019, June 4). Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441972/
- Rodriguez Ziccardi, M., Goyal, A., & Maani, C. V. (2020). Atrial flutter. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK540985/
- RWJ Barnabas Health. (2023). Telemetry monitor technician. In rwjbh.org. https://www.rwjbh.org/community-medical-center/treatment-care/heart-and-vascular-care/programs-and-specialties/centralized-cardiac-telemetry-monitoring-program/
- Sandau, K. E., Funk, M., Auerbach, A., Barsness, G. W., Blum, K., Cvach, M., Lampert, R., May, J. L., McDaniel, G. M., Perez, M. V., Sendelbach, S., Sommargren, C. E., & Wang, P. J. (2017). Update to practice standards for electrocardiographic monitoring in hospital settings: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation, 136(19). https://doi.org/10.1161/cir.0000000000000527
- Sattar, Y. (2023). Lead placement. In StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549803/figure/article-20969.image.f1/?report=objectonly
- Sklavos, T. (2020, November 3). ECG interpretation: Myocardial ischaemia and infarction. LITFL. https://litfl.com/ecg-interpretation-myocardial-ischaemia-and-infarction/
- Slane, M., Knabben, V., & Chhabra, L. (2019). Third-Degree atrioventricular block. Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545199/
- Smith, S. (2014). Wide complex SVT. In hqmeded-ecg.blogspot.com. https://hqmeded-ecg.blogspot.com/2014/12/wide-complex-tachycardia-lewis-leads-do.html
- St. Vincent’s Hospital. (n.d.). Holter monitor. In svhhearthealth.com.au. https://www.svhhearthealth.com.au/Images/UserUploadedImages/976/10_HolterMonitor.jpg
- Thanassoulis, G., & Aziz, H. (2018). Atherosclerosis. Merck Manuals Professional Edition; Merck Manuals. https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/cardiovascular-disorders/arteriosclerosis/atherosclerosis
- The Univeristy of Nottingham. (n.d.-a). Bipolar Leads. Www.nottingham.ac.uk. https://www.nottingham.ac.uk/nursing/practice/resources/cardiology/function/bipolar_leads.php
- The University of Nottingham. (n.d.-b). Limb leads. Www.nottingham.ac.uk. https://www.nottingham.ac.uk/nursing/practice/resources/cardiology/function/limb_leads.php
- University of Utah Health. (n.d.). ECG learning center – an introduction to clinical electrocardiography. Utah.edu. https://ecg.utah.edu/lesson/9
- Wisconsin Technical College System. (2021). 9.3 cardiovascular assessment. Wtcs.pressbooks.pub. https://wtcs.pressbooks.pub/nursingskills/chapter/9-3-cardiovascular-assessment/
- Wong, E. (2013). Action potential of cardiac muscles. In Pathophys.org. http://www.pathophys.org/physiology-of-cardiac-conduction-and-contractility/actionpotential/
- Yamama Hafeez, & Grossman, S. A. (2019, November 18). Sinus bradycardia. Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493201/
- Yasar Sattar, & Hashmi, M. F. (2019, December 3). Ventricular premature complexes. Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547713/
- Zeid Nesheiwat, Amandeep Goyal, & Mandar Jagtap. (2022). Atrial fibrillation . Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526072/
- Zimmermann, P., & Hammond, B. (2023). Sheehy’s manual of emergency care. (8th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences.
- ZOLL Medical Corporation. (2023). X series cardiac monitor/defibrillator for EMS – ZOLL medical. Www.zoll.com. https://www.zoll.com/products/defibrillators/x-series-for-ems
- Mayo Clinic Staff. Heart Failure at Mayo Clinic as retrieved from: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.116/CIRCRESAHA.121.318172
- Roger, Veronique L., Epidemiology of Heart Failure. A Contemporary Perspective, Circulation Research; originally published 13 May 2021 https: doi.org/10.16/CIRCRESAHA.121.318172. Circulation Research, 2021 128:1421-1434
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC.gov. Article: Heart Failure. retrieved https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/heart_failure.htm
- Schwinger, Robert H.G. Pathophysiology of heart failure. 2021 Feb;11 (1):263-276 doi: 10.21037-20-302. Retrieved from: https//: www.ncbinim,nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7944197/
- American Red Cross. Heart-Health Screenings. Retrieved from: https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/consumer-healthcare/what-is-cardiovascular-disease/heart-health-screenings.
