Events | Holidays & Freebies National Nurses Week: Honoring Our Favorite Pop Culture Practitioners National Nurses Week runs from May 6-12, and includes a variety of ways to honor nurses. This year’s theme is “Nurses Make the Difference.” As part...


Pharm D
November 1 to 31 is pancreatic cancer awareness month. Let’s talk about it.
Pancreatic cancer is currently the fourth-most common cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States. According to the American Cancer Society, pancreatic cancer accounts for about 3% of all cancers in the US and about 7% of all cancer deaths.
Approximately 45,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with it each year. The survival rate of pancreatic cancer is low; about 23% of patients survive 1 year after diagnosis, and fewer than 5% of persons with the disease remain alive 5 years after diagnosis.
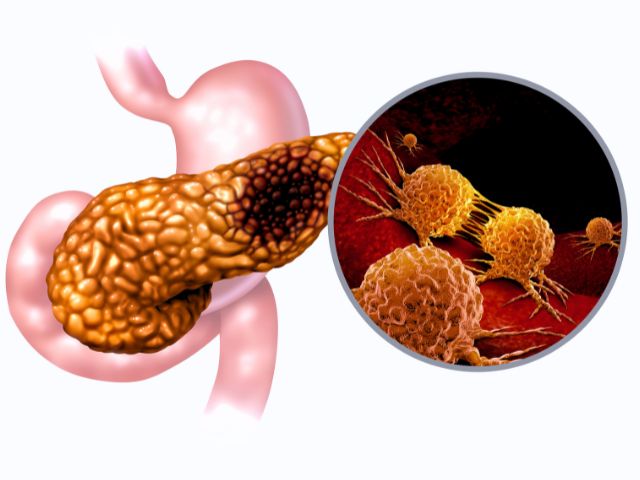
Pancreatic cancer includes carcinomas of the head of the pancreas, the ampulla of Vater, the common bile duct, and the duodenum.
The pancreas serves as an endocrine and exocrine gland. The tumor can develop in any of these functional cells.
However, 95% of cases of pancreatic cancer affect the exocrine cells of the pancreas, referred to as adenocarcinoma. The remaining 5% of cases of pancreatic cancer affect the endocrine cells, named after the hormones they produce, such as insulinomas and glucagonomas.

The exact cause of pancreatic cancer is unknown. However, the incidence is two times more common in smokers than non-smokers. Hence, smoking can play a role in causing pancreatic cancer.
The other associated risk factors for pancreatic cancer can be:
Persons having occupational exposure to gasoline derivatives, naphthylamine, and benzidine are considered to be at higher risk.
Common symptoms of pancreatic cancer are:
Nurses should inspect the patient for the presence of jaundice, which is the presenting symptom in 80% to 90% of patients with cancer of the pancreatic head.
If the cancer blocks the release of pancreatic juices into the intestines, the patient may have difficulty digesting fatty foods; this will result in pale, bulky, greasy stools that tend to float in the toilet.
The buildup of bilirubin in the blood and skin can cause dark urine and pruritus, assess the patient for that. Note the presence of liver or spleen enlargement. Dullness on percussion may indicate the presence of ascites or gallbladder enlargement due to pancreatic cancer.
The tools that help in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer are:
Other diagnostic tests used in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer are:
Surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy all are used to treat pancreatic cancer. The common chemotherapeutic agents used are:
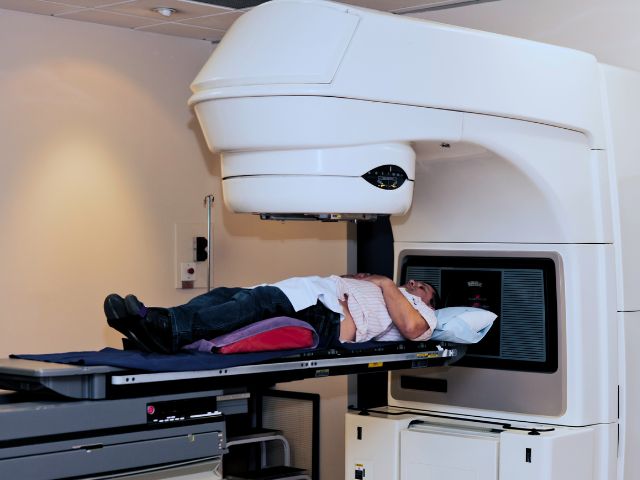
Quitting smoking may help lower the incidence of pancreatic cancer because it is more common in smokers, compared to non-smokers.
Till now, there have been no screening tests for early detection of pancreatic cancer. Usually, when it is diagnosed, it has already metastasized to other organs which makes it difficult to treat, leading to poor prognosis.
As a nurse, counsel the patient as they are very anxious when a cancer is diagnosed. Lend them a listening ear, and with the palliative treatment, connect them to a counselor who can help them to cope with the situation mentally.
Love what you read?
Share our insider knowledge and tips!
Read More

Events | Holidays & Freebies National Nurses Week: Honoring Our Favorite Pop Culture Practitioners National Nurses Week runs from May 6-12, and includes a variety of ways to honor nurses. This year’s theme is “Nurses Make the Difference.” As part...
Events National Cancer Prevention Month February is National Cancer Prevention Month 2024! Nurses can be an educational resource for patients on how to protect themselves. Cancer prevention can look like lifestyle changes to minimize modifiable risk factors and...

Events International Prenatal Infection Prevention Month 2024 February is International Prenatal Infection Prevention Month 2024! Learn about a nurse’s role in educating patients on how to protect themselves. Common prenatal infections you can explore with...