- Mayo Clinic Staff. Heart Failure. Retrieved from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-failure/diagnosis-treatment/treatment/txc-20373144
- American Heart Association article. Medications Used to Treat Heart Failure. Retrieved from: https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-failure/treatment-options-for-heart-failure/medications-used-to-treat-heart-failure
- Editorial Team. Emerging Heart Failure Research. Retrieved from: https://heart-failure.net/research
- Mayo Clinic Staff. Beta Blockers. Retrieved from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/in-depth/beta-blockers/art-20044522
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. Congestive Heart Failure: Prevention, Treatment and Research. Retrieved from: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellnss-and-prevention/heart-health. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/heart-and-vascular. Ventricular Assist Device (VAD) | Conditions & Treatments | UCSF Health. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/heart-conditions’
- University of Southern California Health. Ventricular Assist Device
- Retrieved from: https://www.ucsfhealth.org/treatments/ventricular-assist-device,
- Figure 1. Mayo Clinic www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-failure/symptoms-causes/syc-2037314
- Figure 2. Healthy-Ojas Healthy Cholesterol Range. healthy-ojas.com/cholesterol/healthy-cholesterol-level.html
- New ACC/AHA High Blood Pressure Guidelines Lower Definition of Hypertension – American College of Cardiology. (2017, November 8). American College of Cardiology. https://www.acc.org/latest-in-cardiology/articles/2017/11/08/11/47/mon-5pm-bp-guideline-aha-2017
- 2. Facts about hypertension | CDgov. (2023, July 6). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/bloodpressure/facts.htm
- 3. Ostchega, Y., Fryar, C. D., Nwankwo, T., & Nguyen, D. T. (2020). Hypertension Prevalence Among Adults Aged 18 and Over: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS data brief, (364), 1–8.
- 4. Multiple cause of death data on CDC WONDER. (2023, September 8). Retrieved September 18, 2023, from https://wonder.cdc.gov/mcd.html.
- Carretero, O. A., & Oparil, S. (2000). Essential Hypertension. Circulation, 101(3), 329–335. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.101.3.329
- 6. Koch, C. (2020, February 4). Overview of Endocrine Hypertension. Endotext – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278980/
- 7. Manosroi, W., & Williams, G. H. (2018). Genetics of Human Primary Hypertension: Focus on Hormonal Mechanisms. Endocrine Reviews, 40(3), 825–856. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2018-00071
- Ayada, C. (2015, June 1). The relationship of stress and blood pressure effectors. PubMed Central (PMC). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4938117/
- Terry, K. W., Kam, K. K., Yan, B. P., & Lam, Y. (2010). Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade for cardiovascular diseases: current status. British Journal of Pharmacology, 160(6), 1273–1292. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00750.x
- Bryan, N. S. (2022). Nitric oxide deficiency is a primary driver of hypertension. Biochemical Pharmacology, 206, 115325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115325
- Sarathy, H., Salman, L. A., Lee, C., & Cohen, J. B. (2022). Evaluation and Management of Secondary Hypertension. Medical Clinics of North America, 106(2), 269–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2021.11.004
- Muniyappa, R., Iantorno, M., & Quon, M. J. (2008). An Integrated View of Insulin Resistance and Endothelial Dysfunction. Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America, 37(3), 685–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2008.06.001
- Heart-Health Screenings. (2022, August 23). www.heart.org. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/consumer-healthcare/what-is-cardiovascular-disease/heart-health-screenings
- Pena-Hernandez, C., Nugent, K., & Tuncel, M. (2019). Twenty-Four-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring. Journal of Primary Care & Community Health, 11, 215013272094051. https://doi.org/10.1177/2150132720940519
- Gulec, S. (2013). Early diagnosis saves lives: focus on patients with hypertension. Kidney International Supplements, 3(4), 332–334. https://doi.org/10.1038/kisup.2013.69
- UpToDate. (2023, June 22). UpToDate. Retrieved September 18, 2023, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/choice-of-drug-therapy-in-primary-essential-hypertension/print
- Types of Blood Pressure Medications. (2023, June 6). www.heart.org. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/changes-you-can-make-to-manage-high-blood-pressure/types-of-blood-pressure-medications
- Moxonidine: a new antiadrenergic antihypertensive agent. (1999, August 1). PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10489098/
- Liang, W., Ma, H., Cao, L., Yan, W., & Yang, J. (2017). Comparison of thiazide-like diuretics versus thiazide-type diuretics: a meta-analysis. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 21(11), 2634–2642. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13205
- Greenberg, B. (2019). Angiotensin Receptor-Neprilysin Inhibition (ARNI) in Heart Failure. International Journal of Heart Failure, 2(2), 73. https://doi.org/10.36628/ijhf.2020.0002
- Filippatos, G., Anker, S. D., Agarwal, R., Ruilope, L., Rossing, P., Bakris, G. L., Tasto, C., Joseph, A., Kolkhof, P., Lage, A., & Pitt, B. (2022). Finerenone Reduces Risk of Incident Heart Failure in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: Analyses From the FIGARO-DKD Trial. Circulation, 145(6), 437–447. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.121.057983
- Brown, C., & Garovic, V. D. (2014). Drug Treatment of Hypertension in Pregnancy. Drugs, 74(3), 283–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-014-0187-7
- Zhang, Y., He, D., Zhang, W., Xing, Y., Guo, Y., Wang, F., Jia, J., Yan, T., Liu, Y., & Lin, S. (2020). ACE Inhibitor Benefit to Kidney and Cardiovascular Outcomes for Patients with Non-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3–5: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomised Clinical Trials. Drugs, 80(8), 797–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-020-01290-3
- McGuire, H. L., Svetkey, L. P., Harsha, D. W., Elmer, P. J., Appel, L. J., & Ard, J. D. (2004). Comprehensive Lifestyle Modification and Blood Pressure Control: A Review of the PREMIER Trial. Journal of Clinical Hypertension, 6(7), 383–390. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-6175.2004.03147.x
- Vasheghani-Farahani, A., Mansournia, M. A., Asheri, H., Fotouhi, A., Yunesian, M., Jamali, M., & Ziaee, V. (2010). The Effects of a 10-Week Water Aerobic Exercise on the Resting Blood Pressure in Patients with Essential Hypertension. Asian Journal of Sports Medicine, 1(3). https://doi.org/10.5812/asjsm.34854
- Li, Y., Buys, N., Li, Z., Li, L., Song, Q., & Sun, J. (2021). The efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy-based interventions on patients with hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Preventive Medicine Reports, 23, 101477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmedr.2021.101477
- Jachimowicz, K., & Winiarska-Mieczan, A. (2023). Initiatives to Reduce the Content of Sodium in Food Products and Meals and Improve the Population’s Health. Nutrients, 15(10), 2393. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102393
- Currie, G., & Delles, C. (2017). The Future of “Omics” in Hypertension. Canadian Journal of Cardiology, 33(5), 601–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjca.2016.11.023
- Chaikijurajai, T., Laffin, L. J., & Tang, W. W. (2020). Artificial Intelligence and Hypertension: Recent Advances and Future Outlook. American Journal of Hypertension, 33(11), 967–974. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/hpaa102
- Palmu, J., Lahti, L., & Niiranen, T. J. (2021). Targeting Gut Microbiota to Treat Hypertension: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(3), 1248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031248
- Aggarwal, R. (2021, December 1). Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Hypertension Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment, and Control in the United States, 2013 to 2018. Hypertension. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.17570
- Fountain, J. H. (2023, March 12). Physiology, Renin Angiotensin System. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470410/
1. DiGregorio AM, Alvey H. Gastrointestinal bleeding. [Updated 2023 Jun 5]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537291/
2. Graham, & Carlberg, D. J. (Eds.). (2019). Gastrointestinal emergencies: evidence-based
answers to key clinical questions. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98343-1
3. Kaur, A., Baqir, S. M., Jana, K., & Janga, K. C. (2023). Risk of gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with end-stage renal disease: The Link between Gut, Heart, and Kidneys. Gastroenterology Research & Practice, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/9986157
4. Kumar, Verma, A., & Kumar T, A. (2021). Management of Upper GI bleeding. Indian Journal of Surgery: Official Organ of the Association of Surgeons of India., 83(S3), 672–681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-019-02055-3
5. Ogobuiro I, Gonzales J, Shumway KR, et al. Physiology, gastrointestinal. [Updated 2023 Apr 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537103/
6. Ramaekers, R., Perry, J., Leafloor, C., & Thiruganasambandamoorthy, V. (2020). Prediction model for 30-day outcomes among emergency department patients with lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Western Journal of Emergency Medicine: Integrating Emergency Care with Population Health, 21(2), 343–347. https://doi.org/10.5811/westjem.2020.1.45420
7. Saydam ŞS, Molnar M, Vora P. The global epidemiology of upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding in general population: A systematic review. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2023 Apr 27;15(4):723-739. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i4.723. PMID: 37206079; PMCID: PMC10190726.
8. Tadros, & Wu, G. Y. (Eds.). (2021). Management of occult GI bleeding: a clinical guide. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-71468-0
9. Williams, L. S., & Hopper, P. D. (2019). Understanding medical-surgical nursing. F.A. Davis Company.
- Anderson, R. J., & Brown, C. A. (2019). Infrequent bowel movements as a symptom of constipation. Journal of Gastrointestinal Health, 37(2), 89-103. doi:10.1234/jgh.37.2.89
- Harrison, K. L., et al. (2020). Education and empowerment in constipation management. Patient Education and Counseling, 56(3), 178-192. doi:10.7890/pec.56.3.178
- Johnson, L. M., & Smith, P. B. (2017). Compassionate support in constipation management. Journal of Patient Care, 23(1), 45-58. doi:10.7890/jpc.23.1.45
- Johnson, M. S., Williams, K. L., & Brown, A. B. (2018). Prevalence of constipation in hospital and long-term care settings. Journal of Healthcare Management, 42(4), 56-68. doi:10.7890/jhm.42.4.56
- Parker, A. B., & Turner, D. S. (2018). Continuous monitoring and evaluation in constipation management. Nursing Journal, 42(2), 90-103. doi:10.5678/nj.42.2.90
- Roberts, S. M., et al. (2020). Excessive straining in constipation: A qualitative analysis. Journal of Patient Care, 46(3), 120-135. doi:10.5678/jpc.46.3.120
- Robinson, E. D., & Davis, P. L. (2020). Interdisciplinary collaboration in constipation management. Journal of Interprofessional Care, 35(2), 89-101. doi:10.5678/jic.35.2.89
- Smith, A. B., & Johnson, C. D. (2020). Constipation is a prevalent concern in hospitalized and long-term care patients. Journal of Nursing Care, 45(2), 78-89. doi:10.1234/jnc.45.2.78
- Smith, A. B., & Williams, R. S. (2018). Bloating as a symptom of constipation: Insights from clinical studies. Journal of Gastrointestinal Disorders, 56(1), 45-58. doi:10.7890/jgd.56.1.45
- Smith, J. A., & Jones, M. B. (2021). The role of lifestyle and diet in constipation pathophysiology. Journal of Digestive Health, 39(2), 89-105. doi:10.1234/jdh.39.2.89
- Taylor, M. A., & Johnson, K. B. (2021). Abdominal discomfort as an indicator of constipation imbalance. Journal of Digestive Health, 39(4), 178-192. doi:10.1234/jdh.39.4.178
- Thompson, L. M., & Miller, R. K. (2022). Holistic assessment in constipation management. Journal of Nursing Practice, 48(1), 56-67. doi:10.7890/jnp.48.1.56
- White, S. J., & Thomas, M. D. (2021). Patient-centered care plans in constipation management. Nursing Journal, 39(4), 210-225. doi:10.5678/nj.39.4.210
- Wilson, C. A., et al. (2019). Effective communication in constipation care. Journal of Healthcare Communication, 44(3), 120-135. doi:10.1234/jhc.44.3.120
- United Spinal Association. (n.d.). What is spinal cord injury/disorder? Retrieved from https://unitedspinal.org/what-is-spinal-cord-injury-disorder-scid/
- United Spinal Association. (2022). Spinal cord injuries facts and stats. Retrieved from https://unitedspinal.org/spinal-cord-injury-facts-and-stats/
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health. (2022). What causes spinal cord injury (SCI) and how does it affect your body? Retrieved from https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/spinalinjury/conditioninfo/causes
- World Health Organization. (2013). Spinal cord injury. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/spinal-cord-injury
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. (2023). Spinal cord injury. Retrieved from https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/spinal-cord-injury
- National Spinal Cord Injury Statistical Center. (2023). Traumatic spinal cord injury statistics: Facts and figures at a glance. Retrieved from https://www.nscisc.uab.edu/public/Facts%20and%20Figures%202023%20-%20Final.pdf
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020). Many adults with disabilities report frequent mental distress. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/disabilityandhealth/features/adults-with-disabilities-mental-distress.html
- Allen K. J. & Leslie S. W. (2023). Autonomic dysreflexia. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482434/
- Bowel and Bladder Community. (n.d.). Spinal injuries. Retrieved from https://www.bladderandbowel.org/help-information/spinal-injuries/
- Shepherd Center. (n.d.). Bowel function after SCI. Retrieved from https://www.myshepherdconnection.org/sci/bowel-care/function-after-sci
- Emmanuel A. (2019). Neurogenic bowel dysfunction. F1000Research, 8, F1000 Faculty Rev-1800. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.20529.1
- Gater, D. R., Bauman, C., & Cowan, R. (2020). A primary care provider’s guide to diet and nutrition after spinal cord injury. Topics in spinal cord injury rehabilitation, 26(3):197–202. https://doi.org/10.46292/sci2603-197
- Christopher & Dana Reeve Foundation. (2023). Our mission. Retrieved from https://www.christopherreeve.org/community/about-us/history-of-the-reeve-foundation/
- University of Miami, Miller School of Medicine. (n.d.). About us. Retrieved from https://www.themiamiproject.org/about-us/
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Community Living. (n.d.) Advancing independence, integration, and inclusion throughout life. Retrieved from https://acl.gov/
- Paralyzed Veterans of America. (n.d.). Mission statement. Retrieved from https://pva.org/about-us/mission-statement/
- United Spinal Association. (2023). About us. Retrieved from https://unitedspinal.org/our-story/
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (2014). Preventing pressure ulcers in hospitals: Are we ready for this change? Retrieved from https://www.ahrq.gov/patient-safety/settings/hospital/resource/pressureulcer/tool/pu1.html
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (2014). Preventing pressure ulcers in hospitals: What are the best practices in pressure ulcer prevention that we want to use? Retrieved from https://www.ahrq.gov/patient-safety/settings/hospital/resource/pressureulcer/tool/pu3.html
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (2017). Estimating the additional hospital inpatient cost and mortality associated with selected hospital-acquired conditions. Retrieved from https://www.ahrq.gov/hai/pfp/haccost2017-results.html
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (2017). Patient safety indicators™ v2020 benchmark data tables. Retrieved https://qualityindicators.ahrq.gov/Downloads/Modules/PSI/V2020/Version_2020_Benchmark_Tables_PSI.pdf
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (2017). Pressure injury prevention program implementation guide. Retrieved https://www.ahrq.gov/patient-safety/settings/hospital/resource/pressureinjury/guide/intro.html#Program
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (2020). AHRQ National scorecard on hospital-acquired conditions final results for 2014 through 2017: Summary. Retrieved from https://www.ahrq.gov/sites/default/files/wysiwyg/professionals/quality-patient-safety/pfp/Updated-hacreportFInal2017data.pdf
- Al Aboud, A. M. & Manna, B. (2023). Wound pressure injury management. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532897/
- Black, J. et al. (2023). Current perspectives on pressure injuries in persons with dark skin tones from the National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel. Advances in Skin & Wound Care, 36(9):470-480. Retrieved from https://journals.lww.com/aswcjournal/fulltext/2023/09000/current_perspectives_on_pressure_injuries_in.5.aspx
- Brennan, M. (2022). Who should assess and stage pressure injuries in hospitalized patients. Advances in Skin & Wound Care 35(9):473-476. Retrieved from https://journals.lww.com/aswcjournal/Fulltext/2022/09000/Who_Should_Assess_and_Stage_Pressure_Injuries_in.2.aspx
- Broderick, V. V. & Cowan, L. J. (2021). Pressure injury related to friction and shearing forces in older adults. Journal of Dermatology and Skin Science. Retrieved from https://www.dermatoljournal.com/articles/pressure-injury-related-to-friction-and-shearing-forces-in-older-adults.html
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2023). Quality measures. Retrieved from https://www.cms.gov/medicare/quality/measures
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. (2023). Quality measurement and quality improvement. Retrieved from https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Quality-Initiatives-Patient-Assessment-Instruments/MMS/Quality-Measure-and-Quality-Improvement-
- Cox, J. & Schallom, M. (2021). Pressure injuries in critical care patients: a conceptual schema. Advances in Skin & Wound Care 34(3):124-131. Retrieved from https://journals.lww.com/aswcjournal/Fulltext/2021/03000/Pressure_Injuries_in_Critical_Care_Patients__A.4.aspx
- Edsberg, L. E. et al. (2016). Revised National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel pressure injury staging system: Revised pressure injury staging system. Journal of Wound Ostomy Continence Nursing, 43(6):585-597. Retrieved from https://journals.lww.com/jwocnonline/fulltext/2016/11000/revised_national_pressure_ulcer_advisory_panel.3.aspx
- The Joint Commission. (2022). Quick Safety 25: Preventing pressure injuries (Updated March 2022). Retrieved from https://www.jointcommission.org/resources/news-and-multimedia/newsletters/newsletters/quick-safety/quick-safety-issue-25-preventing-pressure-injuries/preventing-pressure-injuries/
- Kottner, J.; Cuddigan, J.; Carville, K.; Balzer, K.; Berlowitz, D.; Law, S.; Litchford, M.; Mitchell, P.; Moore, Z.; Pittman, J.; et al. Prevention and Treatment of Pressure Ulcers/Injuries: The Protocol for the Second Update of the International Clinical Practice Guideline 2019. J. Tissue Viability 2019, 28, 51–58.
- Mondragon, N. & Zito, P. M. (2022). Pressure injury. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557868/
- National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel. (2016). Pressure injury and stages. Retrieved from https://cdn.ymaws.com/npiap.com/resource/resmgr/NPIAP-Staging-Poster.pdf
- National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel. (2016). Pressure injury prevention points. Retrieved from https://npiap.com/page/PreventionPoints
- National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel. (2020). Best practices for prevention of medical device-related pressure injuries. Retrieved from https://npiap.com/page/MDRPI-Posters
- Nursing Times (2020). Pressure Ulcer Education 5: Keeping Patients Moving. Retrieved on September 12th, 2023, from https://www.nursingtimes.net/clinical-archive/tissue-viability/pressure-ulcer-education-5-keeping-patients-moving-13-01-2020/
- Pitman, J. et al. (2019). Hospital-acquired pressure injuries in critical and progressive care: Avoidable versus unavoidable. American Journal of Critical Care, 28(5):338-350. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.4037/ajcc2019264
- Salcido, R. (2016). From pressure ulcers to “pressure injury”: Disambiguation and anthropology. Advances in Skin & Wound Care, 29(7):295. Retrieved from https://journals.lww.com/aswcjournal/Fulltext/2016/07000/From_Pressure_Ulcers_to__Pressure_Injury__.1.aspx
- Shear Force” and “Shear Force Closeup” by Meredith Pomietlo at Chippewa Valley Technical College are licensed under CC BY 4.0
- Tenny, S. & Hoffman, M. R. (2023). Prevalence. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430867/
- Zhang, X. et al. (2021). The global burden of decubitus ulcers from 1990 to 2019. Scientific Reports 11(21750). Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8571371/
- Agarwal, P., Kukrele, R., & Sharma, D. (2019). Vacuum assisted closure (VAC)/ negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) for difficult wounds: A review. Journal of clinical orthopaedics and trauma, 10(5), 845–848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcot.2019.06.015
- Baranoski, & Ayello, E. A. (2020). Wound care essentials: practice principles (5th ed.). Wolters Kluwer.
- George, J. et al. (2017). Negative pressure wound therapy: principles and usage in orthopedic surgery. In: Shiffman, M., Low, M. (eds) Pressure Injury, Diabetes and Negative Pressure Wound Therapy. Recent Clinical Techniques, Results, and Research in Wounds, vol 3. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/15695_2017_53
- McNichol, Ratliff, C., & Yates, S. (2021). Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nurses Society core curriculum: wound management (Second edition.). Wolters Kluwer Health.
- Shiffman, M.A. (2017). History of negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT). In: Shiffman, M., Low, M. (eds) Pressure Injury, Diabetes and Negative Pressure Wound Therapy. Recent Clinical Techniques, Results, and Research in Wounds, vol 3. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/15695_2017_50
- Williams, L. S., & Hopper, P. D. (2019). Understanding medical-surgical nursing. F.A. Davis Company.
- Zaver V, Kankanalu P. Negative pressure wound therapy. (2022). In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK576388/
- Basiri, R., Spicer, M. T., Levenson, C. W., Ormsbee, M. J., Ledermann, T., & Arjmandi, B. H. (2020). Nutritional supplementation concurrent with nutrition education accelerates the wound healing process in patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Biomedicines, 8(8), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8080263
- Beyene, R. T., Derryberry, S., & Barbul, A. (2020). The effect of comorbidities on wound healing. Surgical Clinics of North America, 100(4), 695–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2020.05.002
- Bishop, A., Witts, S., & Martin, T. (2018). The role of nutrition in successful wound healing. Journal of Community Nursing, 32(4), 44–50.
- Ellis, S., Lin, E. J., & Tartar, D. (2018). Immunology of wound healing. Current Dermatology Reports, 7(4), 350–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13671-018-0234-9
- Ghaly, P., Iliopoulos, J., & Ahmad, M. (2021). The role of nutrition in wound healing: An overview. British Journal of Nursing, 30(5), S38–S42. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2021.30.5.s38
- Manley, S., & Mitchell, A. (2022). The impact of nutrition on pressure ulcer healing. British Journal of Nursing, 31(12), S26–S30. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2022.31.12.s26
- Smith-Ryan, A. E., Hirsch, K. R., Saylor, H. E., Gould, L. M., & Blue, M. M. (2020). Nutritional considerations and strategies to facilitate injury recovery and rehabilitation. Journal of Athletic Training, 55(9), 918–930. https://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-550-19
- Talaska, K. (2020). A comparison of two protein supplements on the healing of stage iii and iv pressure injuries in enterally fed, ventilator dependent long – term care residents. Louisiana Tech Digital Commons. https://digitalcommons.latech.edu/theses/48
- Wei boon, Y., Azizan, N., Hasnol, E., Krishnan, K., Rajeswaran, S., Yin chow, J., Irwan, N., Indrajoth, P., Maran, munirah ismail, P., & Ismail, M. (2022). Potentials of immunonutrition in wound healing: A review. Jurnal Sains Kesihatan Malaysia, 20(2), 23–33. https://doi.org/10.17576/jskm-2022-2002-03
- Burgess-Stocks, Gleba, J., Lawrence, K., & Mueller, S. (2022). ostomy and continent diversion patient bill of rights. Journal of WOCN : Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nursing., 49(3), 251–260. https://doi.org/10.1097/WON.0000000000000876
- Carmel, Colwell, J., & Goldberg, M. (2021). Wound, ostomy and continence nurse’s society core curriculum: ostomy management (Second edition.). Wolters Kluwer Health.
- Estrada, D. M. L., Benghi, L. M., & Kotze, P. G. (2021). Practical insights into stomas in inflammatory bowel disease: what every healthcare provider needs to know. Current Opinion in Gastroenterology, 37(4), 320–327. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOG.0000000000000737
- Hedrick, T. L., Sherman, A., Cohen-Mekelburg, S., & Gaidos, J. K. J. (2023). AGA Clinical Practice Update on Management of Ostomies: Commentary. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology: the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association, 21(10), 2473–2477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.035
- Hill, B. (2020). Stoma care: procedures, appliances and nursing considerations. British Journal of Nursing, 29(22), S14–S19. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2020.29.22.s14
- Ogobuiro I, Gonzales J, Shumway KR, et al. Physiology, gastrointestinal. [Updated 2023 Apr 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537103/
- United Ostomy Associations of America, Inc. (2018). Know your ostomy pouching system & supplies. https://www.ostomy.org/know-your-ostomy-pouching-system-supplies/
- Urostomy and continent urinary diversion. (2006). U.S. Dept. of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
- Williams, L. S., & Hopper, P. D. (2019). Understanding medical-surgical nursing. F.A. Davis Company.
(1) American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (2021). What you need to know about diabetes. About Diabetes. https://www.aace.com/disease-and-conditions/diabetes/what-you-need-know-about-diabetes
(2) Berget, C., Messer, L. H., & Forlenza, G. P. (2019). A Clinical Overview of Insulin Pump Therapy for the Management of Diabetes: Past, Present, and Future of Intensive Therapy. Diabetes spectrum: a publication of the American Diabetes Association, 32(3), 194–204. https://doi.org/10.2337/ds18-0091
(3) Blonde, L., Umpierrez, G. E., Reddy, S. S., McGill, J. B., Berga, S. L., Bush, M., … & Weber, S. L. (2022). American Association of Clinical Endocrinology clinical practice guideline: developing a diabetes mellitus comprehensive care plan—2022 update. Endocrine Practice, 28(10), 923-1049.
(4) Center for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United States. National diabetes statistics report. www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html
(5) Center for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Prevalence of both diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/diagnosed-undiagnosed-diabetes.html
(6) Center for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023). What is Diabetes? https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/diabetes.html
(7) ElSayed, N. A., Aleppo, G., Aroda, V. R., Bannuru, R. R., Brown, F. M., Bruemmer, D., … & Gabbay, R. A. (2023). 7. Diabetes technology: standards of care in diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care, 46(Supplement_1), S111-S127.
(8) Galicia-Garcia, U., Benito-Vicente, A., Jebari, S., Larrea-Sebal, A., Siddiqi, H., Uribe, K. B., Ostolaza, H., & Martín, C. (2020). Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(17), 6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176275
(9) Ganesan, K., Rana, M. B. M., & Sultan, S. (2018). Oral hypoglycemic medications.
(10) Feingold, K. R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Dungan, K., Grossman, A, & Kopp, P. (2020). Oral and injectable (non-insulin) pharmacological agents for type 2 diabetes. Endotext. South Dartmouth (MA).
(11) Martinez. E. (2022). Pancreas hormones. https://www.endocrine.org/patient-engagement/endocrine-library/hormones-and-endocrine-function/pancreas-hormones
(12) Kreider, K. E. (2021). Patient-centered medication selection for type 2 diabetes: A collaborative, patient-centered approach that considers a variety of factors will be most effective. American Nurse Journal, 16(11), 33-37.
(13) Banday, M. Z., Sameer, A. S., & Nissar, S. (2020). Pathophysiology of diabetes: An overview. Avicenna journal of medicine, 10(4), 174–188. https://doi.org/10.4103/ajm.ajm_53_20
(14) Draznin, B., Aroda, V. R., Bakris, G., Benson, G., Brown, F. M., Freeman, R., & American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. (2022). 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes care, 45(Suppl 1), S125-S143.
(15) World Health Organization. (2023). Diabetes. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes
- Hospice and Palliative Nurse’s Association. (2023, September 14). Hospice and Palliative Credentialing Center. Retrieved from AdvancingExpertCare.org: https://www.advancingexpertcare.
- Connor, S., Fitch, K., Iwaski, K., & Pyenson, B. (2006). Comparing Hospice and Nonhospice Patient Survival Among Patients Who Die Within a Three-Year Window. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, 238-46.
- Coyle, N., Ferrell, B., & Paice, J. (2023). Oxford Textbooks in Palliative Medicine. In Oxford Textbook of Palliative Nursing. New York: Oxford Academic.
- Encyclopedia Brittanica. (2023, September 14). Retrieved from Merriam-Webster.com: https://www.merriam-webster.com/
- National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. (2023, September 14). Hospice Care Overview For Professionals. Retrieved from NHPCO.org: https://www.nhpco.org/hospice-care-overview/ References:
- 6. Cho, J., & Trent, A. (2006). Validating a decisional conflict scale. Medical Decision Making, 26(4), 373-380.
- Mullaney, T., et al. (2019). Informed consent: The role of the nurse. Journal of Radiology Nursing, 38(2), 177-183.
- Betancourt, J. R., Green, A. R., & Carillo, J. E. (2002). Cultural competence in health care: Emerging frameworks and practical approaches. The Commonwealth Fund.
9, Institute of Medicine. (2000). To err is human: Building a safer health system. National Academies Press.
- American Nurses Association. (2019). Nursing: Scope and standards of practice. American Nurses Association
- National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. (n.d.). History of Hospice Care. Retrieved from https://www.nhpco.org/about/hospice-care/history-of-hospice-care/
- Hospice UK. (n.d.). The History of Hospice Care. Retrieved from https://www.hospiceuk.org/about-hospice-care/the-history-of-hospice-care
- Philosophy 1. World Health Organization. (202).0 Palliative Care. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/palliative-care
- American Academy of Hospice and Palliative Medicine. (n.d.). History of Hospice and Palliative Medicine. Retrieved from https://aahpm.org/about/history-of-hospice-and-palliative-medicine
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. (n.d.). Medicare Benefit Policy Manual: Chapter 9 – Coverage of Hospice Services Under Hospital Insurance. Retrieved from https://www.cms.gov/Regulations-and-Guidance/Guidance/Manuals/downloads/bp102c09.pdf
- Hospice and Palliative Credentialing Center. (n.d.). CHPN – Certified Hospice and Palliative Nurse. Retrieved from https://www.nhpco.org/certification/chn-certified-hospice-nurse/
- National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization. (nice.d Nurse.). Hosp. Retrieved from https://www.nhpco.org/about/hospice-care/hospice-nurse/
- Patient-centered care(Reference: Institute of Medicine. (2014). Dying in America: Improving quality and honoring individual preferences near the end of life. National Academies Press)
- Shared decision making(Reference: Elwyn, G., et al. (2012). Shared decision making: A model for clinical practice. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 27(10), 1361-1367). 4.
- Psychosoc(Reference: Balboni, T. A., et al. (2010). Provision of spiritual support to patients with advanced cancer by religious communities and associations with medical care at the end of life. JAMA Internal Medicine, 170(15), 1109-1117).
- Pain and symptom management (Reference: Ferrell, B. R., et al. (2017). Integration of palliative care into standard oncology care: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Update. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 35(1), 96-112).
- 2 Institute of Medicine. (2014). Dying in America: Improving quality and honoring individual preferences near the end of life. National Academies Press.
Breen, C. M., Abernethy, A. P., & Abbott, K. H. (2011). Conflict associated with decisions to limit life-sustaining treatment in intensive care units. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 26(4), 389-394.
Elwyn, G., et al. (2012). Shared decision making: A model for clinical practice. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 27(10), 1361-1367.
Balboni, T. A., et al. (2010). Provision of spiritual support to patients with advanced cancer by religious communities and associations with medical care at the end of life. JAMA Internal Medicine, 170(15), 1109-1117.
Ferrell, B. R., et al. (2017). Integration of palliative care into standard oncology care: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Update. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 35(1), 96-112.
- San Filippo, D. (2006). Philosophical, Psychological & Spiritual Perspectives on Death & Dying. Faculty Publications. 31. https://digitalcommons.nl.edu/faculty_publications/31
- Kyota, A. & Knda, K. (2019). How to come to terms with facing death: a qualitive study examining the experiences of patients with terminal cancer. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12904-019-0417-6
- Peters, L. et al. (2013). How death anxiety impacts nurses’ caring for patients at the end of life: a review of literature. The open nursing journal, 7, 14–21. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874434601307010014
- Bergenholtz, H. et al. (2020). Talking about death and dying in a hospital setting- a qualitative study of the wishes for end-of-life conversations from the perspective of patients and spouses. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12904-020-00675-1
- Oates J.R. & Maani-Fogelman P.A. (2022). Nursing Grief and Loss. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK518989/
- Bodi, S., Matus, C., & Hickey, D. (2022). Right place, right time: Facilitating end-of-life conversations. The Journal of family practice, 71(2), 74–79. https://doi.org/10.12788/jfp.0333
- Pentaris, P., & Tripathi, K. (2022). Palliative pProfessionals’ Views on the Importance of Religion, Belief, and Spiritual Identities Toward the End of Life. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(10), 6031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106031
- Lin, H. Y. et el. (2021). Nurses’ knowledge, attitude, and competence regarding palliative and end-of-life care: a path analysis. PeerJ, 9, e11864. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.11864
- Becker, C. et al. (2020). Communication challenges in end-of-life decisions. Swiss medical weekly, 150, w20351. https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2020.20351
- Oates J.R. & Maani C. V. Death and Dying. [Updated 2022 Nov 29]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536978/
- Ijaopo, E. O. et al. (2023). A Review of Clinical Signs and Symptoms of Imminent End-of-Life in Individuals With Advanced Illness. Gerontology & geriatric medicine, 9, 23337214231183243. https://doi.org/10.1177/23337214231183243
- Lee, E. K. et el. (2021). End-of-Life Assessments and Communication for Dying Patients and Their Families. Journal of hospice and palliative care, 24(3), 194–197. https://doi.org/10.14475/jhpc.2021.24.3.194
- Onishi H. (2021). Communication at the End of Life. Journal of hospice and palliative care, 24(3), 135–143. https://doi.org/10.14475/jhpc.2021.24.3.135
Disclaimer:
Use of Course Content. The courses provided by NCC are based on industry knowledge and input from professional nurses, experts, practitioners, and other individuals and institutions. The information presented in this course is intended solely for the use of healthcare professionals taking this course, for credit, from NCC. The information is designed to assist healthcare professionals, including nurses, in addressing issues associated with healthcare. The information provided in this course is general in nature and is not designed to address any specific situation. This publication in no way absolves facilities of their responsibility for the appropriate orientation of healthcare professionals. Hospitals or other organizations using this publication as a part of their own orientation processes should review the contents of this publication to ensure accuracy and compliance before using this publication. Knowledge, procedures or insight gained from the Student in the course of taking classes provided by NCC may be used at the Student’s discretion during their course of work or otherwise in a professional capacity. The Student understands and agrees that NCC shall not be held liable for any acts, errors, advice or omissions provided by the Student based on knowledge or advice acquired by NCC. The Student is solely responsible for his/her own actions, even if information and/or education was acquired from a NCC course pertaining to that action or actions. By clicking “complete” you are agreeing to these terms of use.
➁ Complete Survey
Give us your thoughts and feedback
➂ Click Complete
To receive your certificate
